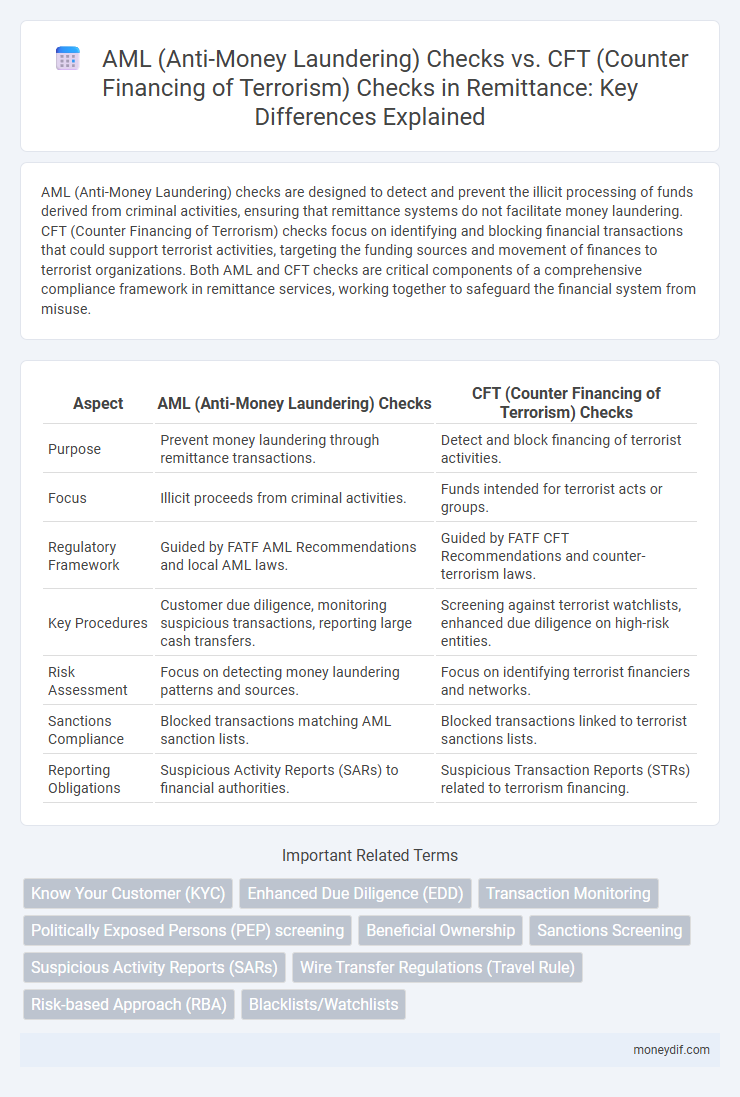
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) checks are designed to detect and prevent the illicit processing of funds derived from criminal activities, ensuring that remittance systems do not facilitate money laundering. CFT (Counter Financing of Terrorism) checks focus on identifying and blocking financial transactions that could support terrorist activities, targeting the funding sources and movement of finances to terrorist organizations. Both AML and CFT checks are critical components of a comprehensive compliance framework in remittance services, working together to safeguard the financial system from misuse.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | AML (Anti-Money Laundering) Checks | CFT (Counter Financing of Terrorism) Checks |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevent money laundering through remittance transactions. | Detect and block financing of terrorist activities. |
| Focus | Illicit proceeds from criminal activities. | Funds intended for terrorist acts or groups. |
| Regulatory Framework | Guided by FATF AML Recommendations and local AML laws. | Guided by FATF CFT Recommendations and counter-terrorism laws. |
| Key Procedures | Customer due diligence, monitoring suspicious transactions, reporting large cash transfers. | Screening against terrorist watchlists, enhanced due diligence on high-risk entities. |
| Risk Assessment | Focus on detecting money laundering patterns and sources. | Focus on identifying terrorist financiers and networks. |
| Sanctions Compliance | Blocked transactions matching AML sanction lists. | Blocked transactions linked to terrorist sanctions lists. |
| Reporting Obligations | Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) to financial authorities. | Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs) related to terrorism financing. |
Understanding AML and CFT in the Remittance Industry
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) checks in the remittance industry focus on identifying and preventing the laundering of illicit funds by monitoring suspicious transactions and verifying customer identities. CFT (Counter Financing of Terrorism) checks aim to detect and block financial flows that support terrorist activities, requiring enhanced due diligence and continuous monitoring of high-risk individuals and transactions. Both AML and CFT measures are critical for compliance with regulatory frameworks, safeguarding the remittance ecosystem from financial crimes and maintaining global security standards.
Key Differences Between AML and CFT Checks
AML checks primarily focus on detecting and preventing money laundering activities by monitoring suspicious transactions and verifying customer identities, while CFT checks specifically target the identification and disruption of funds used to finance terrorism. AML procedures involve tracking the origin and movement of illicit funds through financial systems, whereas CFT emphasizes identifying connections between financial transactions and terrorist organizations or activities. Both processes complement each other but have distinct regulatory frameworks and risk indicators tailored to their unique objectives in financial crime prevention.
Regulatory Frameworks Governing AML and CFT
Regulatory frameworks governing AML and CFT require financial institutions to implement robust customer due diligence and continuous transaction monitoring to detect suspicious activities. AML regulations focus on preventing money laundering through identification, reporting, and record-keeping requirements, while CFT emphasizes disrupting terrorist financing networks by targeting suspicious fund flows. Key international bodies such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) establish standards and best practices that member countries adopt to ensure comprehensive enforcement of AML and CFT measures.
