Forecast budget provides an estimate of expected expenses and revenues based on planned activities and market conditions. Actual budget reflects the real financial performance, highlighting variances where spending or income deviates from projections. Comparing forecast budget vs actual budget enables businesses to identify inefficiencies, adjust strategies, and improve future financial planning accuracy.
Table of Comparison
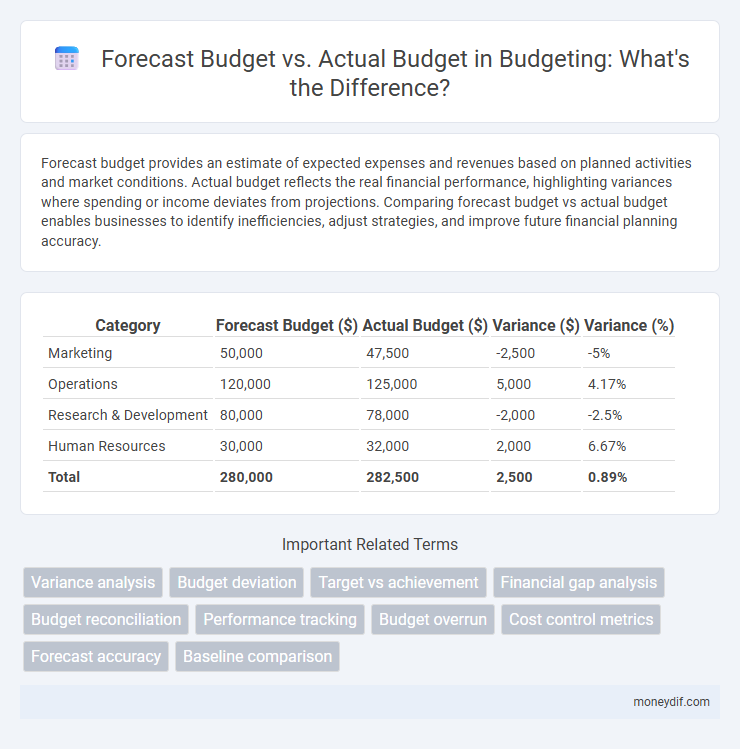
| Category | Forecast Budget ($) | Actual Budget ($) | Variance ($) | Variance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing | 50,000 | 47,500 | -2,500 | -5% |
| Operations | 120,000 | 125,000 | 5,000 | 4.17% |
| Research & Development | 80,000 | 78,000 | -2,000 | -2.5% |
| Human Resources | 30,000 | 32,000 | 2,000 | 6.67% |
| Total | 280,000 | 282,500 | 2,500 | 0.89% |
Introduction to Forecast Budget vs Actual Budget
Forecast budget projects anticipated revenues and expenses based on historical data, market trends, and strategic goals, providing a financial framework for the upcoming period. Actual budget records reflect the real financial performance, capturing revenues and expenditures as they occur. Comparing forecast budget versus actual budget highlights variances that inform decision-making and improve future budget accuracy.
Importance of Budget Forecasting
Budget forecasting provides a crucial framework for anticipating revenues and expenses, enabling organizations to allocate resources efficiently and avoid financial shortfalls. Comparing forecasted budgets against actual budgets reveals variances that help identify trends, optimize spending, and improve future financial planning accuracy. This practice supports informed decision-making and enhances overall fiscal accountability within businesses.
Key Differences Between Forecast and Actual Budgets
Forecast budgets estimate future financial outcomes based on projected revenue and expenses, providing a guideline for planning and decision-making. Actual budgets reflect the real financial performance after transactions occur, offering a precise account of income and expenditures. Key differences include accuracy, timing, and adaptability, where forecast budgets rely on assumptions while actual budgets capture concrete results.
Methods for Creating Accurate Budget Forecasts
Using historical financial data and trend analysis improves the accuracy of budget forecasts by reflecting real spending patterns and revenue fluctuations. Incorporating zero-based budgeting techniques forces a detailed review of all expenses, ensuring forecasts align with actual resource needs. Leveraging advanced predictive analytics tools helps identify potential variances early, enabling proactive adjustments to maintain budget alignment.
Common Causes of Variances in Budgets
Forecast budget vs actual budget variances commonly arise from inaccurate revenue projections, unexpected expense increases, and changes in market conditions. Operational inefficiencies, shifts in consumer demand, and unforeseen regulatory costs further contribute to discrepancies. Understanding these causes enables better financial planning and variance analysis for future budget adjustments.
