Cov-lite loans feature fewer borrower restrictions, offering more flexibility but higher risk for lenders due to limited protective covenants. Covenant-heavy loans impose strict financial and operational requirements, enhancing lender control and reducing risk but restricting borrower freedom. Selecting between cov-lite and covenant-heavy loans depends on the balance between borrower flexibility and lender risk tolerance.
Table of Comparison
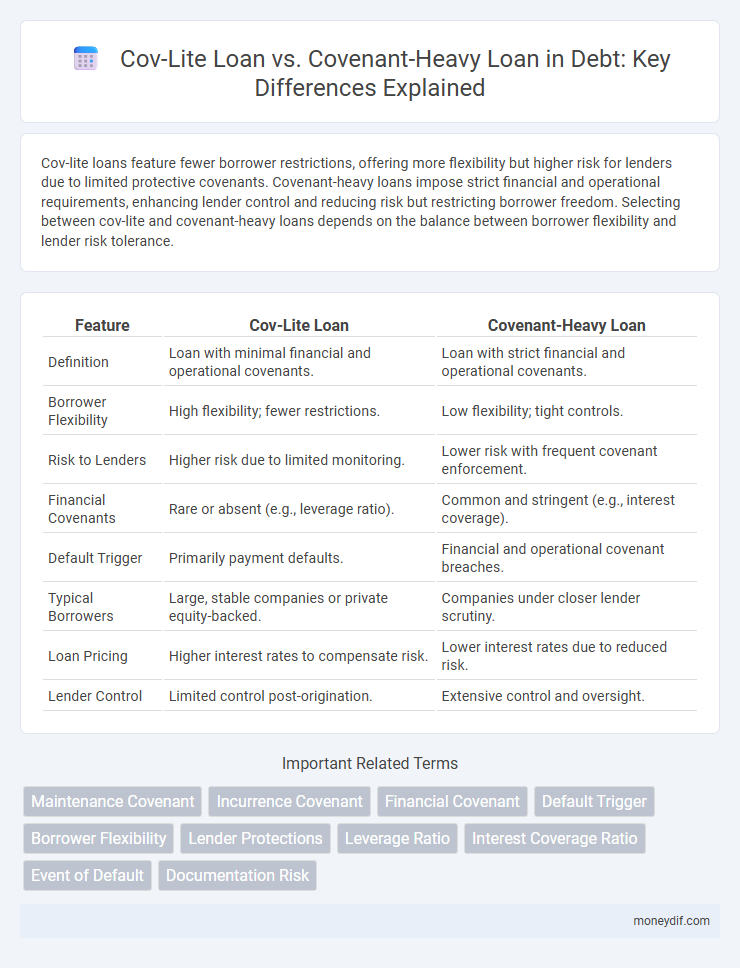
| Feature | Cov-Lite Loan | Covenant-Heavy Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loan with minimal financial and operational covenants. | Loan with strict financial and operational covenants. |
| Borrower Flexibility | High flexibility; fewer restrictions. | Low flexibility; tight controls. |
| Risk to Lenders | Higher risk due to limited monitoring. | Lower risk with frequent covenant enforcement. |
| Financial Covenants | Rare or absent (e.g., leverage ratio). | Common and stringent (e.g., interest coverage). |
| Default Trigger | Primarily payment defaults. | Financial and operational covenant breaches. |
| Typical Borrowers | Large, stable companies or private equity-backed. | Companies under closer lender scrutiny. |
| Loan Pricing | Higher interest rates to compensate risk. | Lower interest rates due to reduced risk. |
| Lender Control | Limited control post-origination. | Extensive control and oversight. |
Understanding Cov-Lite and Covenant-Heavy Loans
Cov-lite loans feature fewer borrower restrictions and lack maintenance covenants, increasing risk for lenders but offering more operational flexibility to borrowers. Covenant-heavy loans impose strict financial and operational requirements, providing lenders with early warning signs and control mechanisms to mitigate default risk. Understanding the trade-offs between these loan types is crucial for investors and borrowers to balance risk and flexibility in debt financing.
Key Features of Cov-Lite Loans
Cov-lite loans feature minimal financial maintenance covenants, reducing restrictions on borrowers' operational and financial flexibility. They often rely on incurrence covenants, which only trigger upon specific events like additional borrowing, allowing companies greater freedom between reviews. These loans typically have higher risk profiles for lenders due to limited early warning mechanisms of financial distress.
Key Features of Covenant-Heavy Loans
Covenant-heavy loans impose strict financial maintenance covenants requiring borrowers to meet specific financial ratios like leverage and interest coverage, ensuring continuous lender oversight. They often include affirmative and negative covenants restricting actions such as additional debt issuance, asset sales, or dividend payments, thereby protecting creditor interests. The stringent monitoring reduces default risk but may limit borrower flexibility compared to cov-lite loans.
Major Differences Between Cov-Lite and Covenant-Heavy Loans
Cov-lite loans feature fewer borrower restrictions and limited lender protections, often lacking maintenance covenants that require regular financial health checks, which increases risk exposure for lenders. Covenant-heavy loans include strict financial maintenance and performance covenants, enabling lenders to monitor borrower stability and trigger remedies if conditions deteriorate. The major differences hinge on the degree of borrower discipline and lender oversight, influencing risk, pricing, and negotiation leverage in debt agreements.
