Debt consolidation combines multiple debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate, simplifying payments and potentially reducing overall costs. Debt settlement negotiates with creditors to reduce the total amount owed, often resulting in a lump-sum payment that is less than the original debt. Choosing between debt consolidation and debt settlement depends on factors like credit score, financial goals, and the urgency to resolve outstanding debts.
Table of Comparison
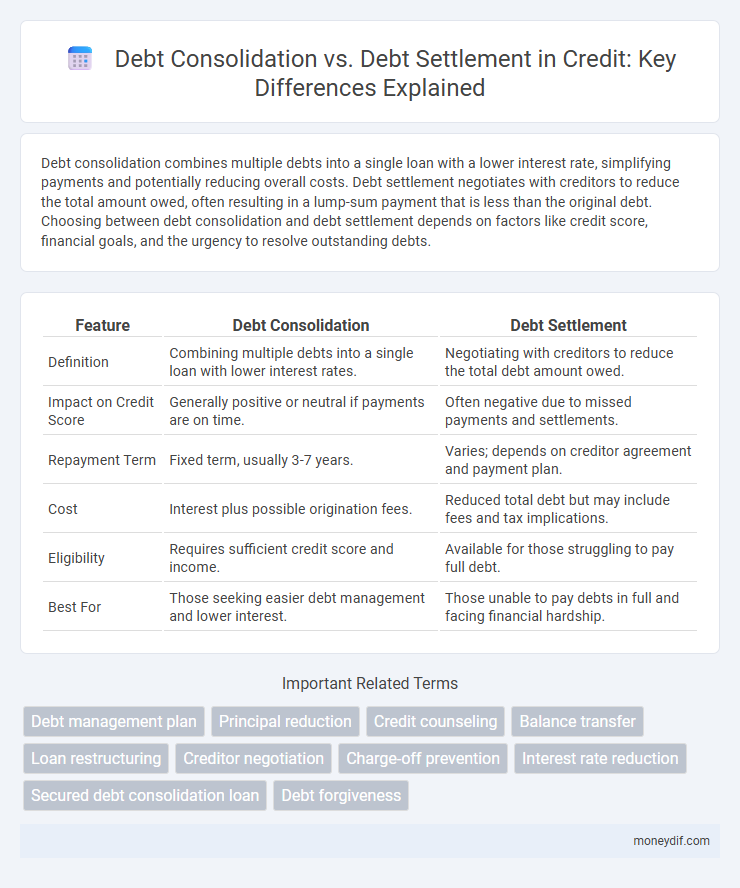
| Feature | Debt Consolidation | Debt Settlement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining multiple debts into a single loan with lower interest rates. | Negotiating with creditors to reduce the total debt amount owed. |
| Impact on Credit Score | Generally positive or neutral if payments are on time. | Often negative due to missed payments and settlements. |
| Repayment Term | Fixed term, usually 3-7 years. | Varies; depends on creditor agreement and payment plan. |
| Cost | Interest plus possible origination fees. | Reduced total debt but may include fees and tax implications. |
| Eligibility | Requires sufficient credit score and income. | Available for those struggling to pay full debt. |
| Best For | Those seeking easier debt management and lower interest. | Those unable to pay debts in full and facing financial hardship. |
Understanding Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation involves combining multiple high-interest debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate, simplifying repayment and potentially reducing monthly payments. This approach helps borrowers manage credit card balances, personal loans, and other unsecured debts more efficiently by streamlining finances under one payment plan. Understanding debt consolidation is essential for evaluating its impact on credit scores and overall financial health compared to debt settlement options.
What Is Debt Settlement?
Debt settlement is a negotiation process where a debtor agrees to pay a lump sum amount less than the total owed to creditors to resolve outstanding debts. This method can significantly reduce debt but may negatively impact credit scores and involve tax consequences on forgiven amounts. Debt settlement is typically pursued when individuals face severe financial hardship and seek an alternative to bankruptcy.
Key Differences Between Debt Consolidation and Debt Settlement
Debt consolidation combines multiple debts into a single loan with a potentially lower interest rate, simplifying payments and improving credit scores by making on-time payments. In contrast, debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to reduce the total debt owed, which can significantly impact credit scores and may include upfront fees or tax consequences. While debt consolidation aims for full repayment over time, debt settlement focuses on paying less than the full balance but often carries greater risks to credit health.
Pros and Cons of Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation involves combining multiple debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate, potentially simplifying repayment and reducing monthly payments. It can improve credit scores by timely payments, but may extend the repayment period and increase total interest paid. However, it requires discipline to avoid accruing new debt and may involve fees or collateral, especially with secured consolidation loans.
Benefits and Risks of Debt Settlement
Debt settlement can reduce the total amount of debt owed by negotiating with creditors for a lower payoff, which may improve cash flow and help avoid bankruptcy. However, this approach involves risks such as damaging credit scores, potential tax liabilities on forgiven debt, and the possibility that creditors refuse to negotiate, resulting in continued collection efforts. Careful consideration of these factors is crucial before choosing debt settlement as a solution.
