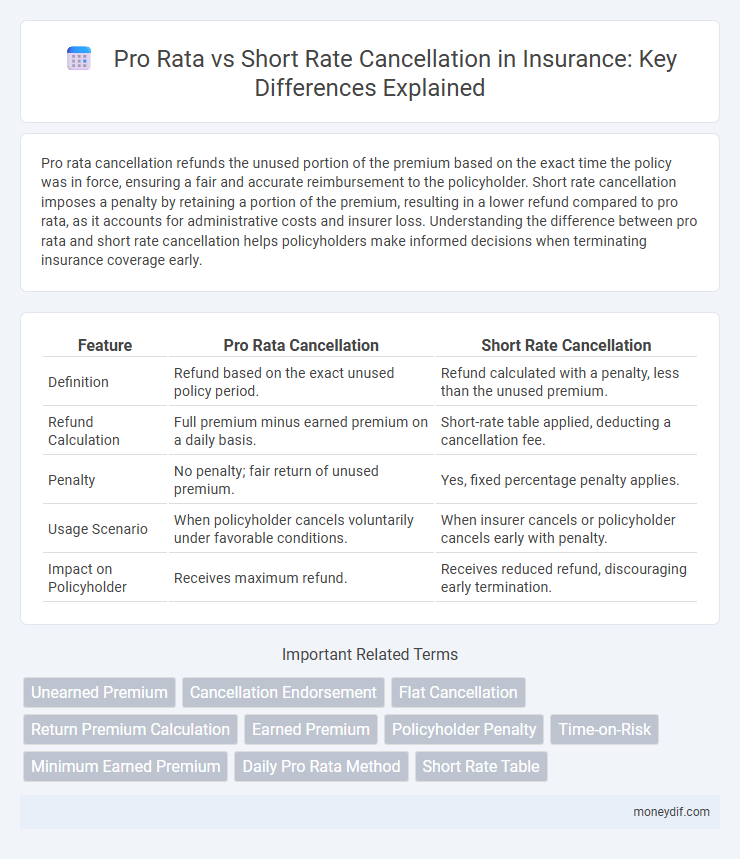
Pro rata cancellation refunds the unused portion of the premium based on the exact time the policy was in force, ensuring a fair and accurate reimbursement to the policyholder. Short rate cancellation imposes a penalty by retaining a portion of the premium, resulting in a lower refund compared to pro rata, as it accounts for administrative costs and insurer loss. Understanding the difference between pro rata and short rate cancellation helps policyholders make informed decisions when terminating insurance coverage early.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pro Rata Cancellation | Short Rate Cancellation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refund based on the exact unused policy period. | Refund calculated with a penalty, less than the unused premium. |
| Refund Calculation | Full premium minus earned premium on a daily basis. | Short-rate table applied, deducting a cancellation fee. |
| Penalty | No penalty; fair return of unused premium. | Yes, fixed percentage penalty applies. |
| Usage Scenario | When policyholder cancels voluntarily under favorable conditions. | When insurer cancels or policyholder cancels early with penalty. |
| Impact on Policyholder | Receives maximum refund. | Receives reduced refund, discouraging early termination. |
Understanding Pro Rata Cancellation
Pro Rata Cancellation in insurance refers to the method where the premium refund is calculated based on the exact time the policy was in effect, ensuring a fair return for the unused coverage period. This approach contrasts with Short Rate Cancellation, which typically involves a penalty fee and results in a reduced refund. Understanding Pro Rata Cancellation helps policyholders anticipate the precise amount refunded when terminating their insurance policy early.
What Is Short Rate Cancellation?
Short rate cancellation is a type of insurance policy termination where the insurer retains a higher premium percentage than the earned premium to cover administrative costs and potential losses. Unlike pro rata cancellation, which returns the unused portion of the premium on a proportional basis, short rate cancellations impose a penalty that results in less premium being refunded to the policyholder. This method is commonly applied when the policyholder initiates the cancellation before the policy expiration date.
Key Differences Between Pro Rata and Short Rate
Pro Rata cancellation refunds the unused premium based on the exact coverage period, ensuring a fair, time-based return to the policyholder. Short Rate cancellation involves a penalty fee, resulting in a lower refund than the pro rata amount, as insurers charge for administrative costs and risk exposure. Understanding these differences is crucial for policyholders managing cancellations to minimize financial loss.
Financial Implications for Policyholders
Pro rata cancellation results in a precise refund based on the unused portion of the premium, minimizing financial loss for policyholders. Short rate cancellation imposes a penalty by retaining a higher premium percentage, leading to increased out-of-pocket costs. Understanding these financial implications helps policyholders make informed decisions when terminating insurance contracts early.
Calculating Refunds: Pro Rata vs Short Rate
Calculating refunds in insurance cancellations involves understanding the difference between pro rata and short rate methods. Pro rata cancellation refunds the unearned premium based on the exact time left on the policy, resulting in a precise, fair return to the policyholder. Short rate cancellation refunds a lesser amount than pro rata, applying a penalty by retaining a larger portion of the premium to cover administrative costs.
When to Choose Pro Rata Cancellation
Choose pro rata cancellation when the insured cancels a policy early and expects a full premium refund based strictly on the unused coverage period, reflecting unused risk exposure. This method is ideal for straightforward cancellations without penalties, often applied in personal lines like auto or homeowners insurance. Pro rata cancellation ensures fair premium adjustment aligned with actual coverage duration, benefiting customers seeking transparent and equitable policy termination.
