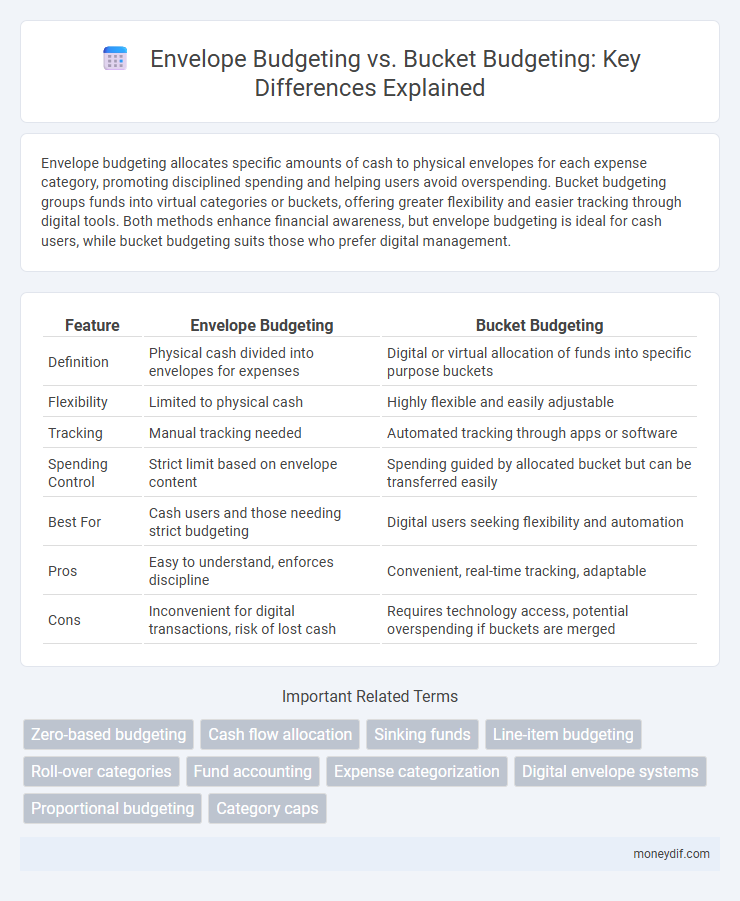
Envelope budgeting allocates specific amounts of cash to physical envelopes for each expense category, promoting disciplined spending and helping users avoid overspending. Bucket budgeting groups funds into virtual categories or buckets, offering greater flexibility and easier tracking through digital tools. Both methods enhance financial awareness, but envelope budgeting is ideal for cash users, while bucket budgeting suits those who prefer digital management.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Envelope Budgeting | Bucket Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical cash divided into envelopes for expenses | Digital or virtual allocation of funds into specific purpose buckets |
| Flexibility | Limited to physical cash | Highly flexible and easily adjustable |
| Tracking | Manual tracking needed | Automated tracking through apps or software |
| Spending Control | Strict limit based on envelope content | Spending guided by allocated bucket but can be transferred easily |
| Best For | Cash users and those needing strict budgeting | Digital users seeking flexibility and automation |
| Pros | Easy to understand, enforces discipline | Convenient, real-time tracking, adaptable |
| Cons | Inconvenient for digital transactions, risk of lost cash | Requires technology access, potential overspending if buckets are merged |
Introduction to Envelope Budgeting and Bucket Budgeting
Envelope budgeting allocates cash into physical or digital envelopes representing spending categories, ensuring disciplined control by limiting expenses to the money placed in each envelope. Bucket budgeting organizes funds into multiple accounts or "buckets" tailored to specific financial goals, such as savings, bills, or discretionary spending, facilitating targeted resource management. Both methods enhance financial awareness by promoting deliberate allocation and tracking of money to prevent overspending.
Core Principles of Envelope Budgeting
Envelope budgeting centers on allocating a fixed amount of cash into physical or digital envelopes designated for specific expense categories, reinforcing disciplined spending by limiting funds to each envelope's balance. This method promotes mindful financial management by requiring individuals to spend only what is available within each envelope, preventing overspending and encouraging saving. Emphasizing tangible boundaries and real-time tracking, envelope budgeting simplifies expense control and aligns spending habits with predefined financial goals.
Key Features of Bucket Budgeting
Bucket budgeting organizes finances by categorizing funds into distinct "buckets" for specific purposes such as savings, expenses, and investments, enhancing clarity and control. Each bucket holds a set amount of money, ensuring budgets align closely with financial goals and priorities. This method improves tracking accuracy, reduces overspending, and fosters disciplined money management compared to envelope budgeting.
Similarities Between Envelope and Bucket Budgeting
Envelope budgeting and bucket budgeting both involve allocating funds into separate categories to manage spending effectively. Each method emphasizes setting limits for specific expenses, promoting disciplined financial management. Both approaches help users visualize their budget allocations and track progress toward financial goals.
Differences in Implementation
Envelope budgeting requires physically dividing cash into separate labeled envelopes for each spending category, promoting strict discipline and limiting overspending by only using available cash. Bucket budgeting utilizes digital or virtual accounts to allocate funds into various "buckets" based on expenses, income, or savings goals, offering flexibility and easier adjustments with online banking tools. While envelope budgeting enforces tangible boundaries, bucket budgeting provides dynamic management and tracking across multiple financial categories.
