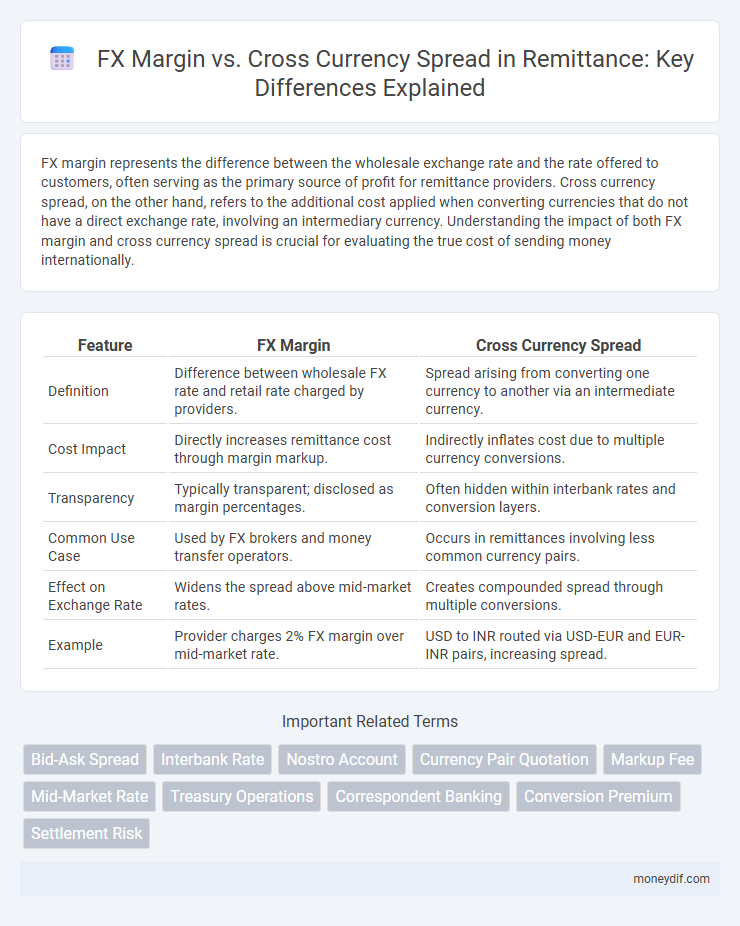
FX margin represents the difference between the wholesale exchange rate and the rate offered to customers, often serving as the primary source of profit for remittance providers. Cross currency spread, on the other hand, refers to the additional cost applied when converting currencies that do not have a direct exchange rate, involving an intermediary currency. Understanding the impact of both FX margin and cross currency spread is crucial for evaluating the true cost of sending money internationally.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | FX Margin | Cross Currency Spread |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Difference between wholesale FX rate and retail rate charged by providers. | Spread arising from converting one currency to another via an intermediate currency. |
| Cost Impact | Directly increases remittance cost through margin markup. | Indirectly inflates cost due to multiple currency conversions. |
| Transparency | Typically transparent; disclosed as margin percentages. | Often hidden within interbank rates and conversion layers. |
| Common Use Case | Used by FX brokers and money transfer operators. | Occurs in remittances involving less common currency pairs. |
| Effect on Exchange Rate | Widens the spread above mid-market rates. | Creates compounded spread through multiple conversions. |
| Example | Provider charges 2% FX margin over mid-market rate. | USD to INR routed via USD-EUR and EUR-INR pairs, increasing spread. |
Understanding FX Margin in Remittance
FX margin in remittance refers to the difference between the mid-market exchange rate and the rate offered by financial institutions, representing their profit margin on currency conversion. This margin impacts the total cost a sender pays when transferring funds internationally, often exceeding the transparent cross currency spread, which is the difference between two currency pairs in the forex market. Understanding FX margin is crucial for cost-effective remittance as it directly influences the amount the recipient receives, with lower margins indicating better value for the sender.
What Is Cross Currency Spread?
Cross currency spread refers to the difference between the bid and ask prices when exchanging one foreign currency for another, excluding the base currency, in remittance transactions. It captures the cost embedded in converting currencies through a cross rate, often reflecting liquidity and market volatility factors. This spread impacts the overall exchange rate cost for senders and recipients, differing from the FX margin which is typically the added percentage over the interbank rate charged by providers.
Key Differences: FX Margin vs Cross Currency Spread
FX margin represents the markup added by a financial institution to the interbank exchange rate during currency conversion, directly impacting the overall cost of remittance transactions. Cross currency spread refers to the difference between bid and ask prices for currency pairs without involving the base currency, often resulting in wider spreads and higher transaction costs for non-USD currency pairs. Understanding the key differences between FX margin and cross currency spread helps in selecting cost-effective remittance services by comparing their impact on exchange rate competitiveness and transaction fees.
Impact on Remittance Costs
FX margin represents the percentage added by money changers to the mid-market exchange rate, directly increasing remittance costs by inflating the currency conversion price. Cross currency spread refers to the difference between the bid and ask rates of currency pairs, often impacting costs when converting through an intermediate currency rather than a direct pair. Higher FX margins and wider cross currency spreads collectively elevate total remittance fees, reducing the amount received by beneficiaries.
How FX Margin Affects International Transfers
FX margin directly impacts the cost of international transfers by adding a percentage fee over the interbank exchange rate, increasing the overall expense for senders and receivers. Higher FX margins reduce the amount of money received in the destination currency, diminishing the value of remittances sent abroad. Understanding FX margin differences among providers is crucial for optimizing cost efficiency in cross-border money transfers.
