Kaizen budgeting emphasizes continuous improvement by incorporating incremental cost reductions and efficiency enhancements into the budget, allowing organizations to adapt and optimize their financial plans regularly. Continuous budgeting involves the ongoing revision and updating of budgets to reflect real-time changes in the business environment, ensuring accuracy and flexibility. While Kaizen budgeting focuses on progressive cost control and operational enhancements, continuous budgeting prioritizes timely adjustments to maintain relevance and responsiveness.
Table of Comparison
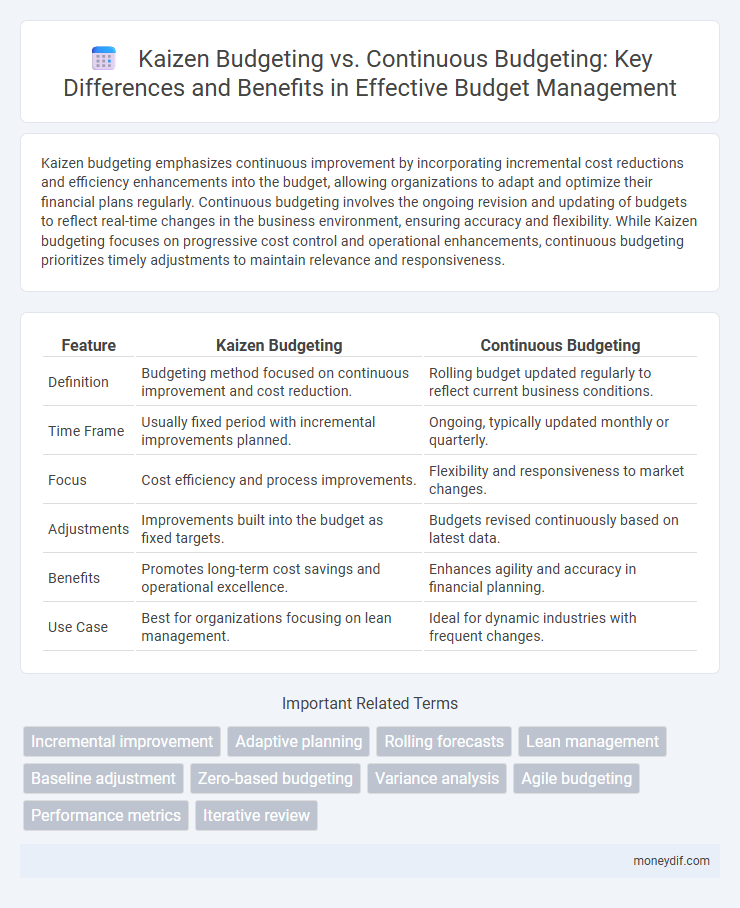
| Feature | Kaizen Budgeting | Continuous Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Budgeting method focused on continuous improvement and cost reduction. | Rolling budget updated regularly to reflect current business conditions. |
| Time Frame | Usually fixed period with incremental improvements planned. | Ongoing, typically updated monthly or quarterly. |
| Focus | Cost efficiency and process improvements. | Flexibility and responsiveness to market changes. |
| Adjustments | Improvements built into the budget as fixed targets. | Budgets revised continuously based on latest data. |
| Benefits | Promotes long-term cost savings and operational excellence. | Enhances agility and accuracy in financial planning. |
| Use Case | Best for organizations focusing on lean management. | Ideal for dynamic industries with frequent changes. |
Introduction to Kaizen Budgeting and Continuous Budgeting
Kaizen budgeting emphasizes continuous, incremental improvements by integrating cost reduction goals into the budgeting process, fostering efficiency and waste elimination over time. Continuous budgeting involves regularly updating budgets to reflect changing business conditions, enabling dynamic financial planning and real-time resource allocation. Both approaches support adaptive management, but Kaizen budgeting drives ongoing operational improvements, while continuous budgeting ensures flexibility and responsiveness in financial control.
Core Principles of Kaizen Budgeting
Kaizen budgeting emphasizes continuous, incremental improvements focused on efficiency and cost reduction, aligning budget targets with real-time operational data and employee input. This approach prioritizes waste elimination, process optimization, and adaptive cost management to support long-term value creation. Core principles include participative goal-setting, flexible allocation of resources, and sustained performance monitoring to drive sustainable financial discipline.
Key Features of Continuous Budgeting
Continuous budgeting involves regularly updating budgets to reflect real-time financial data, enabling agile decision-making and enhanced forecast accuracy. It integrates rolling forecasts with dynamic resource allocation, ensuring alignment with strategic goals and market fluctuations. This approach emphasizes flexibility, ongoing performance monitoring, and proactive adjustments to optimize financial management.
Differences Between Kaizen and Continuous Budgeting
Kaizen budgeting emphasizes continuous improvement by incorporating incremental cost reductions and efficiency gains into the budgeting process, promoting a culture of ongoing operational enhancements. Continuous budgeting involves regularly updating budgets throughout the fiscal period to reflect changes in business conditions, allowing for more flexible and real-time financial planning. The key difference lies in Kaizen budgeting's focus on systematic cost improvements embedded in the budget, whereas continuous budgeting prioritizes dynamic adjustments to align with evolving organizational goals.
Advantages of Kaizen Budgeting
Kaizen budgeting enables organizations to achieve continuous cost reduction and operational efficiency by incorporating ongoing incremental improvements directly into the budgeting process. This approach promotes employee involvement and realistic target setting, leading to greater accuracy and adaptability compared to traditional continuous budgeting. Companies using Kaizen budgeting experience enhanced resource allocation, improved cost control, and sustained performance improvements aligned with strategic objectives.
