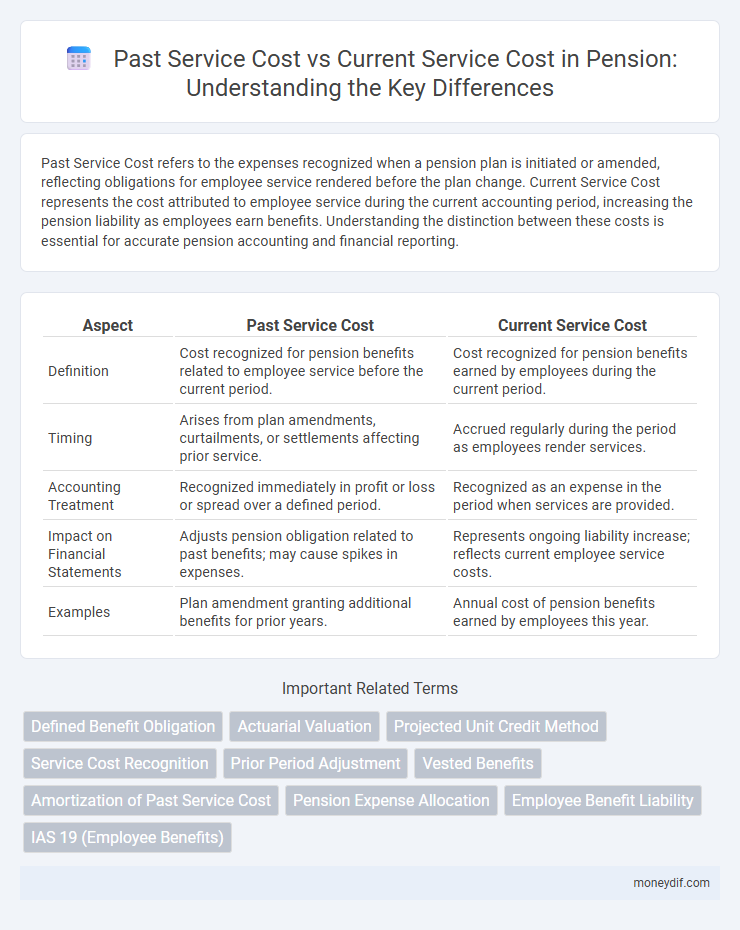
Past Service Cost refers to the expenses recognized when a pension plan is initiated or amended, reflecting obligations for employee service rendered before the plan change. Current Service Cost represents the cost attributed to employee service during the current accounting period, increasing the pension liability as employees earn benefits. Understanding the distinction between these costs is essential for accurate pension accounting and financial reporting.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Past Service Cost | Current Service Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cost recognized for pension benefits related to employee service before the current period. | Cost recognized for pension benefits earned by employees during the current period. |
| Timing | Arises from plan amendments, curtailments, or settlements affecting prior service. | Accrued regularly during the period as employees render services. |
| Accounting Treatment | Recognized immediately in profit or loss or spread over a defined period. | Recognized as an expense in the period when services are provided. |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Adjusts pension obligation related to past benefits; may cause spikes in expenses. | Represents ongoing liability increase; reflects current employee service costs. |
| Examples | Plan amendment granting additional benefits for prior years. | Annual cost of pension benefits earned by employees this year. |
Understanding Past Service Cost in Pensions
Past Service Cost in pensions represents the expense recognized when a company changes its pension plan benefits related to employee service accrued in prior periods. This cost reflects the present value of increased obligations due to plan amendments, early retirements, or curtailments affecting benefits earned before the current period. Understanding Past Service Cost is crucial for accurately measuring pension liabilities and ensuring compliance with accounting standards such as IAS 19 or ASC 715.
Defining Current Service Cost in Pension Schemes
Current Service Cost in pension schemes represents the increase in the present value of a defined benefit obligation resulting from employees' service in the current period. It reflects the pension benefits earned by employees during the reporting year, directly impacting the company's profit and loss statement. This cost excludes past service, which is accounted for separately as Past Service Cost when changes are made to the pension plan.
Key Differences Between Past and Current Service Costs
Past service cost arises from changes to pension benefits related to employee service periods before the current accounting period, often recognized immediately on the financial statements. Current service cost reflects the increase in pension obligations attributed to employee service during the current reporting period and is recognized as an expense in the income statement. The key difference lies in timing and measurement: past service cost addresses retroactive benefit changes, whereas current service cost pertains to ongoing service accruals within the period.
How Past Service Cost Arises in Pension Plans
Past Service Cost arises in pension plans when changes are made to the benefits formula for service periods prior to the current accounting period, such as plan amendments or curtailments that increase or decrease pension obligations retroactively. This cost reflects the present value of these incremental liabilities and is recognized immediately in the financial statements, impacting the employer's pension expense. Understanding Past Service Cost is crucial for accurate pension accounting and ensuring compliance with relevant standards like IAS 19 or ASC 715.