Role of Cross Currency Spread in Remittance
Cross currency spread plays a critical role in remittance by directly affecting the total cost of currency conversion between two different currencies, often exceeding the base FX margin set by financial institutions. It reflects the difference between bid and ask prices in cross currency pairs, incorporating risks and liquidity factors beyond simple currency pair rates. Effective management of cross currency spreads is essential for senders and receivers to maximize the value of transferred funds and reduce hidden fees in international money transfers.
Transparency in Remittance Fees
Transparency in remittance fees improves when FX margin and cross-currency spread are clearly disclosed, allowing customers to understand the true cost of currency conversion. FX margin represents the difference between the interbank rate and the rate offered to customers, while cross-currency spread refers to the additional markup applied when converting between two non-USD currencies. Providing detailed information on both elements enhances trust and enables more informed decisions during international money transfers.
Choosing Between FX Margin and Cross Currency Spread
Choosing between FX margin and cross currency spread depends on transaction size, currency pairs involved, and market volatility. FX margin offers lower costs for high-volume transfers with tighter spreads, while cross currency spreads provide more transparency and fixed fees beneficial for smaller or less frequent remittances. Evaluating FX margin costs against the spread differences in cross currency conversions ensures optimal remittance value and minimized currency exchange expenses.
Reducing Remittance Expenses: Best Practices
Reducing remittance expenses requires minimizing FX margin and cross currency spread, both of which significantly impact the total cost of international money transfers. Choosing providers with transparent fee structures and competitive exchange rates can substantially lower these hidden costs. Leveraging technology platforms that aggregate real-time currency rates and optimize cross-border transfers helps senders achieve better value and reduce overall remittance expenses.
Future Trends in Remittance Pricing Models
Future trends in remittance pricing models indicate a shift towards dynamic FX margin strategies that leverage real-time market data to optimize margin spreads. Cross currency spreads are expected to narrow due to increased competition and regulatory pressures, enhancing transparency in pricing. Emerging technologies like blockchain and AI-driven analytics will enable more precise, data-driven margin adjustments that reduce costs and improve exchange rate accuracy for consumers.
Important Terms
Bid-Ask Spread
The bid-ask spread in FX margin trading reflects the difference between buying and selling prices of currency pairs, directly impacting trading costs and liquidity. Cross currency spread further influences this spread by incorporating exchange rate differentials between non-USD currency pairs, affecting margin requirements and overall transaction efficiency.
Interbank Rate
Interbank rate serves as a benchmark for evaluating FX margin costs and cross currency spreads, influencing the overall pricing in foreign exchange markets. Differences in interbank rates between currency pairs directly impact the cross currency spread, shaping trading strategies and liquidity access for market participants.
Nostro Account
A Nostro Account facilitates foreign exchange (FX) transactions by holding foreign currency funds, which directly impacts FX margin requirements, typically lowering them due to improved liquidity and reduced counterparty risk. Cross currency spreads, reflecting the cost differential between two currencies, influence the pricing and profitability of FX trades involving Nostro accounts, as tighter spreads reduce transaction costs and enhance market efficiency.
Currency Pair Quotation
Currency pair quotation reflects the exchange rate between two currencies, crucial for calculating FX margin requirements that determine leverage and risk exposure in foreign exchange trading. Cross currency spread influences the bid-ask differential, affecting trading costs and the precision of currency pair pricing in margin accounts.
Markup Fee
Markup fees in FX trading represent the added cost brokers charge over the base interbank rate, directly influencing the overall FX margin. Cross currency spreads, reflecting the difference between bid and ask prices of currency pairs, interact with markup fees to determine the total cost of executing cross currency transactions, impacting trader profitability and market liquidity.
Mid-Market Rate
The Mid-Market Rate represents the midpoint between the bid and ask prices in the foreign exchange market, serving as a benchmark for currency conversion costs. FX Margin refers to the profit charged by brokers above this rate, while the Cross Currency Spread reflects the difference in exchange rates when converting between two non-USD currencies, often impacting overall transaction costs.
Treasury Operations
Treasury operations closely monitor FX margin and cross currency spread to optimize foreign exchange risk management and liquidity. FX margin reflects the cost difference between spot and forward rates, while cross currency spread measures the yield differential between two currencies, both critical for pricing and hedging currency exposures.
Correspondent Banking
Correspondent banking involves intermediaries facilitating international payments, where FX margin represents the profit added on currency exchange rates, while cross currency spread reflects the difference between bid and ask prices across currency pairs. Understanding the interplay between FX margin and cross currency spread is crucial for managing costs and risks in correspondent banking transactions.
Conversion Premium
Conversion Premium reflects the added cost in FX Margin trading compared to Cross Currency Spread, representing the difference between the spot rate and the forward rate due to interest rate differentials between two currencies. This premium impacts trading strategies by influencing the effective cost of holding positions in cross currency pairs, making it crucial to consider for accurate risk management and profit calculations.
Settlement Risk
Settlement risk in foreign exchange (FX) margin trading arises when there is a timing mismatch in the final exchange of currencies, potentially leading to financial loss if one party defaults. This risk differs from cross-currency spread, which refers to the difference in interest rates and pricing between two currency pairs, impacting the cost of hedging and the profitability of FX margin strategies.
FX Margin vs Cross Currency Spread Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com