How Debt Consolidation Impacts Your Credit Score
Debt consolidation typically improves your credit score by streamlining multiple debts into a single monthly payment, reducing the risk of missed payments and lowering your credit utilization ratio. Paying off consolidated loans on time demonstrates responsible credit behavior, which can boost your credit rating over time. However, applying for new consolidation loans may result in a temporary dip due to hard inquiries on your credit report.
Credit Score Effects of Debt Settlement
Debt settlement often significantly impacts credit scores by marking accounts as settled for less than the full balance, which can lower credit ratings. Unlike debt consolidation, which usually involves new loans that may temporarily reduce scores but help maintain repayment history, debt settlement can remain on credit reports for up to seven years. This negative notation may hinder future credit approvals or increase borrowing costs despite providing short-term debt relief.
Choosing Between Debt Consolidation and Debt Settlement
Choosing between debt consolidation and debt settlement depends on individual financial situations and credit goals. Debt consolidation combines multiple debts into a single loan with a potentially lower interest rate, improving credit score by timely payments. Debt settlement negotiates reduced payoff amounts but may negatively impact credit ratings and involve tax consequences on forgiven debt.
When to Consider Debt Consolidation
Debt consolidation is ideal when multiple high-interest debts create overwhelming monthly payments that are difficult to manage, enabling borrowers to combine balances into a single loan with a lower interest rate. It's a strategic option for individuals with a stable income and a good credit score who aim to simplify their finances and reduce interest expenses over time. Considering debt consolidation early, before missing payments or damaging credit, can help maintain financial stability and improve credit utilization ratios.
When Debt Settlement Might Be the Right Option
Debt settlement might be the right option when an individual cannot keep up with minimum payments and faces mounting unsecured debt like credit cards or medical bills. This approach involves negotiating with creditors to reduce the total amount owed, often resulting in a lower payoff balance and potentially impacting credit scores less severely than bankruptcy. It is most suitable for those with a lump sum payment available and who are struggling to manage multiple high-interest debts without a steady income to support consolidation loans.
Important Terms
Debt management plan
A Debt Management Plan (DMP) involves structured repayment of debts typically through credit counseling, contrasting with Debt Consolidation which combines multiple debts into a single loan often with lower interest rates, and Debt Settlement which negotiates reduced balances for lump-sum payments. DMPs focus on manageable monthly payments without severe credit impacts, while Debt Settlement can significantly affect credit scores, and Debt Consolidation depends on credit approval for new financing terms.
Principal reduction
Principal reduction lowers the actual loan balance, making it a more effective strategy in debt settlement compared to debt consolidation, which primarily restructures or combines debts without reducing the total owed. By negotiating a principal reduction, debt settlement can significantly decrease overall debt, whereas debt consolidation focuses on simplifying payments and interest rates without directly cutting down the principal amount.
Credit counseling
Credit counseling offers personalized financial guidance to evaluate options like debt consolidation, which combines multiple debts into a single lower-interest loan, or debt settlement, where creditors agree to accept less than the full amount owed. Choosing between debt consolidation and debt settlement depends on factors such as credit score impact, monthly payment affordability, and long-term debt relief goals.
Balance transfer
Balance transfer allows debt consolidation by moving high-interest credit card balances to a card with lower interest rates, simplifying payments and reducing overall debt faster. In contrast, debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to reduce the total owed, potentially impacting credit scores but providing immediate relief from burdensome debts.
Loan restructuring
Loan restructuring involves modifying existing debt terms to improve repayment conditions, often by extending loan tenure or reducing interest rates. Debt consolidation combines multiple debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate, while debt settlement negotiates to reduce the total owed amount, both serving distinct roles in managing financial obligations.
Creditor negotiation
Creditor negotiation involves directly working with lenders to reduce the total debt, often resulting in lower interest rates or extended payment plans, which differs from debt consolidation that combines multiple debts into a single loan with a potentially lower interest rate. Debt settlement, by contrast, seeks to negotiate a lump-sum payment for less than the owed balance, which can impact credit scores more significantly than creditor negotiation or consolidation methods.
Charge-off prevention
Debt consolidation streamlines multiple debts into a single loan with lower interest rates, reducing the risk of charge-offs by improving payment management and credit score. Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to reduce total debt, which can lead to charge-offs if payments are missed or settlements are not completed, negatively impacting credit health.
Interest rate reduction
Interest rate reduction plays a crucial role in debt consolidation by lowering the overall borrowing cost through a single loan with a reduced interest rate, making monthly payments more manageable. In contrast, debt settlement focuses on negotiating with creditors to reduce the total debt balance, often without directly impacting the interest rates, potentially leading to a shorter payoff period but possible credit score implications.
Secured debt consolidation loan
Secured debt consolidation loans use collateral to combine multiple debts into a single payment, typically offering lower interest rates compared to unsecured options. Unlike debt settlement, which negotiates to reduce the total amount owed and can negatively impact credit scores, secured consolidation focuses on restructuring debt to improve repayment terms without immediate credit damage.
Debt forgiveness
Debt forgiveness often plays a critical role in debt settlement, where creditors agree to reduce the outstanding balance, contrasting with debt consolidation that restructures multiple debts into a single loan without necessarily lowering the principal owed. While debt settlement can improve financial relief by eliminating part of the debt, debt consolidation typically focuses on manageable payments and lower interest rates without direct forgiveness.
Debt consolidation vs Debt settlement Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com