How AML Checks Detect Illicit Funds in Remittances
AML checks detect illicit funds in remittances by analyzing transaction patterns, verifying customer identities, and monitoring unusually large or frequent transfers to uncover money laundering activities. These checks involve screening against sanctions lists and employing automated systems to flag suspicious behavior linked to criminal organizations. Effective AML protocols ensure that remittance channels do not facilitate the integration of illicit proceeds into the legitimate financial system.
Role of CFT Checks in Preventing Terrorist Financing
CFT checks play a critical role in preventing terrorist financing by identifying and disrupting funds intended for terrorist activities, complementing AML measures that target broader financial crimes. These checks involve rigorous monitoring of transactions, screening of customers against terrorism-related watchlists, and enhanced due diligence to detect suspicious patterns specific to terrorism risks. Integrating CFT checks within remittance processes ensures compliance with international regulations and protects the financial system from exploitation by terrorist networks.
Overlapping Procedures: Where AML and CFT Intersect
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and CFT (Counter Financing of Terrorism) checks share overlapping procedures such as customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and risk assessment to identify suspicious activities. Both frameworks utilize Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for high-risk customers to prevent illicit financial flows. These intersecting protocols ensure comprehensive screening to mitigate risks associated with money laundering and terrorist financing in remittance operations.
Unique Challenges in AML vs. CFT Compliance for Remittance Firms
Remittance firms face unique challenges in AML and CFT compliance due to the high volume of low-value transactions often conducted by unbanked populations, making it difficult to identify suspicious activities. AML efforts primarily focus on detecting money laundering patterns through customer due diligence and transaction monitoring, while CFT requires vigilance against the funding of terrorism, which often involves more covert and decentralized networks. The overlapping regulatory requirements necessitate robust, adaptable systems capable of balancing stringent verification processes without impeding the speed and accessibility essential to remittance services.
International Standards for AML and CFT in Remittance Services
International standards for AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and CFT (Counter Financing of Terrorism) in remittance services are primarily guided by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations, which mandate comprehensive customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and reporting suspicious activities to mitigate risks. Remittance providers must implement robust AML/CFT frameworks that include risk-based approaches tailored to cross-border money transfers, ensuring transparency and compliance with global regulatory expectations. Effective AML and CFT checks are critical for safeguarding the integrity of remittance channels and preventing their misuse for illicit financial flows and terrorist financing on an international scale.
Technology Solutions for AML and CFT Checks
Advanced technology solutions for AML and CFT checks leverage AI and machine learning to enhance transaction monitoring and identify suspicious activity in real-time. These systems utilize big data analytics and blockchain to improve the accuracy and speed of compliance processes, reducing false positives and operational costs. Integration of biometric verification and regulatory reporting automation further strengthens anti-money laundering and counter financing of terrorism measures.
Strengthening Remittance Security: Best Practices for AML and CFT
Robust AML and CFT checks are essential for strengthening remittance security by preventing illicit financial flows and terrorist financing. Implementing comprehensive customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and real-time risk assessment enhances detection of suspicious activities. Leveraging advanced technology and regulatory compliance ensures effective prevention of money laundering and terrorism financing in remittance services.
Important Terms
Know Your Customer (KYC)
Know Your Customer (KYC) processes are essential for both Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks to identify and prevent financial crimes and Counter Financing of Terrorism (CFT) checks to detect and block funding sources for terrorist activities.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) in AML focuses on identifying and mitigating high-risk money laundering activities, while in CFT it targets detecting and preventing financing sources linked to terrorism.
Transaction Monitoring
Transaction monitoring systems analyze financial activities to detect suspicious patterns indicative of money laundering and terrorism financing, leveraging algorithms tailored to AML and CFT regulations. AML checks focus on identifying illicit funds movement and layering activities, while CFT checks prioritize detecting transactions linked to terrorist organizations and funds intended to support terrorism.
Politically Exposed Persons (PEP) screening
Politically Exposed Persons (PEP) screening is a critical component of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter Financing of Terrorism (CFT) frameworks, designed to identify individuals with prominent public functions who may pose higher risks of involvement in financial crimes. Enhanced due diligence measures are applied to PEPs during AML and CFT checks to prevent illicit fund transfers and terrorist financing, ensuring compliance with global regulatory standards such as FATF recommendations.
Beneficial Ownership
Beneficial ownership verification is crucial in AML and CFT checks to identify the true individuals controlling entities, preventing money laundering and terrorist financing by ensuring transparency and accountability.
Sanctions Screening
Sanctions screening enhances AML and CFT efforts by identifying individuals and entities subject to financial restrictions, preventing money laundering and terrorist financing through real-time monitoring of global watchlists.
Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs)
Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) play a critical role in AML and CFT compliance by identifying and reporting transactions indicative of money laundering or terrorist financing activities to regulatory authorities.
Wire Transfer Regulations (Travel Rule)
Wire Transfer Regulations under the Travel Rule mandate rigorous AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and CFT (Counter Financing of Terrorism) checks to ensure the accurate identification and verification of originators and beneficiaries, minimizing illicit fund transfers.
Risk-based Approach (RBA)
Risk-based Approach (RBA) prioritizes AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and CFT (Counter Financing of Terrorism) checks by assessing and mitigating specific risks associated with money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
Blacklists/Watchlists
Blacklists and watchlists play a critical role in AML and CFT checks by enabling financial institutions to identify and prevent transactions involving sanctioned individuals, entities, or countries linked to money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) checks vs CFT (Counter Financing of Terrorism) checks Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com