Benefits of Continuous Budgeting
Continuous budgeting ensures real-time financial adjustments, enhancing responsiveness to market fluctuations and operational changes. It facilitates proactive resource allocation by consistently updating forecasts, improving accuracy and strategic planning. Organizations benefit from increased agility, reduced budgetary lag, and enhanced decision-making compared to traditional Kaizen budgeting approaches.
Implementation Challenges for Both Methods
Kaizen budgeting faces implementation challenges such as resistance to continuous incremental changes and the need for ongoing employee involvement in identifying efficiency improvements. Continuous budgeting requires significant resources and real-time data integration, making it difficult to maintain accuracy and responsiveness without advanced technological support. Both methods demand cultural shifts in organizations, with Kaizen emphasizing constant incremental enhancement and continuous budgeting focusing on dynamic financial forecasting.
Industry Suitability: Kaizen vs. Continuous Budgeting
Kaizen budgeting suits manufacturing and production industries emphasizing incremental improvements and cost control through continuous process enhancements. Continuous budgeting fits dynamic sectors like technology and retail, where ongoing budget revisions accommodate rapid market changes and fluctuating demand. Both methods align with strategic goals, but Kaizen budgeting drives stability, while continuous budgeting fosters adaptability in volatile environments.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case studies on Kaizen budgeting reveal its effectiveness in manufacturing environments where incremental cost reductions drive long-term efficiency gains. Continuous budgeting shows strong performance in service industries by enabling dynamic allocation of resources aligned with shifting market demands. Real-world applications highlight improved financial agility and enhanced operational control as key benefits of both approaches.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Approach for Your Organization
Kaizen budgeting emphasizes continuous improvement by integrating incremental cost reductions into each budget cycle, ideal for organizations seeking long-term efficiency gains. Continuous budgeting involves ongoing updates and revisions to budget plans, allowing for real-time adjustments that reflect dynamic market conditions and operational changes. Selecting the right approach depends on your organization's agility, strategic goals, and resource management capabilities, ensuring that budgeting practices align with overall business performance and adaptability.
Important Terms
Incremental improvement
Incremental improvement in budgeting focuses on making small, consistent enhancements to financial plans, aligning closely with Kaizen budgeting's philosophy of continuous, gradual cost management and efficiency gains. Continuous budgeting, however, emphasizes frequent updates and revisions to budgets based on real-time data, supporting adaptability but often requiring more dynamic resource allocation compared to the steady, improvement-driven approach of Kaizen budgeting.
Adaptive planning
Adaptive planning integrates the iterative improvement principles of Kaizen budgeting, focusing on incremental cost improvements and flexible resource allocation, while Continuous budgeting emphasizes ongoing budget revisions to reflect real-time operational changes. Both approaches enhance financial agility, but adaptive planning uniquely supports long-term strategic adjustments through continuous learning and process refinement.
Rolling forecasts
Rolling forecasts enhance financial agility by continuously updating projections based on real-time data, aligning closely with Kaizen budgeting's focus on incremental improvements. Unlike Continuous budgeting, which maintains fixed periodic budgets, Rolling forecasts integrate ongoing adjustments, enabling dynamic resource allocation and more responsive strategic planning.
Lean management
Lean management emphasizes waste reduction and value creation through efficient processes, where Kaizen budgeting focuses on incremental improvements and cost reductions aligned with continuous operational enhancements. Continuous budgeting supports Lean by providing flexible, real-time financial planning that adapts to ongoing process improvements and fluctuating business conditions.
Baseline adjustment
Baseline adjustment in Kaizen budgeting involves setting incremental cost targets based on continuous process improvements, contrasting with continuous budgeting's flexible revision of financial plans to reflect real-time operational changes; this approach drives efficiency by embedding performance gains into the baseline rather than merely adapting budgets periodically. Kaizen budgeting emphasizes gradual, measurable enhancements that update the baseline, while continuous budgeting focuses on iterative financial planning adjustments without necessarily anchoring them to specific operational improvements.
Zero-based budgeting
Zero-based budgeting requires each expense to be justified from scratch, contrasting with kaizen budgeting's focus on continuous cost improvements aligned with lean principles. Continuous budgeting maintains ongoing budget updates based on real-time performance data, whereas zero-based budgeting resets allocations entirely, enabling more strategic resource optimization.
Variance analysis
Variance analysis in Kaizen budgeting focuses on identifying deviations between actual costs and progressively improved standards, emphasizing small, continuous cost reductions and efficiency gains. Continuous budgeting variance analysis compares actual results to static budgets maintained throughout the period, highlighting deviations without necessarily incorporating ongoing process improvements.
Agile budgeting
Agile budgeting emphasizes flexibility and iterative funding adjustments to support rapidly changing business environments, aligning closely with Kaizen budgeting's focus on continuous, incremental cost improvements driven by employee input. Unlike Continuous budgeting, which involves ongoing updates to financial plans throughout the fiscal year, Agile budgeting integrates iterative feedback loops and adaptive resource allocation, enabling faster response to market dynamics and operational changes.
Performance metrics
Kaizen budgeting focuses on continuous improvement by integrating performance metrics that emphasize cost reduction and efficiency gains over time, aligning targets with incremental process enhancements. Continuous budgeting monitors real-time financial performance using dynamic forecasts and frequent variance analysis, enabling adaptive resource allocation and more responsive budget adjustments.
Iterative review
Iterative review in Kaizen budgeting involves regular, incremental adjustments based on continuous performance feedback, fostering adaptability and cost efficiency throughout the budgeting cycle. Continuous budgeting also emphasizes real-time updates but focuses more on ongoing alignment with organizational goals rather than the incremental process improvements central to Kaizen budgeting.
Kaizen budgeting vs Continuous budgeting Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com