Advantages of Cov-Lite Loans for Borrowers
Cov-lite loans offer borrowers greater flexibility by reducing the frequency and stringency of financial covenants, allowing businesses to allocate capital towards growth initiatives instead of covenant compliance. These loans typically have fewer restrictions on leverage and liquidity ratios, minimizing the risk of technical defaults that could trigger penalties or loan accelerations. The decreased covenant burden in cov-lite loans enhances borrower autonomy in managing operations and strategic decisions without lender intervention.
Risks of Cov-Lite Loans for Lenders
Cov-lite loans expose lenders to higher credit risk due to fewer financial maintenance covenants, reducing early warning indicators of borrower distress. The lack of strict covenants limits lenders' ability to intervene or restructure terms before defaults occur. Consequently, cov-lite loans often result in greater potential losses and delayed recovery in the event of borrower insolvency.
Benefits of Covenant-Heavy Loans for Lenders
Covenant-heavy loans provide lenders with enhanced risk management by imposing strict financial and operational requirements on borrowers, which facilitates early identification of potential defaults. These loans offer increased control over borrower behavior through enforceable covenants, safeguarding the lender's investment and reducing credit risk. Strong covenants also improve loan recovery rates in distress situations, making them a preferred choice for risk-averse lenders seeking maximum security.
Drawbacks of Covenant-Heavy Loans for Borrowers
Covenant-heavy loans impose strict financial and operational restrictions on borrowers, limiting their flexibility in managing business decisions and capital allocation. These stringent covenants can lead to frequent compliance monitoring and the risk of technical defaults, which may cause lenders to demand immediate repayment or renegotiate terms. Borrowers often face increased administrative costs and reduced negotiating power, hindering growth and strategic initiatives.
Market Trends: Cov-Lite vs Covenant-Heavy Lending
The lending market has seen a significant shift toward cov-lite loans, characterized by fewer borrower restrictions and streamlined terms, appealing to private equity firms and leveraged buyouts. Covenant-heavy loans, traditionally favored for risk mitigation through strict financial covenants and performance triggers, are now less common due to increased lender confidence and competitive market dynamics. Despite this trend, sectors with higher credit risk still rely on covenant-heavy structures to safeguard creditor interests.
Choosing the Right Loan Structure for Your Needs
Choosing between a cov-lite loan and a covenant-heavy loan depends on your financial stability and risk tolerance. Cov-lite loans offer fewer restrictions and greater flexibility but often come with higher interest rates and increased lender risk. Covenant-heavy loans impose strict financial and operational requirements, providing lenders with greater protection while potentially limiting borrower maneuverability.
Important Terms
Maintenance Covenant
Maintenance covenants in cov-lite loans are minimal or absent, reducing borrower restrictions, whereas covenant-heavy loans impose strict maintenance covenants to monitor financial health and trigger remedies upon breaches.
Incurrence Covenant
Incurrence covenants restrict borrowers from taking specific actions like incurring additional debt without lender approval, typical in covenant-heavy loans that offer stringent financial protections. In contrast, cov-lite loans minimize or eliminate incurrence covenants, providing borrowers greater operational flexibility but increasing risk exposure for lenders.
Financial Covenant
Financial covenants in cov-lite loans are minimal or absent, increasing borrower flexibility but raising lender risk, whereas covenant-heavy loans impose strict financial conditions to protect lenders by closely monitoring borrower performance.
Default Trigger
Default triggers in cov-lite loans are less stringent, typically lacking borrower financial maintenance covenants, whereas covenant-heavy loans impose strict performance benchmarks to more readily trigger default consequences.
Borrower Flexibility
Borrower flexibility significantly increases in cov-lite loans due to fewer restrictive covenants compared to covenant-heavy loans that impose stringent financial and operational requirements.
Lender Protections
Lender protections in cov-lite loans are weaker due to fewer financial covenants compared to covenant-heavy loans, which provide stricter terms and monitoring to mitigate credit risk.
Leverage Ratio
Leverage ratio measures a borrower's debt relative to equity, significantly influencing the risk profile of cov-lite loans which feature fewer financial covenants compared to covenant-heavy loans that impose strict leverage thresholds and regular compliance tests. Lower leverage ratios in cov-lite loans result in reduced creditor protections and increased risk transparency challenges, whereas covenant-heavy loans mitigate default risk through stringent requirements and tighter leverage constraints.
Interest Coverage Ratio
Interest Coverage Ratio typically exceeds 4.0x in covenant-heavy loans, indicating strong debt service capacity, while cov-lite loans often feature lower ratios around 2.0x, reflecting reduced financial covenants and higher risk exposure.
Event of Default
Event of Default occurs more frequently in covenant-heavy loans due to strict compliance requirements, whereas cov-lite loans reduce default triggers by limiting financial covenants.
Documentation Risk
Documentation risk increases with cov-lite loans due to fewer borrower restrictions and less enforcement of financial covenants compared to covenant-heavy loans that include detailed protective clauses.
cov-lite loan vs covenant-heavy loan Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com