Period costs are expenses that are not directly tied to the production process and are recorded in the period they are incurred, such as administrative salaries and rent. Product costs include all costs directly associated with manufacturing a product, like raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead, and are inventoried until the product is sold. Understanding the distinction between period and product costs is essential for accurate financial reporting and cost management.
Table of Comparison
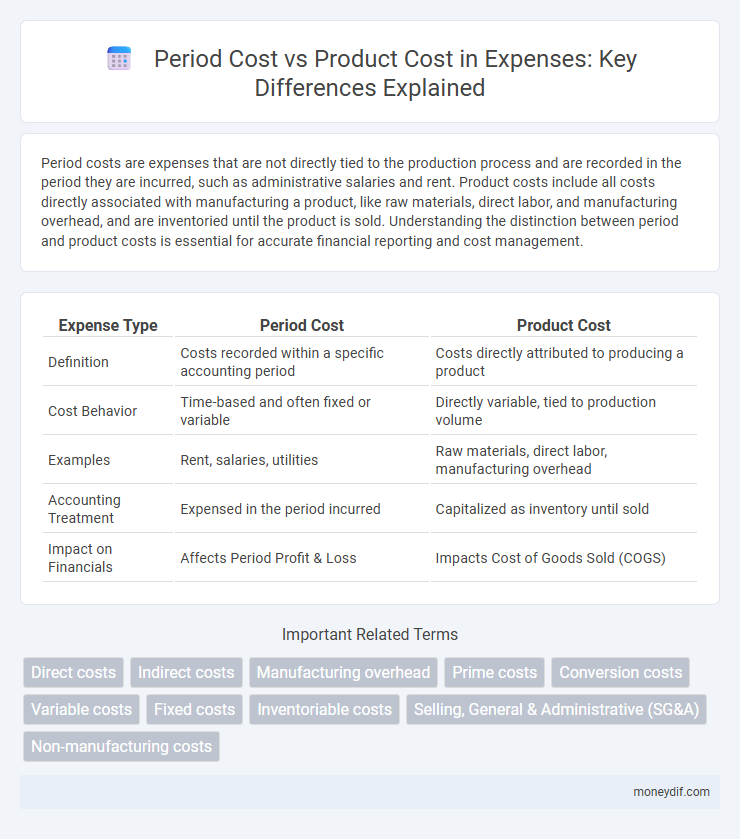
| Expense Type | Period Cost | Product Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Costs recorded within a specific accounting period | Costs directly attributed to producing a product |
| Cost Behavior | Time-based and often fixed or variable | Directly variable, tied to production volume |
| Examples | Rent, salaries, utilities | Raw materials, direct labor, manufacturing overhead |
| Accounting Treatment | Expensed in the period incurred | Capitalized as inventory until sold |
| Impact on Financials | Affects Period Profit & Loss | Impacts Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) |
Understanding Period Costs and Product Costs
Period costs are expenses that are charged to the accounting period in which they are incurred, such as selling, general, and administrative expenses, and are not directly tied to product manufacturing. Product costs include direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead, which are capitalized as inventory and expensed as cost of goods sold when the product is sold. Understanding the distinction helps businesses accurately allocate costs for financial reporting and inventory valuation.
Key Differences Between Period Costs and Product Costs
Period costs are expenses not directly tied to production, such as selling and administrative costs, and are expensed in the period incurred. Product costs include direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead, which are capitalized as inventory until sold. Key differences lie in timing of expense recognition and association with production activities, impacting financial reporting and inventory valuation.
Components of Product Costs
Product costs consist of direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead, all directly tied to the production process. Period costs include non-manufacturing expenses such as selling, general, and administrative costs, which are expensed in the period incurred. Understanding the distinction between these components helps in accurate financial reporting and cost control within manufacturing operations.
Elements Included in Period Costs
Period costs primarily include selling, general, and administrative expenses such as salaries, rent, and office supplies that are not directly tied to production. These costs are expensed in the period incurred rather than being capitalized into inventory. Unlike product costs, period costs do not flow through inventory accounts or affect the cost of goods sold.
Impact on Financial Statements
Period costs, such as selling, general, and administrative expenses, are expensed on the income statement in the period incurred, directly reducing net income for that period. Product costs, including direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead, are initially recorded as inventory on the balance sheet and only become expenses as cost of goods sold when inventory is sold, affecting both the balance sheet and income statement. This distinction impacts financial statements by influencing reported profitability, inventory valuation, and timing of expense recognition.