When Short Rate Cancellation Applies
Short rate cancellation applies when a policyholder chooses to cancel their insurance before the policy term ends, typically resulting in a penalty that reduces the refund amount compared to pro rata cancellation. This method is commonly used by insurers to cover administrative costs and commissions, impacting auto, homeowners, and commercial insurance policies. Policy terms explicitly outline short rate cancellation clauses, guiding policyholders on potential financial implications when terminating coverage early.
Impact on Insurance Premiums
Pro Rata cancellation refunds the unused portion of the insurance premium based on the exact time coverage was in force, resulting in a fair return for policyholders. Short rate cancellation applies a penalty by retaining a portion of the premium, causing higher costs to the insured compared to pro rata refunds. This difference directly affects the customer's financial outcome when terminating a policy early, influencing their decision on insurance adjustments.
Common Scenarios for Each Cancellation Type
Pro Rata cancellation commonly occurs when a policyholder cancels insurance coverage mid-term due to moving to a new location or switching to a different insurer, resulting in a refund of the unused premium based on the exact time coverage was active. Short Rate cancellation is often applied when the insurer initiates policy termination for reasons such as non-payment or underwriting issues, where the policyholder receives a reduced refund to cover administrative costs and potential underwriting losses. Understanding these scenarios helps policyholders anticipate financial outcomes when modifying or ending their insurance contracts.
Pro Tips for Navigating Policy Cancellations
Understanding the difference between pro rata cancellation, which refunds the unused premium exactly for the remaining policy period, and short rate cancellation, which applies a penalty reducing the refund amount, is crucial for managing insurance policy cancellations effectively. To maximize refund potential, review the specific terms outlined in the insurance contract and promptly communicate cancellation intentions to avoid unnecessary fees. Consulting with an insurance advisor can help identify the most cost-effective cancellation strategy tailored to individual policy conditions.
Important Terms
Unearned Premium
Unearned Premium represents the portion of an insurance premium for coverage not yet provided and is calculated differently under Pro Rata Cancellation and Short Rate Cancellation methods. Pro Rata Cancellation refunds the unearned premium based on the exact time coverage was in force, while Short Rate Cancellation applies a penalty reducing the refund amount, reflecting administrative costs and insurer losses.
Cancellation Endorsement
Cancellation endorsements adjust insurance policies when coverage ends before the expiration date, impacting refund calculations. Pro Rata cancellation provides a proportional refund based on unused coverage time, while short rate cancellation applies a penalty, resulting in a reduced refund compared to the pro rata method.
Flat Cancellation
Flat Cancellation refunds the policyholder the full premium for the unused coverage period, unlike Pro Rata Cancellation, which refunds based solely on the exact time unused, and Short Rate Cancellation, where the refund is reduced by a penalty to compensate the insurer for administrative costs and risk exposure. Understanding these cancellation methods is essential for accurately calculating refunds and managing policyholder expectations during early termination.
Return Premium Calculation
Return premium calculation differs significantly between pro rata cancellation and short rate cancellation methods, with pro rata refunding the unused portion of the premium based on the exact time the policy was in force, while short rate applies a penalty, resulting in a lower return premium to the insured. Insurance companies use pro rata cancellations for mutual agreements, favoring policyholders, and short rate cancellations primarily in cancellations initiated by the insured to recoup administrative costs and discourage early termination.
Earned Premium
Earned Premium reflects the portion of the total premium corresponding to the coverage period provided, calculated differently under Pro Rata Cancellation and Short Rate Cancellation methods; Pro Rata Cancellation refunds the unearned premium on a strict time basis, whereas Short Rate Cancellation applies a penalty, resulting in a reduced refund to the policyholder. Insurers use Pro Rata Cancellation for cancellations initiated by them or mutual agreement, while Short Rate Cancellation is common for policyholder-initiated early terminations to discourage frequent cancellations.
Policyholder Penalty
Policyholder penalties vary depending on whether a pro rata cancellation or a short rate cancellation method is applied; pro rata cancellation refunds the unused premium without penalty, while short rate cancellation imposes a reduced refund to cover administrative costs and discourage early policy termination. Insurance companies utilize short rate penalties to recover expenses and maintain risk balance, contrasting with the more equitable pro rata approach favored when the policyholder initiates cancellation for valid reasons.
Time-on-Risk
Time-on-Risk quantifies the exact insurance coverage duration utilized by a policyholder, directly impacting premium calculations during policy termination. Pro Rata Cancellation refunds premiums based strictly on the unused policy period, while Short Rate Cancellation applies a penalty by retaining a higher premium share, reflecting administrative costs and risk exposure.
Minimum Earned Premium
Minimum Earned Premium ensures insurers recover a baseline amount regardless of policy duration, contrasting with Pro Rata Cancellation which refunds premium strictly based on unused time, while Short Rate Cancellation applies a penalty by retaining more premium than Pro Rata to cover administrative costs and potential underwriting losses. Pro Rata Cancellation favors policyholders with fair proportional refunds, whereas Short Rate Cancellation benefits insurers by mitigating revenue loss from early policy termination.
Daily Pro Rata Method
The Daily Pro Rata method calculates earned premium based on the exact number of days the policy was in force, providing a precise cancellation premium that reflects actual coverage. In contrast, Short Rate Cancellation applies a penalty by charging a higher premium for early termination, resulting in less refund compared to the Daily Pro Rata approach.
Short Rate Table
A Short Rate Table determines the percentage of the premium earned when a policy is cancelled before its expiration, typically resulting in a higher cost than pro rata cancellation, which refunds the unearned premium based strictly on time elapsed. Pro rata cancellation provides equitable premium adjustments based on the exact coverage period, while short rate cancellation incorporates cancellation fees or penalties reflected in the Short Rate Table to discourage early termination.
Pro Rata Cancellation vs Short Rate Cancellation Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com