FX spot rates reflect the current exchange value for immediate currency conversion, crucial for remittances requiring quick settlement. FX forward rates lock in an exchange rate for a future date, helping senders and recipients hedge against currency volatility in remittance transactions. Comparing these rates enables users to decide between immediate conversion cost and future currency risk management.
Table of Comparison
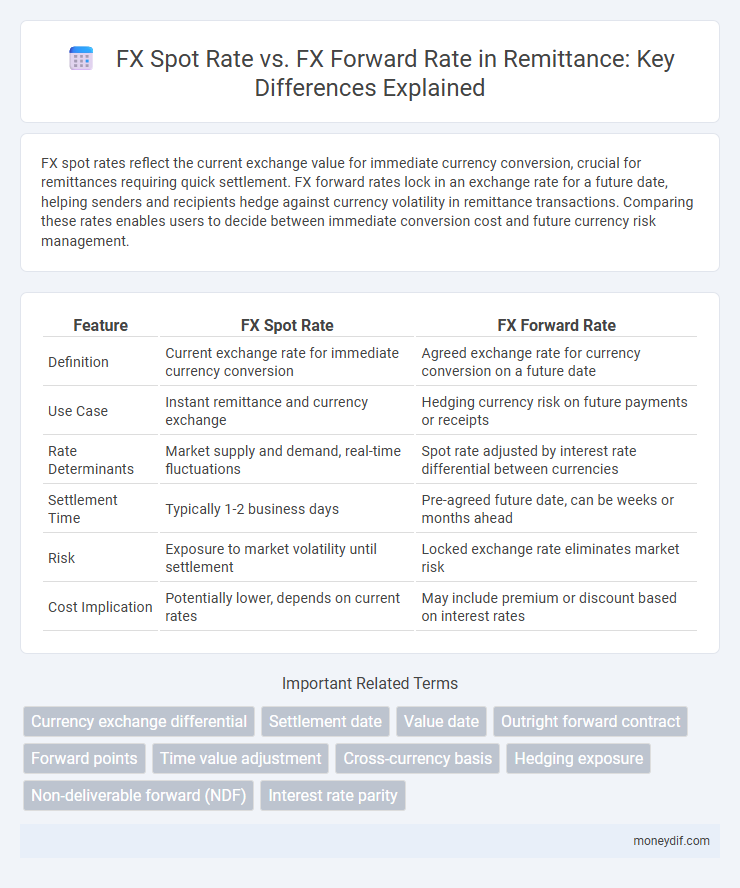
| Feature | FX Spot Rate | FX Forward Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Current exchange rate for immediate currency conversion | Agreed exchange rate for currency conversion on a future date |
| Use Case | Instant remittance and currency exchange | Hedging currency risk on future payments or receipts |
| Rate Determinants | Market supply and demand, real-time fluctuations | Spot rate adjusted by interest rate differential between currencies |
| Settlement Time | Typically 1-2 business days | Pre-agreed future date, can be weeks or months ahead |
| Risk | Exposure to market volatility until settlement | Locked exchange rate eliminates market risk |
| Cost Implication | Potentially lower, depends on current rates | May include premium or discount based on interest rates |
Understanding FX Spot and Forward Rates in Remittance
FX spot rates represent the current exchange rate at which currencies can be exchanged immediately, making them essential for real-time remittance transactions. FX forward rates are agreed upon today for currency exchange at a specified future date, providing certainty against market fluctuations in cross-border money transfers. Understanding the difference between spot and forward rates helps individuals and businesses manage currency risk and optimize remittance costs.
Key Differences: FX Spot Rate vs FX Forward Rate
The FX spot rate refers to the current exchange rate at which currencies are traded for immediate delivery, typically within two business days, while the FX forward rate is an agreed-upon exchange rate for a currency transaction that will occur at a specified future date. The spot rate reflects real-time market conditions, influenced by supply and demand, whereas the forward rate incorporates expected changes in interest rates and market volatility to hedge against currency risk. Understanding the distinction between spot and forward rates is crucial for managing remittance timing, cost predictability, and foreign exchange exposure.
How FX Spot Rates Affect International Money Transfers
FX spot rates determine the immediate exchange rate for currency conversion in international money transfers, directly impacting the amount received by beneficiaries. Fluctuations in spot rates can cause significant variations in the transferred sum's value when funds are converted instantly. Businesses and individuals often monitor spot rates closely to time transfers for favorable currency valuations, reducing potential losses in remittance transactions.
Benefits of Using FX Forward Rates for Remittances
FX forward rates offer protection against currency fluctuations by locking in exchange rates for future remittance payments, ensuring cost certainty. This risk management tool helps individuals and businesses avoid adverse FX spot rate movements, preventing unexpected losses on cross-border transfers. Utilizing FX forward contracts enables better financial planning and budgeting, enhancing overall remittance efficiency and stability.
