Revolving credit provides flexible access to funds up to a preset limit, allowing borrowers to draw, repay, and redraw as needed, making it ideal for managing short-term cash flow fluctuations. Term loans offer a fixed amount of money with a predetermined repayment schedule and interest rate, suitable for financing specific projects or major purchases. Choosing between revolving credit and a term loan depends on whether ongoing liquidity or structured repayment suits your financial needs best.
Table of Comparison
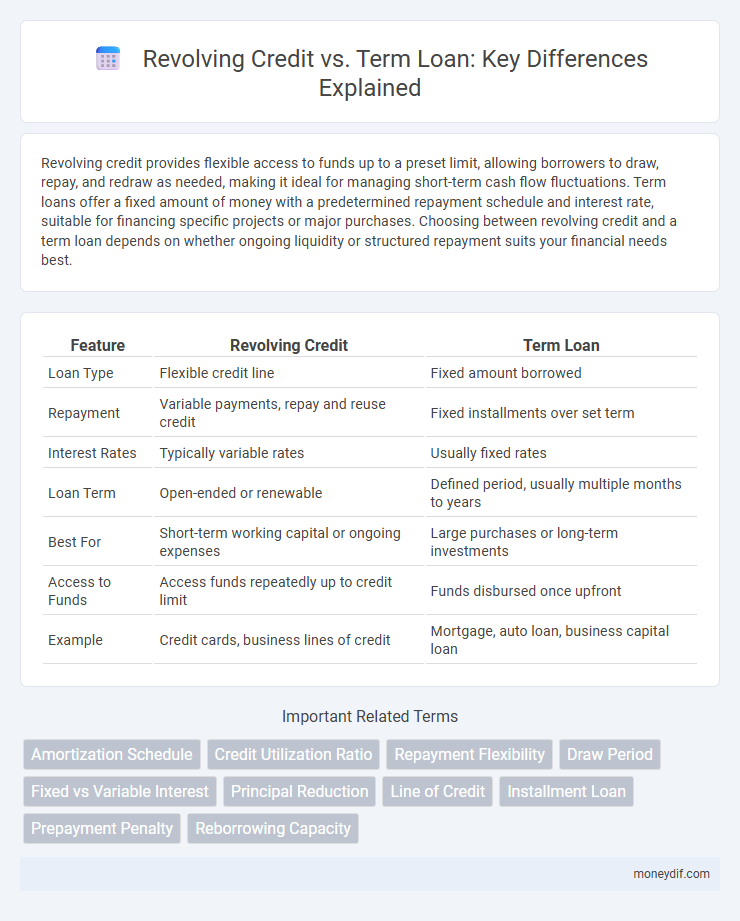
| Feature | Revolving Credit | Term Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Type | Flexible credit line | Fixed amount borrowed |
| Repayment | Variable payments, repay and reuse credit | Fixed installments over set term |
| Interest Rates | Typically variable rates | Usually fixed rates |
| Loan Term | Open-ended or renewable | Defined period, usually multiple months to years |
| Best For | Short-term working capital or ongoing expenses | Large purchases or long-term investments |
| Access to Funds | Access funds repeatedly up to credit limit | Funds disbursed once upfront |
| Example | Credit cards, business lines of credit | Mortgage, auto loan, business capital loan |
What is Revolving Credit?
Revolving credit is a type of loan that allows borrowers to access funds repeatedly up to a pre-approved limit, making it ideal for managing ongoing cash flow needs. Unlike term loans which have fixed repayment schedules and lump-sum disbursements, revolving credit offers flexibility to borrow, repay, and borrow again as needed. Common examples include credit cards and lines of credit, which provide continuous access to funds while interest is charged only on the outstanding balance.
What is a Term Loan?
A term loan is a type of loan where a fixed amount of money is borrowed and repaid over a set period with predetermined interest rates. Unlike revolving credit, which allows borrowing up to a limit repeatedly, term loans provide lump-sum financing that is repaid in regular installments. Businesses often use term loans for major investments, purchasing equipment, or expanding operations due to their structured payment schedules.
Key Differences Between Revolving Credit and Term Loans
Revolving credit offers flexible borrowing with a variable credit limit that can be accessed repeatedly as long as the balance is within the limit, ideal for managing short-term cash flow fluctuations. Term loans provide a fixed amount of capital with set repayment schedules and interest rates, suited for long-term investments or asset purchases. The main distinctions lie in repayment structure, credit flexibility, and usage purpose, with revolving credit emphasizing ongoing access and term loans focusing on lump-sum financing.
