Sector funds concentrate investments within a specific industry, offering targeted exposure to areas like technology, healthcare, or energy. Thematic funds, on the other hand, invest based on broad, cross-sector trends such as sustainability, innovation, or demographic shifts. Investors choose sector funds for precise industry bets, while thematic funds appeal to those seeking growth aligned with overarching economic themes.
Table of Comparison
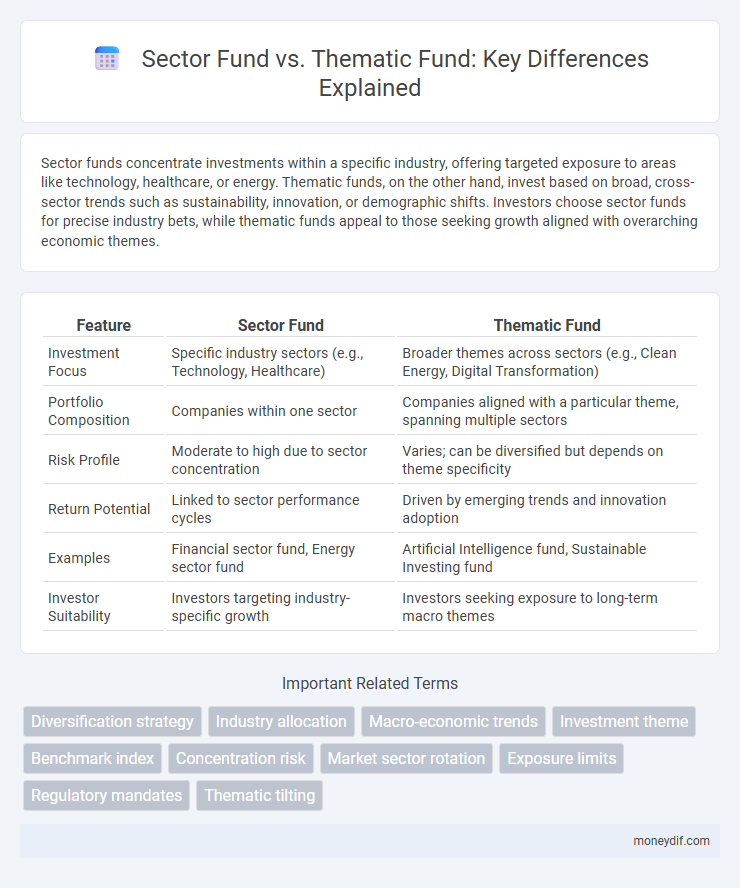
| Feature | Sector Fund | Thematic Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Focus | Specific industry sectors (e.g., Technology, Healthcare) | Broader themes across sectors (e.g., Clean Energy, Digital Transformation) |
| Portfolio Composition | Companies within one sector | Companies aligned with a particular theme, spanning multiple sectors |
| Risk Profile | Moderate to high due to sector concentration | Varies; can be diversified but depends on theme specificity |
| Return Potential | Linked to sector performance cycles | Driven by emerging trends and innovation adoption |
| Examples | Financial sector fund, Energy sector fund | Artificial Intelligence fund, Sustainable Investing fund |
| Investor Suitability | Investors targeting industry-specific growth | Investors seeking exposure to long-term macro themes |
Understanding Sector Funds: Definition and Key Features
Sector funds invest primarily in companies within a specific industry or economic sector, such as technology, healthcare, or energy, allowing investors to target growth opportunities tied to sector performance. These funds offer concentrated exposure and can deliver higher returns during sector booms but also carry increased risk due to lack of diversification. Key features include focused portfolio allocation, sector-specific risk factors, and potential for above-average growth associated with industry trends.
