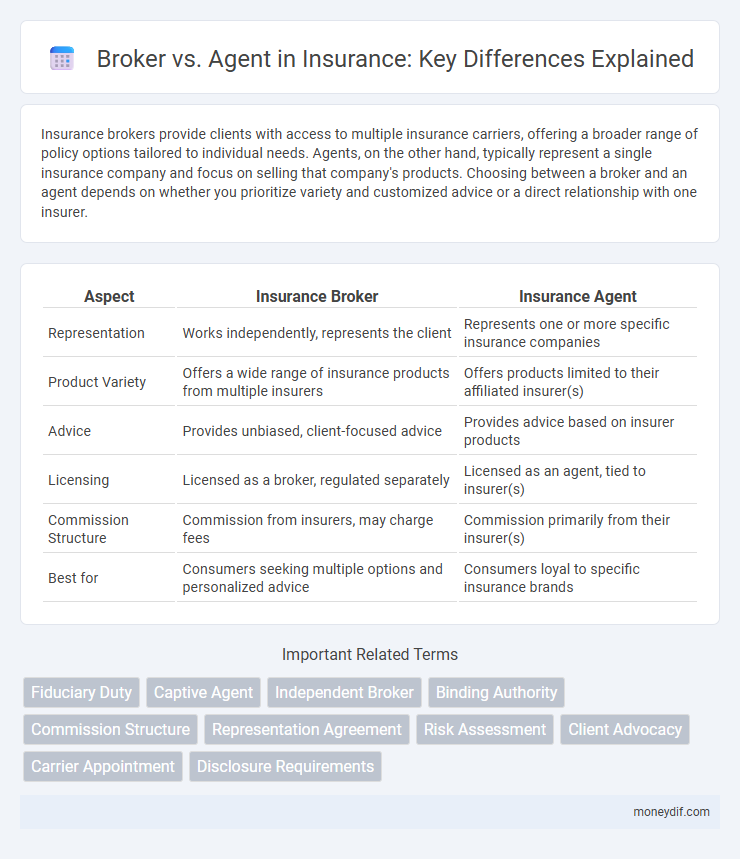
Insurance brokers provide clients with access to multiple insurance carriers, offering a broader range of policy options tailored to individual needs. Agents, on the other hand, typically represent a single insurance company and focus on selling that company's products. Choosing between a broker and an agent depends on whether you prioritize variety and customized advice or a direct relationship with one insurer.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Insurance Broker | Insurance Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Representation | Works independently, represents the client | Represents one or more specific insurance companies |
| Product Variety | Offers a wide range of insurance products from multiple insurers | Offers products limited to their affiliated insurer(s) |
| Advice | Provides unbiased, client-focused advice | Provides advice based on insurer products |
| Licensing | Licensed as a broker, regulated separately | Licensed as an agent, tied to insurer(s) |
| Commission Structure | Commission from insurers, may charge fees | Commission primarily from their insurer(s) |
| Best for | Consumers seeking multiple options and personalized advice | Consumers loyal to specific insurance brands |
Understanding the Roles: Broker vs Agent
Insurance brokers act as intermediaries who represent multiple insurance carriers to find the best policy options tailored to clients' needs, while insurance agents typically represent one or more specific insurers and sell their products directly. Brokers provide unbiased advice and access to a wider range of coverage, enhancing consumer choice and negotiating terms on behalf of the insured. Agents focus on building relationships within their assigned companies, often offering specialized knowledge about their insurer's policies and claims processes.
Key Differences Between Insurance Brokers and Agents
Insurance brokers operate as independent intermediaries who represent multiple insurers, offering clients a wide range of policy options tailored to their specific needs. Agents typically represent one or more insurance companies, providing coverage options directly from those carriers and often focusing on selling products from their affiliated insurers. Brokers have a fiduciary duty to their clients to find the best coverage at the best price, whereas agents primarily prioritize the interests of the insurance companies they represent.
How Brokers Represent Their Clients
Insurance brokers represent their clients by acting as independent intermediaries who seek the best policies across multiple insurers, ensuring personalized coverage tailored to the client's unique needs. Unlike agents who typically represent one insurance company, brokers prioritize the client's interests by providing unbiased advice and negotiating terms that optimize protection and cost-effectiveness. This client-centric approach enables brokers to deliver comprehensive risk management solutions, enhancing overall satisfaction and trust.
Agents: Who Do They Work For?