The Calculation Method for Current Service Cost
The calculation method for Current Service Cost involves determining the present value of benefits accrued by employees during the current accounting period, based on expected future salary increases and service duration. Actuarial assumptions such as discount rate, employee turnover, mortality rates, and salary growth projections are essential inputs to accurately estimate the cost. This cost is recognized in the profit and loss statement as part of pension expenses for the period, reflecting the increase in pension obligations due to employee service in that year.
Impact of Plan Amendments on Past Service Cost
Plan amendments that alter pension benefits retroactively create past service costs, which represent the present value of increased obligations for prior employee service. These costs must be recognized immediately in pension expense, influencing the company's financial statements by increasing liabilities and reducing net income. Accurate measurement of past service costs requires actuarial valuation reflecting the amended terms and their impact on previously accrued benefits.
Accounting Standards for Service Costs in Pensions
Past Service Cost represents the impact of plan amendments on the defined benefit obligation for prior service periods and is recognized immediately in profit or loss under IAS 19 and ASC 715. Current Service Cost reflects the increase in the pension liability arising from employee service in the current period and is recorded as an expense in the income statement for the period. Both costs are critical components in pension accounting, with Past Service Cost addressing retrospective changes and Current Service Cost capturing ongoing service expense according to IFRS and US GAAP standards.
Financial Statement Reporting: Past vs Current Service Cost
Past service cost reflects the expense recognized in financial statements for changes to pension benefits related to employee service before the current reporting period, often resulting from plan amendments. Current service cost represents the expense attributable to employee service rendered during the current period, impacting pension obligations and profit and loss accounts. Accurate differentiation between past and current service costs ensures transparent pension liability reporting and compliance with accounting standards like IAS 19 or ASC 715.
Examples Illustrating Past and Current Service Costs
Past service cost arises when a company amends its pension plan to increase benefits for employee service periods before the amendment date, such as granting additional years of service credit retroactively. Current service cost represents the increase in pension liability attributed to employee service earned during the current reporting period, for example, the annual expense of benefits accrued by employees this year. An illustration of past service cost is a company enhancing pension benefits for prior years' service, while an example of current service cost is the normal cost expense recorded for service earned by employees in the current year.
Implications for Pension Plan Sponsors and Members
Past Service Cost represents the expense linked to retroactive benefits awarded during plan amendments, impacting pension plan sponsors by increasing their immediate financial liabilities and potentially requiring higher contributions. Current Service Cost reflects the expense of benefits earned by employees during the current period, influencing ongoing funding requirements and cash flow management for sponsors. For pension plan members, Past Service Cost adjustments can enhance accrued benefits, while Current Service Cost affects the value of future pension entitlements.
Important Terms
Defined Benefit Obligation
Defined Benefit Obligation increases with Current Service Cost reflecting employee benefits earned during the period, while Past Service Cost arises from plan amendments affecting prior service periods and impacts the obligation immediately.
Actuarial Valuation
Actuarial valuation distinguishes past service cost as expenses linked to changes in pension benefits for prior periods, while current service cost represents the present cost of pension benefits accrued during the current financial year.
Projected Unit Credit Method
The Projected Unit Credit Method allocates pension costs by recognizing past service cost immediately when plan amendments increase benefits for service rendered in prior periods, while current service cost reflects the expense attributed to services rendered during the current period. This actuarial approach ensures comprehensive cost measurement by incorporating both accrued liabilities from past service and expenses arising from ongoing employee work.
Service Cost Recognition
Service cost recognition distinguishes between past service cost, arising from plan amendments affecting prior periods and recognized immediately in profit or loss, and current service cost, representing the increase in the defined benefit obligation during the reporting period due to employee service. Accurate differentiation ensures compliance with accounting standards such as IAS 19 and improves the precision of pension expense measurement in financial statements.
Prior Period Adjustment
Prior period adjustments correct financial statements for past service costs recognized retrospectively, while current service costs reflect expenses for employee benefits earned during the current reporting period.
Vested Benefits
Vested benefits represent employees' accrued rights that are guaranteed regardless of future service, contrasting with past service cost which accounts for pension obligations from previous periods while current service cost reflects the expense for benefits earned during the current reporting period.
Amortization of Past Service Cost
Amortization of Past Service Cost systematically allocates the expense of retroactive pension benefits over future periods, contrasting with Current Service Cost, which represents the pension expense for benefits earned during the current reporting period.
Pension Expense Allocation
Pension expense allocation distinguishes past service cost, which arises from plan amendments affecting prior periods, from current service cost representing benefits earned by employees during the current reporting period.
Employee Benefit Liability
Employee Benefit Liability reflects obligations from both Past Service Cost, which arises from retroactive changes in employee benefits and increases the liability based on prior service periods, and Current Service Cost, representing the expense related to benefits earned by employees during the current period. Accurately distinguishing these costs is crucial for precise financial reporting and actuarial valuation of defined benefit plans.
IAS 19 (Employee Benefits)
IAS 19 defines Past Service Cost as the change in the present value of the defined benefit obligation resulting from plan amendments or curtailments, while Current Service Cost represents the increase in the present value of the defined benefit obligation due to employee service in the current period.
Past Service Cost vs Current Service Cost Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com