Locking Exchange Rates: Spot vs Forward Strategies
Locking exchange rates through FX spot and forward contracts offers distinct advantages for remittance senders seeking cost certainty. Spot rates enable immediate currency conversion at current market prices, ideal for urgent transfers, while forward rates secure a predetermined exchange rate for future transactions, mitigating exposure to currency volatility. Choosing the right strategy depends on timing needs and risk tolerance, with forward contracts providing a hedge against unfavorable rate fluctuations in cross-border remittances.
Cost Implications for Remitters: Spot Rate vs Forward Rate
The FX spot rate reflects the current market value for immediate currency exchange, often resulting in unpredictable costs due to market volatility for remitters. FX forward rates lock in an exchange rate for a future date, providing cost certainty and protection against adverse currency fluctuations. Choosing a forward rate can mitigate financial risk and optimize budgeting for remittance transactions, whereas spot rates may offer better rates at the expense of exposure to price movements.
Managing Currency Risk in Remittances
FX spot rates represent the current exchange rate for immediate currency conversion, while FX forward rates are agreed-upon rates for currency exchange at a future date, helping businesses and individuals manage currency risk in remittances. Utilizing FX forward contracts allows remitters to lock in favorable rates, reducing uncertainty caused by exchange rate fluctuations during the transfer period. Effective currency risk management through forward contracts ensures predictable costs and protects recipients from potential financial losses due to adverse currency movements.
Choosing Between Spot and Forward Rates for Large Transfers
Choosing between FX spot and forward rates for large remittance transfers depends on market volatility and timing certainty. Spot rates provide immediate currency exchange at current rates, ideal for urgent transfers, while forward rates lock in a predetermined exchange rate, mitigating risk against currency fluctuations. Utilizing forward contracts can protect large transactions from adverse movements, ensuring cost predictability in cross-border payments.
Real-world Scenarios: Spot vs Forward Rates in Remittance
In remittance transactions, FX spot rates apply to currency exchanges settled immediately, reflecting current market conditions and providing transparency for urgent transfers. FX forward rates lock in exchange rates for future settlements, enabling senders to hedge against currency volatility and budget remittances with predictable costs. Real-world applications show that spot rates benefit recipients needing instant funds, while forward contracts suit businesses or individuals aiming to manage currency risk in cross-border payments.
Future Trends in FX Rates and Their Impact on Remittances
FX forward rates reflect market expectations of future spot rates adjusted for interest rate differentials, providing a hedge against currency volatility in remittances. Emerging trends indicate that increased global economic uncertainty and central bank interventions will amplify discrepancies between spot and forward rates. This divergence impacts remittance strategies by influencing the timing and cost efficiency of cross-border money transfers.
Important Terms
Currency exchange differential
The currency exchange differential represents the difference between the FX spot rate and the FX forward rate, reflecting interest rate parity and market expectations of currency value changes.
Settlement date
The settlement date determines whether the FX spot rate applies for immediate currency exchange or the FX forward rate is used for transactions settled at a future agreed date.
Value date
The value date determines the settlement day for FX spot rates, typically two business days after the trade date, while FX forward rates settle on a future value date agreed upon by both parties to hedge against exchange rate fluctuations.
Outright forward contract
An outright forward contract locks in an agreed FX forward rate for a future date, allowing businesses to hedge against potential fluctuations between the current FX spot rate and the predetermined forward rate.
Forward points
Forward points represent the difference between the FX forward rate and the FX spot rate, reflecting interest rate differentials between the two currencies.
Time value adjustment
Time value adjustment quantifies the difference between the FX spot rate and the FX forward rate by accounting for interest rate differentials and the time until contract maturity in foreign exchange transactions.
Cross-currency basis
Cross-currency basis represents the deviation between the FX spot rate and the FX forward rate, reflecting market-implied funding cost differentials and currency-specific liquidity conditions.
Hedging exposure
Hedging exposure through FX forward contracts mitigates risk from unfavorable fluctuations between the FX spot rate and the locked-in forward rate.
Non-deliverable forward (NDF)
Non-deliverable forward (NDF) contracts are financial derivatives used to hedge or speculate on currencies that are not freely convertible, settling the difference between the agreed FX forward rate and the prevailing FX spot rate at contract maturity without physical currency exchange. The NDF's value depends on the discrepancy between the locked-in FX forward rate and the actual spot rate on the settlement date, reflecting market expectations and interest rate differentials.
Interest rate parity
Interest rate parity explains the relationship between FX spot rates and FX forward rates by ensuring that the forward exchange rate offsets interest rate differentials between two currencies to prevent arbitrage opportunities.
FX spot rate vs FX forward rate Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com