Pros and Cons of Envelope Budgeting
Envelope budgeting offers clear visual control by allocating cash into physical or digital envelopes for specific expenses, promoting disciplined spending and preventing overspending. It lacks flexibility as funds are fixed per envelope, making it difficult to adjust for unexpected costs or shifts in financial priorities. This method can be time-consuming to manage manually but enhances awareness of spending habits through tangible allocation.
Pros and Cons of Bucket Budgeting
Bucket budgeting offers greater flexibility by allowing funds to be allocated into multiple specific categories, making it easier to track spending and savings goals. It can enhance financial discipline by segmenting income into designated buckets, reducing the risk of overspending in one area. However, managing numerous buckets can become complex and time-consuming, potentially leading to confusion or neglected categories if not regularly monitored.
Envelope Budgeting: Best for Whom?
Envelope budgeting is ideal for individuals seeking a hands-on approach to control spending by allocating specific cash amounts to distinct categories, ensuring disciplined expense management. It suits people who prefer tangible limits and want to avoid overspending by physically separating funds into envelopes for groceries, bills, and entertainment. This method works best for those with fluctuating incomes or variable expenses needing strict, visual budget constraints to enhance financial accountability.
Bucket Budgeting: Ideal Users and Scenarios
Bucket budgeting suits individuals seeking flexible financial management by grouping expenses and savings into separate "buckets" based on goals or categories. Ideal users include those with irregular incomes or multiple financial objectives, as this method allows dynamic allocation and reallocation of funds to adapt to changing priorities. Scenarios like vacation planning, emergency funds, and debt repayment benefit from bucket budgeting's targeted approach to tracking and controlling specific monetary goals.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Method for Your Financial Goals
Envelope budgeting allocates specific amounts of cash to physical envelopes for different expenses, promoting disciplined spending and preventing overspending by using tangible limits. Bucket budgeting divides your income into digital "buckets" or categories, offering flexibility and clear visibility into savings, investments, and spending priorities. Selecting the right method depends on your financial goals, spending habits, and preference for physical or digital organization, with envelope budgeting excelling in controlling discretionary spending and bucket budgeting enhancing long-term financial planning.
Important Terms
Zero-based budgeting
Zero-based budgeting requires justifying every expense from scratch, making it more precise than envelope budgeting, which allocates fixed cash amounts for predefined categories, and bucket budgeting, which divides funds into separate accounts or "buckets" based on spending goals. Unlike envelope and bucket budgeting that emphasize spending limits, zero-based budgeting prioritizes detailed expense analysis to improve financial efficiency and resource allocation.
Cash flow allocation
Cash flow allocation in envelope budgeting involves assigning specific amounts of cash to physical or digital envelopes for discrete expense categories, promoting strict spending limits and enhanced financial control. Bucket budgeting, however, allocates cash into broader, thematic "buckets" such as savings, expenses, and investments, offering flexibility while still maintaining an organized approach to money management.
Sinking funds
Sinking funds allocate money gradually for specific future expenses, making envelope budgeting effective by physically separating cash into labeled envelopes for each fund, ensuring disciplined spending. Bucket budgeting aggregates funds into broader categories or digital accounts, offering flexibility but potentially less precision in tracking individual sinking fund goals.
Line-item budgeting
Line-item budgeting allocates funds to specific categories such as salaries and office supplies, providing detailed financial control unlike envelope budgeting which physically separates cash into envelopes for each expense category. Bucket budgeting, similar to envelope budgeting, divides income into different "buckets" but often applies to digital or broader savings goals rather than strictly controlled monthly expenditures.
Roll-over categories
Roll-over categories in envelope budgeting allow unspent funds to carry over to the next period, maintaining flexibility within predefined spending limits, while bucket budgeting segments income into distinct accounts or "buckets" that may limit roll-over to encourage discipline. Envelope budgeting emphasizes controlled spending through physical or digital containers, whereas bucket budgeting focuses on allocation based on goals, often making roll-over less automatic but more goal-oriented.
Fund accounting
Fund accounting allocates resources into distinct categories or funds to ensure accurate tracking of specific financial activities, enhancing transparency and compliance. Envelope budgeting assigns spending limits to individual expense categories, while bucket budgeting aggregates funds into broader categories, offering more flexibility but less granularity in tracking.
Expense categorization
Expense categorization in envelope budgeting involves assigning specific cash amounts to distinct spending categories, promoting strict control over each category's budget. Bucket budgeting, by contrast, groups expenses into broader categories or savings goals, offering flexible allocation that adapts to changing financial priorities.
Digital envelope systems
Digital envelope systems streamline financial management by categorizing income into predefined virtual envelopes, promoting disciplined spending aligned with envelope budgeting principles. In contrast, bucket budgeting aggregates funds into broader categories, offering flexibility but potentially less detailed tracking compared to the precise allocation and monitoring enabled by digital envelopes.
Proportional budgeting
Proportional budgeting allocates funds based on fixed percentage ratios to different spending categories, contrasting with envelope budgeting, which divides money into physical or digital envelopes for specific expenses, and bucket budgeting, which groups funds into broader categories or 'buckets' without strict percentage constraints. This method ensures a balanced distribution of resources by predefined proportions, promoting disciplined financial planning and preventing overspending in any single category.
Category caps
Category caps in envelope budgeting impose strict spending limits within predefined categories, ensuring precise control over expenses by allocating fixed amounts to each envelope. Bucket budgeting, by contrast, groups funds into broader spending buckets, offering more flexibility with category caps that are less rigid, allowing users to adjust allocations as priorities shift.
envelope budgeting vs bucket budgeting Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com