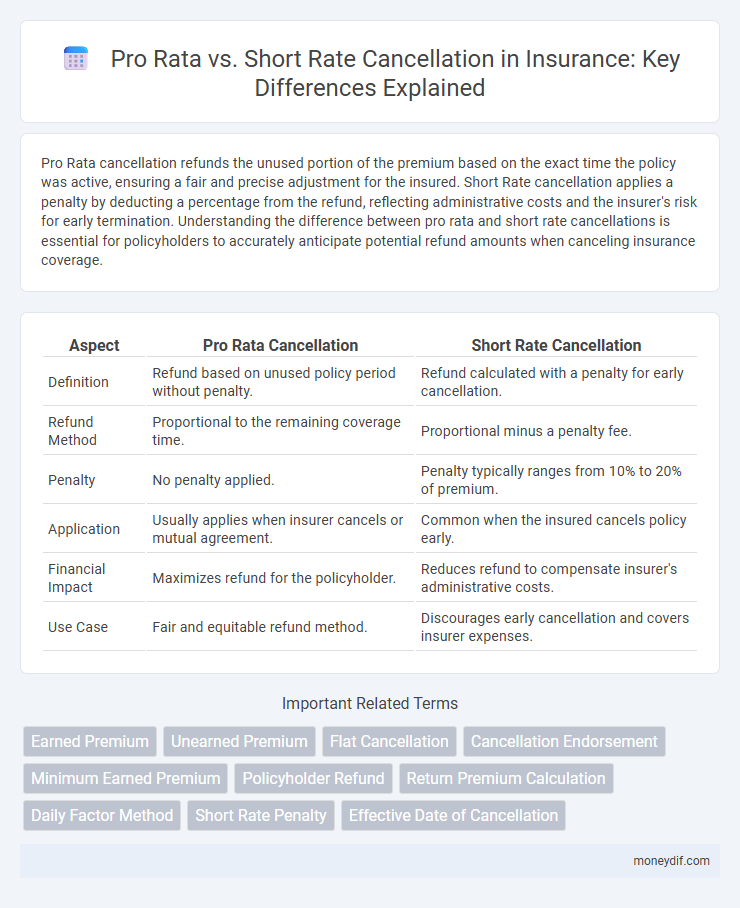
Pro Rata cancellation refunds the unused portion of the premium based on the exact time the policy was active, ensuring a fair and precise adjustment for the insured. Short Rate cancellation applies a penalty by deducting a percentage from the refund, reflecting administrative costs and the insurer's risk for early termination. Understanding the difference between pro rata and short rate cancellations is essential for policyholders to accurately anticipate potential refund amounts when canceling insurance coverage.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pro Rata Cancellation | Short Rate Cancellation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refund based on unused policy period without penalty. | Refund calculated with a penalty for early cancellation. |
| Refund Method | Proportional to the remaining coverage time. | Proportional minus a penalty fee. |
| Penalty | No penalty applied. | Penalty typically ranges from 10% to 20% of premium. |
| Application | Usually applies when insurer cancels or mutual agreement. | Common when the insured cancels policy early. |
| Financial Impact | Maximizes refund for the policyholder. | Reduces refund to compensate insurer's administrative costs. |
| Use Case | Fair and equitable refund method. | Discourages early cancellation and covers insurer expenses. |
Understanding Pro Rata Cancellation in Insurance
Pro Rata cancellation in insurance refers to the process where the insurer refunds the unearned premium based on the exact number of days the policy was active before cancellation. This method ensures policyholders receive a fair, proportionate premium refund without penalties, calculated strictly by the ratio of the unused policy term. Unlike short rate cancellation, which imposes a penalty reducing the refund, pro rata provides a transparent and equitable premium adjustment aligned with coverage duration.
What Is Short Rate Cancellation?
Short Rate Cancellation is a type of insurance policy termination where the insurer retains a higher percentage of the premium than the pro rata amount, often applying penalties for early cancellation. This method reduces the refunded amount to the policyholder, reflecting administrative costs and potential underwriting losses incurred by the insurer. Understanding the difference between Short Rate and Pro Rata cancellations is crucial for policyholders seeking to minimize financial loss when ending coverage prematurely.
Key Differences Between Pro Rata and Short Rate
Pro Rata cancellation calculates refunds based on the exact unused portion of the policy term, ensuring a fair and proportional return to the insured. Short Rate cancellation imposes a penalty by retaining a higher premium amount than the pro rata basis, reflecting administrative costs and insurer losses. The primary difference lies in refund calculation: pro rata returns a precise unused premium, while short rate reduces the refund to compensate the insurer for early termination.
When to Choose Pro Rata Cancellation
Pro Rata cancellation should be chosen when policyholders seek a fair refund based on the exact coverage period unused, typically during voluntary cancellations or policy upgrades. This method calculates premiums precisely from the policy's start date to the cancellation date, avoiding penalties and ensuring equitable treatment. Pro Rata is ideal for avoiding disputes and maintaining customer satisfaction in straightforward termination scenarios.
Situations Favoring Short Rate Cancellation
Short rate cancellation applies when a policyholder cancels before the term expires, and the insurer retains a larger portion of the premium to cover administrative costs and underwriting expenses. This type of cancellation favors situations such as policyholder-initiated changes, early termination for personal reasons, or non-renewal by the insured. Insurers prefer short rate cancellations to discourage frequent policy changes and recover costs associated with issuing the policy.
How Cancellation Refunds Are Calculated
Cancellation refunds for pro rata insurance policies are calculated based on the exact time the policy was active, returning the unused premium without penalties. Short rate cancellations involve a refund calculated with a penalty, retaining a percentage of the premium to cover administrative costs despite the early termination. Understanding the distinctions in refund calculations helps policyholders assess financial impacts when deciding to cancel their insurance coverage.