Insurance agents work directly for insurance companies, representing their products and policies to clients. They are licensed to sell specific insurers' products and act as intermediaries between the company and policyholders. Agents may be captive, working exclusively for one company, or independent, representing multiple insurers to offer a broader range of options.
Licensing and Qualifications: Broker vs Agent
Insurance brokers typically hold broader licensing, allowing them to represent multiple insurance companies and offer a wider range of policies, whereas agents are usually licensed to sell products from one or more specific insurers. Brokers must often complete advanced training and certification, such as passing state-specific exams and obtaining professional designations like Chartered Property Casualty Underwriter (CPCU). Agents, while also required to be licensed, may have more limited qualifications depending on the state and the insurance lines they sell, focusing primarily on product-specific knowledge and sales.
Pros and Cons of Choosing a Broker
Choosing an insurance broker offers the advantage of access to a wide range of insurance products from multiple carriers, providing personalized advice tailored to individual needs and often resulting in more competitive pricing. Brokers work independently and represent the buyer's interests, but this can lead to higher fees compared to agents who are typically compensated by insurers. However, brokers may require more detailed information and negotiations, which can lengthen the insurance selection process.
Pros and Cons of Choosing an Agent
Choosing an insurance agent offers personalized service and direct access to specific insurance companies, ensuring tailored policy options and streamlined claims support. However, agents may have limited product offerings compared to brokers, as they typically represent one insurer, restricting the variety and competitiveness of available coverage. Their expertise can simplify the purchasing process, but it might come at the cost of fewer choices and potential bias toward promoting their affiliated company's policies.
Cost Implications: Broker vs Agent Services
Insurance brokers typically incur higher upfront fees due to their independent market access, allowing clients to compare multiple quotes for cost-effective policies. Agents often work for specific insurers, resulting in lower direct costs but limited options, potentially reducing competitive pricing. Choosing a broker may lead to better long-term savings by leveraging broader market insights, while agents offer simpler, often more affordable transactions.
Which Is Right for You: Broker or Agent?
Choosing between an insurance broker and an agent depends on your need for personalized options versus loyalty to specific insurers. Brokers represent multiple insurance companies, offering a wider range of policies tailored to your unique requirements, while agents typically represent one insurer, providing in-depth knowledge of their products. Evaluating your preference for flexibility or specialized expertise can help determine whether a broker or an agent best serves your insurance needs.
Frequently Asked Questions about Insurance Brokers and Agents
Insurance brokers represent multiple insurance companies, offering clients a broad range of policy options tailored to their specific needs. Insurance agents typically work for one company, selling its products and providing specialized knowledge about those specific policies. Common questions include the differences in fees, the level of personalized service, and how each professional handles claims and policy renewals.
Important Terms
Fiduciary Duty
Fiduciary duty in the context of a broker versus an agent establishes a legal obligation to act in the best interest of the client, prioritizing loyalty, confidentiality, and full disclosure. Brokers typically have a broader fiduciary duty encompassing negotiation and transaction management, while agents focus on representing client interests within specific transactions or services.
Captive Agent
A captive agent exclusively sells insurance products for a single insurer, whereas a broker represents multiple insurers to provide clients with a wider range of options.
Independent Broker
An independent broker operates autonomously, representing multiple clients without exclusive allegiance to any single insurance company, unlike agents who typically represent one insurer.
Binding Authority
Binding authority allows brokers, unlike agents who require direct principal approval, to legally commit insurers to coverage contracts on behalf of the insurer.
Commission Structure
Brokers typically earn commissions from multiple agents' transactions, while agents receive commissions directly from their own sales or leases.
Representation Agreement
A Representation Agreement legally defines the fiduciary duties and obligations between a client and either a broker or an agent, clarifying their roles in real estate transactions.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment reveals that brokers face higher liability due to broader client representation compared to agents who typically handle specific transactions.
Client Advocacy
Client advocacy in real estate prioritizes a broker's fiduciary duty to protect clients' interests, whereas an agent primarily facilitates transactions without the same level of legal responsibility.
Carrier Appointment
A carrier appointment formalizes the relationship between an insurance broker or agent and an insurance company, authorizing them to sell or service the carrier's products within specific markets.
Disclosure Requirements
Broker disclosure requirements mandate transparent communication of commission structures, fiduciary duties, and conflict of interest policies, whereas agents are required to disclose their brokerage affiliation, role, and any potential personal interests impacting client transactions.
Broker vs Agent Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com