Analyzing Budget Variances
Analyzing budget variances involves comparing forecasted budgets with actual expenditures to identify discrepancies and underlying causes. Accurate variance analysis enables organizations to adjust financial plans, improve resource allocation, and enhance future budgeting accuracy. Key metrics include variance amount, percentage deviation, and trend patterns across budget periods.
Tools for Tracking Budget Performance
Budget tracking tools such as spreadsheets, financial software, and cloud-based platforms provide accurate comparisons between forecasted and actual budgets, enabling real-time performance monitoring. Features like customizable dashboards, automated alerts, and variance analysis streamline identifying discrepancies and inform timely adjustments. Integrating these tools with accounting systems enhances data accuracy and supports strategic budget management.
Best Practices for Managing Budget Variances
Tracking budget variances in real-time using integrated financial software ensures accurate comparison of forecasted versus actual expenses. Implementing a regular review process with key performance indicators helps identify discrepancies early and facilitates timely corrective actions. Clear communication across departments and flexible budget adjustments maintain alignment with organizational goals while minimizing financial risks.
Impact of Budget Deviations on Business Strategy
Budget deviations between forecasted and actual amounts directly affect resource allocation and operational plans, potentially disrupting strategic objectives. Significant variances can lead to cash flow challenges, forcing businesses to revise marketing, production, or investment strategies to maintain competitiveness. Accurate monitoring of budget deviations enables timely decision-making, ensuring alignment with long-term business goals.
Continuous Improvement in Budgeting Processes
Analyzing forecast budget versus actual budget variances enables organizations to identify patterns and improve accuracy in future projections. Implementing continuous improvement methodologies, such as regular review cycles and feedback loops, enhances budgeting processes by minimizing discrepancies and optimizing resource allocation. Leveraging data analytics and automated tools supports real-time adjustments, fostering more informed decision-making and efficient financial management.
Important Terms
Variance analysis
Variance analysis evaluates differences between forecasted budgets and actual expenditures to identify cost overruns or savings. This process enhances financial control by pinpointing performance deviations, enabling informed adjustments to future budgeting and operational strategies.
Budget deviation
Budget deviation measures the variance between the forecast budget and the actual budget, highlighting discrepancies in projected versus real expenditures or revenues. Accurate analysis of budget deviation helps organizations identify areas of overspending or underspending, enabling more precise financial planning and resource allocation.
Target vs achievement
Comparing target versus achievement highlights discrepancies between forecasted budget allocations and actual budget expenditures, revealing efficiency and financial management accuracy. Analyzing variance percentages and expenditure timelines helps organizations align operational goals with fiscal discipline and optimize future budgeting processes.
Financial gap analysis
Financial gap analysis evaluates the variances between forecasted budgets and actual expenditures to identify deviations affecting organizational performance. This process enables precise budget adjustments by highlighting overspending or underspending trends critical for strategic financial planning.
Budget reconciliation
Budget reconciliation involves analyzing discrepancies between forecasted budgets and actual expenditures to ensure financial accuracy and accountability. This process identifies variances, enabling organizations to adjust future budget forecasts and improve financial planning strategies.
Performance tracking
Performance tracking in budget management involves comparing forecasted budget figures against actual expenditures to identify variances and improve financial accuracy. Utilizing real-time analytics and historical data enables organizations to adjust spending strategies, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall fiscal discipline.
Budget overrun
Budget overrun occurs when actual expenditures exceed the forecast budget, indicating inaccurate financial planning or unforeseen costs. Effective budget management requires continuous monitoring and adjustment to align forecasted estimates with real-world spending patterns.
Cost control metrics
Cost control metrics such as Cost Performance Index (CPI) and Budget Variance (BV) are essential for comparing forecast budget versus actual budget, enabling precise measurement of project financial efficiency. Tracking these metrics helps identify deviations early, supporting timely corrective actions to maintain budget adherence and optimize resource allocation.
Forecast accuracy
Forecast accuracy measures the precision of predicting budgeted amounts compared to actual expenditures, reflecting the reliability of financial planning. High forecast accuracy minimizes variances between forecast budget and actual budget, enabling better resource allocation and financial control.
Baseline comparison
Baseline comparison between forecast budget and actual budget highlights variances by measuring planned expenditure against real costs, enabling accurate financial performance analysis and improved future budgeting. Tracking deviations in budget categories such as labor, materials, and overhead supports data-driven decision-making and resource allocation optimization.
forecast budget vs actual budget Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com