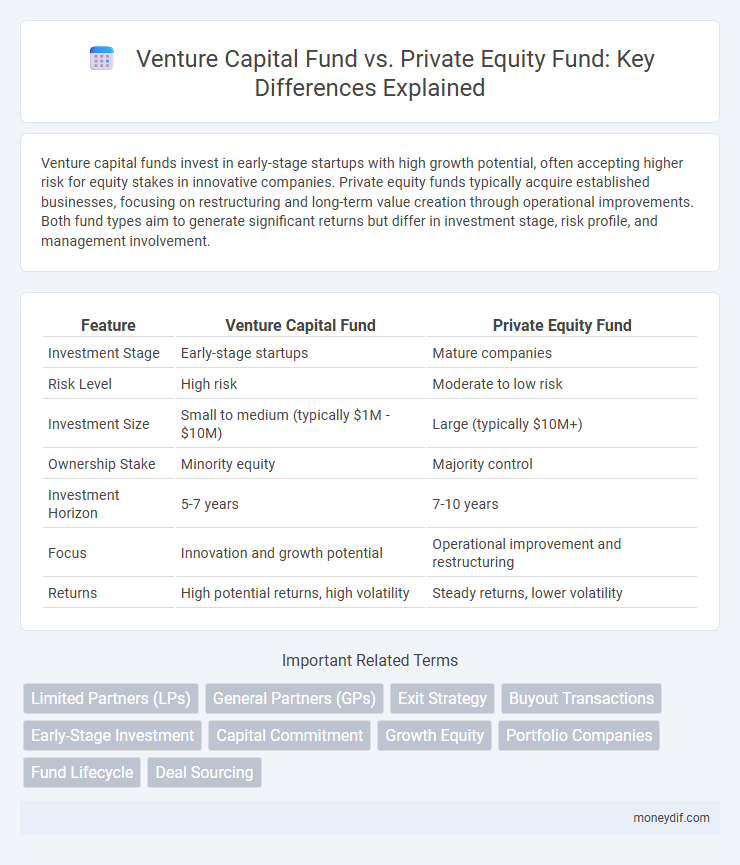
Venture capital funds invest in early-stage startups with high growth potential, often accepting higher risk for equity stakes in innovative companies. Private equity funds typically acquire established businesses, focusing on restructuring and long-term value creation through operational improvements. Both fund types aim to generate significant returns but differ in investment stage, risk profile, and management involvement.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Venture Capital Fund | Private Equity Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Stage | Early-stage startups | Mature companies |
| Risk Level | High risk | Moderate to low risk |
| Investment Size | Small to medium (typically $1M - $10M) | Large (typically $10M+) |
| Ownership Stake | Minority equity | Majority control |
| Investment Horizon | 5-7 years | 7-10 years |
| Focus | Innovation and growth potential | Operational improvement and restructuring |
| Returns | High potential returns, high volatility | Steady returns, lower volatility |
Introduction to Venture Capital and Private Equity Funds
Venture capital funds invest in early-stage startups with high growth potential, providing not only capital but also strategic support to accelerate innovation and market entry. Private equity funds typically acquire mature companies, aiming to improve operational efficiency and profitability before exiting through sales or public offerings. Both fund types play crucial roles in financing business growth but differ significantly in investment stage, risk profile, and value creation strategies.
Definition and Core Features of Venture Capital Funds
Venture Capital Funds are investment vehicles that provide capital to early-stage, high-growth startups in exchange for equity, targeting innovative companies with significant growth potential. These funds focus on high-risk, high-reward investments, emphasizing technology, healthcare, and disruptive industries while actively supporting portfolio companies through mentorship and strategic guidance. Unlike Private Equity Funds, which invest in mature companies often via buyouts, Venture Capital Funds prioritize nurturing nascent businesses to accelerate market entry and scalability.
Definition and Core Features of Private Equity Funds
Private Equity Funds are pooled investment vehicles that acquire equity ownership in private companies, often focusing on long-term value creation through operational improvements and strategic guidance. They typically involve large capital commitments, longer investment horizons ranging from 5 to 10 years, and active management with the intent to exit via IPO, sale, or recapitalization. Differentiated from Venture Capital Funds, Private Equity Funds invest in more mature, established companies rather than early-stage startups, emphasizing buyouts and significant control stakes.
Key Differences Between Venture Capital and Private Equity Funds
Venture capital funds primarily invest in early-stage startups with high growth potential, focusing on innovation-driven sectors such as technology and biotechnology. Private equity funds target more mature companies, often acquiring significant or controlling stakes to restructure, improve operations, and increase profitability. The investment horizon for venture capital is usually longer and riskier, while private equity emphasizes stability, cash flow improvements, and eventual exit through buyouts or public offerings.
Investment Strategies: Venture Capital vs Private Equity
Venture capital funds primarily invest in early-stage startups with high growth potential, focusing on technology-driven sectors and innovation. Private equity funds target more mature companies, aiming for operational improvements, financial restructuring, or market expansion to increase value before exit. Both strategies involve active management, but venture capital emphasizes high risk/high reward investments, while private equity focuses on stable cash flow and long-term value creation.