What Are Thematic Funds? An Overview
Thematic funds concentrate investments on specific trends, sectors, or themes such as technology innovation, clean energy, or healthcare advancements, aiming to capture growth driven by long-term societal changes. Unlike sector funds that target broad market segments like financials or consumer goods, thematic funds focus on interdisciplinary opportunities reflecting evolving consumer behaviors and technological disruptions. These funds provide investors exposure to future-oriented themes potentially delivering higher returns through focused yet diversified portfolios aligned with macroeconomic shifts.
Core Differences Between Sector and Thematic Funds
Sector funds concentrate investments within a specific industry like technology or healthcare, offering targeted exposure to well-defined market segments. Thematic funds invest across multiple sectors based on broader trends or themes such as clean energy or digital innovation, capturing opportunities beyond individual industries. The core difference lies in the investment scope--sector funds emphasize concentrated industry risk, while thematic funds pursue diversified thematic trends for growth potential.
Risk Profiles: Sector Fund vs Thematic Fund
Sector funds concentrate investments in specific industry sectors such as technology or healthcare, resulting in moderate risk due to exposure to established market segments. Thematic funds target broader investment themes like sustainability or innovation, often encompassing multiple sectors, which can lead to higher volatility and risk due to dependency on emerging trends. Risk profiles differ as sector funds typically offer more stability tied to sector performance, whereas thematic funds carry increased uncertainty driven by shifting consumer preferences and regulatory changes.
Investment Objectives: Sector Funds vs Thematic Funds
Sector funds focus on investing in companies within a specific industry, aiming to capitalize on the growth and performance of that particular sector, such as technology or healthcare. Thematic funds target broader investment themes or trends that may span multiple sectors, like clean energy or artificial intelligence, seeking long-term growth driven by macroeconomic shifts or societal changes. Both funds align investment objectives with distinct market opportunities, but sector funds emphasize concentrated industry exposure while thematic funds pursue diversified trends across various sectors.
Portfolio Diversification: Which Fund Offers More?
Sector funds concentrate investments in a specific industry, leading to limited portfolio diversification due to exposure to sector-specific risks. Thematic funds invest based on broader, cross-sector trends or ideas, offering a wider range of asset classes and enhancing diversification within the portfolio. Investors seeking greater diversification benefits should consider thematic funds for their ability to spread risk across multiple sectors linked by a common theme.
Performance Trends: Sector vs Thematic Funds
Sector funds concentrate investments in specific industries like technology or healthcare, often showing performance driven by industry cycles and regulatory changes. Thematic funds invest based on broader trends such as clean energy or artificial intelligence, typically capturing long-term growth potential across multiple sectors. Historical data indicates that sector funds may deliver sharper but more volatile returns, while thematic funds offer diversified exposure with smoother performance trends aligned to macroeconomic shifts.
Ideal Investors for Sector vs Thematic Funds
Sector funds attract investors seeking targeted exposure within a specific industry, such as technology or healthcare, aiming to capitalize on sector-specific growth trends. Thematic funds suit investors interested in broad, long-term trends like sustainability or digital innovation, offering diversified holdings across multiple sectors aligned with a particular theme. Ideal investors for sector funds typically possess a higher risk tolerance and sector expertise, while thematic fund investors often prioritize thematic conviction and trend longevity.
Factors to Consider Before Investing
Evaluating Sector Funds versus Thematic Funds requires examining factors such as market volatility, investment goals, and risk tolerance. Sector Funds concentrate assets in specific industry sectors, offering targeted exposure but higher sector-specific risk, while Thematic Funds focus on broader trends like sustainability or technology innovation, providing diversified thematic exposure. Investors should analyze fund performance history, expense ratios, and alignment with their portfolio strategy before committing capital.
Sector Fund vs Thematic Fund: Which Should You Choose?
Sector funds invest in specific industries such as technology, healthcare, or energy, offering targeted exposure based on economic sectors, while thematic funds focus on broader investment themes like clean energy, artificial intelligence, or demographic trends, crossing multiple sectors. Investors should choose sector funds for specialized industry growth and higher volatility tolerance, whereas thematic funds suit those seeking long-term thematic growth aligned with global trends and innovation. Evaluating risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market trends helps determine whether a sector or thematic fund best aligns with individual financial goals.