Examples of Product Costs in Various Industries
Product costs encompass expenses directly tied to manufacturing or acquiring goods, including raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. In the automotive industry, product costs cover steel, engine parts, and assembly line wages, while in the apparel sector, they include fabric, sewing labor, and factory rent. These costs are capitalized as inventory until the products are sold, differentiating them from period costs that are expensed immediately.
Period Costs: Typical Examples Explained
Period costs include expenses that are not directly tied to the production process, such as selling, general, and administrative costs. Typical examples are office rent, executive salaries, and marketing expenses, which are expensed during the period in which they are incurred. Unlike product costs, period costs do not become part of inventory valuation and are recorded immediately on the income statement.
How Period and Product Costs Affect Profitability
Period costs, such as administrative and selling expenses, directly reduce net income in the period they are incurred without being tied to product production. Product costs, including direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead, are capitalized as inventory and only impact profitability when goods are sold, affecting cost of goods sold and gross margin. Accurate allocation of period and product costs is essential for precise profit measurement and strategic pricing decisions.
Treatment of Costs Under Different Accounting Methods
Period costs are expensed in the accounting period in which they occur, reflecting costs such as administrative salaries and rent that do not directly tie to production. Product costs are capitalized as inventory on the balance sheet under absorption costing and expensed as cost of goods sold when the product is sold, including direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Variable costing treats only variable manufacturing costs as product costs, expensing fixed manufacturing overhead as period costs immediately.
Best Practices for Allocating Period and Product Costs
Accurate allocation of period costs and product costs enhances financial reporting and decision-making by distinguishing between expenses related to production and those incurred regardless of output levels. Best practices include applying product costs directly to inventory and cost of goods sold, while period costs should be expensed in the period incurred to reflect operational activities properly. Utilizing activity-based costing techniques and ensuring consistent cost assignment aligns with accounting standards and improves cost control and profitability analysis.
Important Terms
Direct costs
Direct costs refer to expenses that can be directly traced to the production of goods or services, making them primarily product costs; these include raw materials and direct labor. Period costs, such as administrative salaries and rent, are not directly tied to production and are expensed in the period incurred, contrasting with product costs that are inventoried until sold.
Indirect costs
Indirect costs refer to expenses not directly traceable to a specific product, commonly classified as period costs when associated with administrative functions, and as product costs when linked to manufacturing overhead. Distinguishing period costs, which are expensed in the period incurred, from product costs, which are capitalized as inventory until sold, optimizes cost allocation and financial reporting accuracy.
Manufacturing overhead
Manufacturing overhead includes indirect costs such as factory utilities, depreciation, and maintenance that are allocated to product costs to accurately determine inventory value. Period costs, in contrast, consist of selling, general, and administrative expenses that are expensed in the period incurred and not included in manufacturing overhead.
Prime costs
Prime costs, consisting of direct materials and direct labor, are crucial for calculating product costs as they directly relate to manufacturing expenses. Period costs, including selling, general, and administrative expenses, are not assigned to products and are expensed in the period incurred.
Conversion costs
Conversion costs, comprising direct labor and manufacturing overhead, are classified as product costs because they are essential to transforming raw materials into finished goods. Period costs, on the other hand, include selling, general, and administrative expenses that are not directly tied to production and are expensed in the period incurred.
Variable costs
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume and are primarily categorized as product costs when tied to manufacturing activities, such as raw materials and direct labor. Period costs, including selling and administrative expenses, are generally fixed and expensed in the period incurred, unlike variable product costs recorded as inventory until sold.
Fixed costs
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production volume and are classified as period costs when related to expenses not directly tied to manufacturing, such as administrative salaries; conversely, fixed manufacturing overheads are included in product costs, being allocated to inventory until goods are sold. Proper distinction between period costs and product costs is essential for accurate financial reporting, cost control, and decision-making in managerial accounting.
Inventoriable costs
Inventoriable costs, directly tied to product cost, include raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead, which are capitalized as inventory and expensed as cost of goods sold when products are sold. Period costs, such as selling, general, and administrative expenses, are expensed immediately within the period incurred and are not included in inventory valuation.
Selling, General & Administrative (SG&A)
Selling, General & Administrative (SG&A) expenses are classified as period costs because they are not directly tied to the production process and are expensed in the period incurred. These costs contrast with product costs, which include direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead that are capitalized as inventory until the goods are sold.
Non-manufacturing costs
Non-manufacturing costs, such as selling, general, and administrative expenses, are classified as period costs because they are not directly tied to production and are expensed in the period incurred. In contrast, product costs include direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead, which are capitalized as inventory and expensed as cost of goods sold when products are sold.
Period cost vs Product cost Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com