Impact on Premium Returns: Pro Rata vs Short Rate
Pro Rata cancellation results in a refund calculated strictly based on the exact unused portion of the insurance policy, typically yielding a higher premium return for the insured. Short Rate cancellation applies a penalty by retaining a portion of the premium, reflecting administrative costs and creating a lower refund compared to Pro Rata. Insurers commonly use Short Rate cancellation to discourage early policy termination and offset processing expenses, impacting the net premium returned.
Common Scenarios for Each Cancellation Method
Pro rata cancellation is commonly used when a policyholder voluntarily terminates coverage mid-term, such as switching insurers or no longer needing the policy, resulting in a refund proportional to the unused policy period. Short rate cancellation typically occurs when the insurer cancels the policy due to non-payment or breach of terms, leading to a reduced refund that includes penalties for early termination. Understanding these scenarios helps policyholders anticipate financial outcomes and legal obligations during policy cancellation.
Pros and Cons of Pro Rata and Short Rate Approaches
Pro Rata cancellation refunds the unused premium based on the exact coverage period, offering policyholders a fair and transparent return but potentially resulting in lower insurer retention revenue. Short Rate cancellation imposes a penalty by retaining a higher portion of the premium to cover administrative costs and risk, benefiting insurers financially but possibly leading to customer dissatisfaction due to reduced refund amounts. Understanding the balance between fair refund calculation and insurer financial protection is key when choosing between Pro Rata and Short Rate cancellation methods.
Tips for Policyholders Considering Policy Cancellation
Policyholders considering cancellation should understand the key difference between pro rata and short rate cancellations: pro rata refunds return the unused premium based on the exact time coverage was in force, while short rate cancellations impose a penalty, reducing the refund amount. Verifying the insurer's cancellation policy and calculating possible refund amounts before initiating cancellation can save money and avoid unexpected charges. Maintaining clear communication with the insurance provider regarding cancellation terms ensures informed decisions and smoother policy adjustments.
Important Terms
Earned Premium
Earned Premium represents the portion of an insurance premium that corresponds to the coverage period already provided, with Pro Rata Cancellation refunding the unearned premium based strictly on the time unused, while Short Rate Cancellation applies a penalty resulting in a smaller refund to the policyholder. Insurance companies use these methods to calculate adjustments on policies terminated before their expiration date, impacting the financial outcomes for both insurer and insured.
Unearned Premium
Unearned premium represents the portion of an insurance premium for which coverage has not yet been provided, calculated differently under Pro Rata and Short Rate cancellation methods. Pro Rata cancellation refunds the unearned premium based on the exact coverage period unused, while Short Rate cancellation applies a penalty, resulting in a lower refund due to administrative fees and underwriting costs.
Flat Cancellation
Flat cancellation allows policyholders to cancel their insurance at any time with a full refund of premiums paid, contrasting with pro rata and short rate cancellations that involve partial refunds calculated based on coverage time or insurer penalties. Pro rata cancellation refunds the unused premium proportionally without penalty, while short rate cancellation applies a penalty, resulting in a smaller refund to the policyholder.
Cancellation Endorsement
Cancellation Endorsement specifies adjustments to an insurance policy upon cancellation, addressing Pro Rata and Short Rate methods. Pro Rata cancellation refunds premiums based on the exact unused coverage period, while Short Rate applies a penalty, resulting in a reduced refund compared to Pro Rata.
Minimum Earned Premium
Minimum Earned Premium is a non-refundable portion of the premium retained by the insurer when a policy is canceled, ensuring coverage costs are partially covered even if cancellation occurs early. Pro Rata cancellation calculates premiums based on exact coverage days, typically refunding unused premium fully, whereas Short Rate cancellation applies a penalty by retaining a higher minimum earned premium to cover administrative and underwriting expenses.
Policyholder Refund
Policyholder refunds under Pro Rata cancellation provide a return based on the exact unused portion of the premium, ensuring fair compensation when a policy is terminated early. Short Rate cancellation refunds are reduced by a penalty fee, resulting in a lower reimbursement than Pro Rata, reflecting administrative costs and insurer risk.
Return Premium Calculation
Return premium calculation under pro rata cancellation refunds the unearned premium based on the exact coverage period used, ensuring a fair and proportionate premium return to the policyholder. In contrast, short rate cancellation imposes a penalty by retaining a higher premium percentage, resulting in a reduced return premium due to administrative fees and insurer penalties.
Daily Factor Method
The Daily Factor Method calculates premiums by multiplying the policy's daily rate by the exact number of days the policy was in force, providing a more precise proration compared to Short Rate Cancellation, which applies a penalty by retaining a portion of the premium. This method ensures fairer refunds in insurance cancellations by accurately reflecting coverage duration without penalizing the insured.
Short Rate Penalty
Short Rate Penalty is a reduced refund applied during policy cancellation, calculated using a short rate table that results in less than the pro rata amount returned to the insured. Pro Rata cancellation refunds the exact unused portion of the premium, while short rate cancellation accounts for administrative costs, making the penalty financially disadvantageous for early termination.
Effective Date of Cancellation
The effective date of cancellation determines whether the refund is calculated on a pro rata basis, refunding the unused premium proportionally, or on a short rate basis, which includes a penalty fee resulting in a reduced refund. In insurance policies, pro rata cancellations often occur when the policyholder initiates cancellation, while short rate cancellations typically apply when the insurer cancels the policy or when early termination clauses impose financial penalties.
Pro Rata vs Short Rate Cancellation Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com