Important Terms
Diversification strategy
Diversification strategy in sector funds focuses on allocating investments across companies within a single industry to reduce risk associated with company-specific factors, while thematic funds diversify by targeting broad trends or themes spanning multiple sectors, such as renewable energy or technology innovation. Sector funds offer concentrated exposure to industry performance, whereas thematic funds provide strategic diversification by integrating varied sectors aligned with long-term growth themes.
Industry allocation
Industry allocation in sector funds focuses on investing within predefined industry categories such as technology, healthcare, or financials, ensuring concentrated exposure to specific economic segments. Thematic funds allocate capital based on broader investment themes like clean energy or digital transformation, often crossing multiple traditional industries to capitalize on emerging trends.
Macro-economic trends
Macro-economic trends influence Sector Funds by driving performance in industries aligned with economic cycles, such as energy or financials, while Thematic Funds capitalize on long-term trends like technology innovation or sustainability regardless of short-term economic fluctuations. Sector Funds tend to exhibit higher volatility due to sensitivity to economic shifts, whereas Thematic Funds offer growth potential through targeted exposure to specific themes that benefit from structural changes in the global economy.
Investment theme
Sector funds concentrate investments on specific industries like technology or healthcare, offering targeted exposure to market segments. Thematic funds invest based on broader trends or themes, such as renewable energy or artificial intelligence, aligning with long-term growth opportunities across multiple sectors.
Benchmark index
Benchmark indexes for sector funds typically track specific industry segments like the S&P 500 Information Technology or the MSCI Healthcare Index, providing a clear performance standard tied to that sector's companies. Thematic funds reference broader, cross-sectoral benchmarks such as the MSCI Global Environment or MSCI Future Mobility Index to capture growth trends driven by overarching themes rather than a single industry.
Concentration risk
Concentration risk in sector funds is higher due to investments focused on a single industry, increasing vulnerability to sector-specific downturns; thematic funds, while also concentrated, diversify across multiple sectors linked by a common theme, potentially mitigating risk through broader exposure. Understanding the portfolio composition and sector correlation is crucial for investors to assess risk levels in sector versus thematic funds.
Market sector rotation
Market sector rotation involves shifting investments among different sectors to capitalize on economic cycles, with sector funds offering diversified exposure to specific industry groups, while thematic funds target broader investment themes that may span multiple sectors. Investors prefer sector funds for concentrated bets on traditional economic drivers, whereas thematic funds appeal to those seeking growth through innovation, demographics, or emerging trends.
Exposure limits
Exposure limits in sector funds typically focus on restricting investment in specific industries to manage risk concentration, while thematic funds set exposure limits based on overarching investment themes such as technology innovation or sustainability trends. Sector funds emphasize diversification within a single industry, whereas thematic funds limit exposure across multiple sectors aligned with the chosen theme to balance potential growth and volatility.
Regulatory mandates
Regulatory mandates for Sector Funds often require stringent compliance with industry-specific exposure limits and disclosure norms set by securities regulators to prevent concentration risks, whereas Thematic Funds must adhere to guidelines ensuring thematic integrity and diversification across multiple sectors within the chosen theme to mitigate volatility. Both fund types are subject to risk management frameworks and reporting standards dictated by regulatory bodies like the SEC or SEBI, emphasizing investor protection and transparency.
Thematic tilting
Thematic tilting involves adjusting portfolio allocation to favor specific themes within broader sectors, enhancing targeted exposure in Sector Funds compared to Thematic Funds, which invest directly in narrowly defined themes. Sector Funds provide diversified exposure within an industry, while Thematic Funds focus more intensely on singular trends, offering higher concentration risk but potentially greater returns.
Sector Fund vs Thematic Fund Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com