Target Companies and Stages of Investment
Venture capital funds primarily target early-stage startups and high-growth companies seeking initial or expansion capital, often investing in seed to Series B funding rounds. Private equity funds focus on mature, established companies that require significant capital for buyouts, restructuring, or expansion, typically investing in later-stage or full acquisitions. The investment stages for venture capital emphasize innovation and scalability, while private equity centers on optimizing operational efficiency and financial restructuring.
Risk and Return Profiles
Venture capital funds typically invest in early-stage startups with high growth potential, resulting in higher risk and the possibility of significant returns, albeit with greater volatility and longer exit horizons. Private equity funds focus on established companies, often utilizing leverage to enhance returns while maintaining moderate risk and more predictable cash flows. The risk-return profile of venture capital is skewed towards high risk and high return, whereas private equity offers comparatively steadier returns with lower risk exposure.
Fund Structures and Lifecycle
Venture capital funds typically follow a limited partnership structure with a fixed term of around 7-10 years, focusing on early-stage investments and multiple funding rounds before exit. Private equity funds also use a limited partnership model but often have longer lifecycles, around 10-12 years, investing in mature companies through buyouts and restructuring. Fundraising, investment, management, and exit phases define the lifecycle of both, though venture capital emphasizes rapid growth stages whereas private equity targets operational improvements and financial engineering.
Role in Business Growth and Innovation
Venture capital funds primarily fuel early-stage startups by providing capital and strategic guidance crucial for rapid innovation and scalable growth. Private equity funds invest in mature companies, emphasizing restructuring and operational improvements to enhance value and market competitiveness. Both fund types catalyze business growth, but venture capital focuses on disruptive technologies while private equity targets sustainable expansion and efficiency.
How to Choose Between Venture Capital and Private Equity Funds
Choosing between venture capital and private equity funds depends primarily on a company's stage of development and risk appetite; venture capital targets early-stage startups with high growth potential, while private equity focuses on mature companies requiring restructuring or expansion. Investment size, return expectations, and involvement level also influence the decision, with venture capital funds typically investing smaller amounts and accepting higher risk for innovation, whereas private equity funds deploy larger capital for stable, established businesses. Assessing the fund's industry expertise, track record, and alignment with business goals ensures a strategic partnership that maximizes growth and value creation.
Important Terms
Limited Partners (LPs)
Limited Partners (LPs) in Venture Capital Funds primarily seek high-growth startups and accept higher risk for potential significant returns, while LPs in Private Equity Funds focus on acquiring mature companies aiming for steady cash flows and more predictable exits. Both types of LPs provide capital but differ in risk tolerance, investment horizon, and expected diversification within the fund's portfolio.
General Partners (GPs)
General Partners (GPs) in Venture Capital Funds specialize in early-stage investments and actively guide startups through growth and scaling phases, leveraging sector expertise and networks. In Private Equity Funds, GPs focus on acquiring established companies, implementing operational improvements and strategic restructuring to maximize long-term value and exit returns.
Exit Strategy
Exit strategy in venture capital funds typically focuses on high-growth startups through initial public offerings (IPOs) or acquisitions, emphasizing rapid value realization within 5-7 years. In contrast, private equity funds prioritize mature companies with stable cash flows, utilizing leveraged buyouts and dividend recaps to exit investments over a longer horizon, often 7-10 years.
Buyout Transactions
Buyout transactions in private equity funds typically involve acquiring majority control of mature companies, whereas venture capital funds focus on minority investments in early-stage startups for high growth potential.
Early-Stage Investment
Early-stage investment primarily occurs through venture capital funds, which focus on funding startups and emerging companies with high growth potential and greater risks. Private equity funds generally invest in more mature companies, providing capital for expansion, restructuring, or buyouts rather than seed or early development stages.
Capital Commitment
Venture capital funds typically have lower capital commitments and focus on early-stage startups, while private equity funds require higher capital commitments for investing in mature companies and buyouts.
Growth Equity
Growth equity bridges venture capital and private equity by investing in established startups with proven revenue, targeting scalable expansion rather than early-stage risks or full buyouts.
Portfolio Companies
Portfolio companies in a venture capital fund typically comprise early-stage startups with high growth potential, while private equity fund portfolio companies are usually more mature businesses targeted for operational improvements and strategic restructuring. Venture capital investments focus on equity stakes in innovative sectors like technology and healthcare, whereas private equity investments often involve leveraged buyouts and majority ownership in established industries.
Fund Lifecycle
Venture Capital Fund lifecycle typically spans 7-10 years focusing on early-stage startup investments through stages of fundraising, investment, growth, and exit, whereas Private Equity Fund lifecycle generally extends 10-12 years targeting mature companies with phases including fundraising, acquisition, management, and exit. Both fund types emphasize value creation and capital return, but venture capital often involves higher risk and innovation-driven growth compared to private equity's operational improvements and leveraged buyouts.
Deal Sourcing
Deal sourcing in venture capital funds focuses on early-stage startups with high growth potential, leveraging networks, accelerators, and tech hubs to identify innovative opportunities. Private equity funds source deals primarily from established companies with stable cash flows, using industry relationships and financial intermediaries to find undervalued assets or companies for buyouts and restructurings.
Venture Capital Fund vs Private Equity Fund Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com