How Revolving Credit Works
Revolving credit provides borrowers with a flexible borrowing limit that replenishes as payments are made, allowing repeated access to funds up to a predetermined credit line. Interest is charged only on the outstanding balance, and minimum monthly payments are typically required to maintain the account in good standing. This credit structure is commonly used for credit cards and business lines of credit, offering continuous liquidity without the need to reapply after each use.
How Term Loans Work
Term loans provide borrowers with a fixed amount of money upfront, which is repaid over a specified period through regular installments that include both principal and interest. These loans typically have a set repayment schedule and fixed or variable interest rates, allowing borrowers to plan their finances with predictable monthly payments. Term loans are ideal for financing long-term investments such as equipment purchases, real estate, or business expansion, offering stability compared to revolving credit lines.
Pros and Cons of Revolving Credit
Revolving credit offers flexibility by allowing borrowers to access funds repeatedly up to a set limit, which is ideal for managing fluctuating cash flow and unexpected expenses. However, the variable interest rates and potential for accumulating high debt make it riskier compared to term loans, which have fixed repayment schedules and predictable costs. While revolving credit improves liquidity and convenience, it requires disciplined financial management to avoid spiraling debt and increased interest expenses.
Pros and Cons of Term Loans
Term loans offer fixed interest rates and structured repayment schedules, providing borrowers with predictable monthly payments and budget stability. However, they often require collateral and have less flexibility compared to revolving credit, making early repayment penalties and strict qualification criteria potential drawbacks. Businesses seeking long-term financing for significant investments typically benefit from term loans despite these limitations.
Best Use Cases for Revolving Credit
Revolving credit is best suited for managing short-term cash flow fluctuations and unexpected expenses, providing flexibility to borrow and repay repeatedly within a credit limit. It is ideal for businesses that require ongoing access to funds for inventory purchases, seasonal demands, or operational expenses without committing to a fixed repayment schedule. Compared to term loans, revolving credit offers more adaptability for variable financing needs and quick liquidity access.
Ideal Situations for Term Loans
Term loans are ideal for businesses requiring a fixed amount of capital to finance specific projects or asset purchases, offering predictable repayment schedules and interest rates. They suit long-term investments like equipment acquisition, real estate, or business expansion where steady cash flow supports regular payments. Unlike revolving credit, term loans provide structured financing with set maturity dates, reducing the risk of fluctuating debt levels.
Which Lending Option is Right For You?
Revolving credit offers flexible borrowing with a credit limit you can repeatedly use and repay, making it ideal for managing cash flow or unexpected expenses. Term loans provide a fixed amount with a set repayment schedule, suitable for long-term investments like purchasing equipment or real estate. Evaluating your financial needs, repayment capacity, and business goals will help determine whether the adaptability of revolving credit or the structured payments of a term loan best fit your situation.
Important Terms
Amortization Schedule
An amortization schedule for a revolving credit typically varies with fluctuating balances and interest rates, while a term loan features a fixed amortization schedule with consistent principal and interest payments over a set period.
Credit Utilization Ratio
Credit utilization ratio measures revolving credit usage relative to available credit, whereas term loans do not impact this ratio since they are fixed installment loans without a credit limit.
Repayment Flexibility
Repayment flexibility is greater with revolving credit, allowing borrowers to make variable payments and borrow repeatedly up to a credit limit, whereas term loans require fixed payments over a set period.
Draw Period
The Draw Period in revolving credit allows flexible borrowing and repayment within a set timeframe, unlike a term loan which provides a fixed lump sum with scheduled repayments over the loan term.
Fixed vs Variable Interest
Fixed interest rates provide consistent payments ideal for term loans with set durations, while variable interest rates fluctuate and suit revolving credit with flexible borrowing limits.
Principal Reduction
Principal reduction in revolving credit offers flexible repayment by lowering outstanding balances, whereas term loans provide fixed principal payments over a set period.
Line of Credit
A line of credit typically functions as revolving credit, allowing borrowers to draw, repay, and redraw funds up to a preset limit, unlike term loans which provide a lump sum with fixed repayment schedules.
Installment Loan
Installment loans differ from revolving credit by offering fixed payment schedules over a set term, unlike revolving credit which allows continuous borrowing up to a limit, making installment loans more comparable to term loans with structured repayment plans.
Prepayment Penalty
Prepayment penalties on revolving credit are rare due to flexible repayment terms, whereas term loans often include prepayment penalties to compensate lenders for lost interest.
Reborrowing Capacity
Reborrowing capacity defines the maximum amount a borrower can access repeatedly under a revolving credit facility, unlike a term loan which provides a fixed principal amount disbursed once and repaid over a set period.
Revolving Credit vs Term Loan Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com