Exchange rate margin significantly impacts the total cost of sending remittances, often exceeding the apparent transaction fee. While transaction fees are typically fixed or transparent, hidden exchange rate margins can lead to less favorable conversion rates, increasing overall expenses. Evaluating both factors is essential for maximizing the value of each remittance transfer.
Table of Comparison
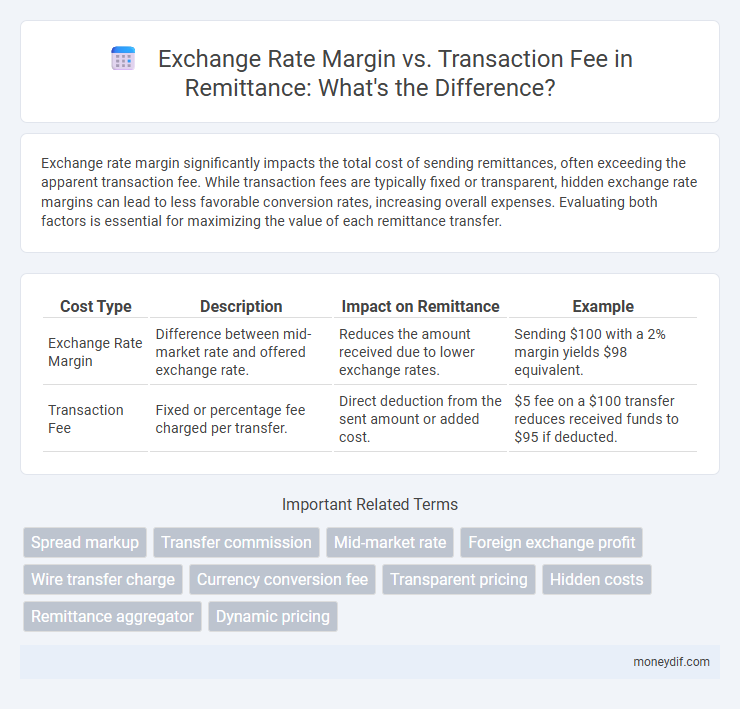
| Cost Type | Description | Impact on Remittance | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exchange Rate Margin | Difference between mid-market rate and offered exchange rate. | Reduces the amount received due to lower exchange rates. | Sending $100 with a 2% margin yields $98 equivalent. |
| Transaction Fee | Fixed or percentage fee charged per transfer. | Direct deduction from the sent amount or added cost. | $5 fee on a $100 transfer reduces received funds to $95 if deducted. |
Understanding Exchange Rate Margins in Remittances
Exchange rate margins represent the difference between the mid-market rate and the rate offered by remittance providers, often constituting the largest hidden cost in international money transfers. Unlike fixed transaction fees, exchange rate margins can vary significantly depending on the currency pair and transfer amount, directly impacting the total cost of sending money abroad. Understanding and comparing exchange rate margins is crucial for remitters aiming to maximize the value received by beneficiaries and minimize overall remittance expenses.
What Are Transaction Fees in Money Transfers?
Transaction fees in money transfers are fixed or variable charges imposed by financial institutions or payment providers for processing remittances. These fees cover operational costs, including currency conversion, payment network usage, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Unlike exchange rate margins, which affect the currency conversion value, transaction fees are explicit costs that directly reduce the total amount received by the beneficiary.
Exchange Rate Margin vs Transaction Fee: Key Differences
Exchange rate margin represents the difference between the mid-market rate and the rate offered by remittance providers, often affecting the total cost by inflating currency conversion. Transaction fees are fixed or percentage-based charges applied per transfer, directly impacting the upfront cost of sending money. Understanding the interplay between exchange rate margins and transaction fees is crucial for selecting the most cost-effective remittance service.
How Exchange Rate Margins Affect Remittance Costs
Exchange rate margins significantly impact remittance costs by increasing the effective amount paid beyond the transaction fee. When sending money internationally, even a small percentage markup on the exchange rate can add up to substantial hidden charges, making the overall cost of remittance higher than the upfront fee suggests. Consumers should compare both exchange rate margins and transaction fees to accurately assess the total expense of transferring funds abroad.
The Impact of Transaction Fees on Your Remittance
Transaction fees significantly affect the total cost of remittance, often surpassing the impact of exchange rate margins on the amount received by the beneficiary. While exchange rate margins vary based on currency pairs and providers, transaction fees are fixed or percentage-based charges that directly reduce the send amount. Evaluating both factors is essential for optimizing remittance value, with lower transaction fees providing a more transparent and immediate cost saving.
Comparing Leading Providers: Margins and Fees
Leading remittance providers show significant variation in exchange rate margins and transaction fees, directly impacting the overall cost of sending money abroad. Providers like Wise and Revolut typically offer lower exchange rate margins, often close to the mid-market rate, while traditional banks and services such as Western Union charge higher margins alongside fixed transaction fees. Evaluating both exchange rate margins and flat fees is crucial for cost-effective remittance, with digital-first platforms generally providing more competitive pricing compared to legacy operators.
Choosing Between Low Fees and Better Exchange Rates
Selecting between a lower transaction fee or a better exchange rate margin significantly affects the total cost of remittance. A smaller fee may seem advantageous, but a wider exchange rate margin can reduce the actual amount received by the beneficiary. Careful comparison of both components helps maximize the value transferred in international money transfers.
Hidden Costs in International Money Transfers
Exchange rate margin often represents the largest hidden cost in international money transfers, as providers mark up the exchange rate to earn profit beyond the visible transaction fee. Many customers focus on the upfront transaction fee, overlooking that unfavorable exchange rates can significantly reduce the amount received by the beneficiary. Comparing both exchange rate margins and transaction fees is essential to accurately assess the total cost of a remittance service.
Tips to Minimize Total Remittance Costs
To minimize total remittance costs, compare both exchange rate margins and transaction fees before sending money internationally. Opt for providers offering competitive exchange rates with low or no transaction fees to maximize the amount received. Use online tools to calculate the effective cost, combining fees and exchange rates for a clearer cost comparison.
The True Cost of Sending Money Abroad
The true cost of sending money abroad includes both the exchange rate margin and the transaction fee, with the exchange rate margin often representing a larger hidden expense. Exchange rate margins can add up to 5% or more on the principal amount, significantly increasing the overall cost compared to flat transaction fees. Consumers should compare providers' exchange rates alongside transaction fees to accurately assess the total cost of international remittances.
Important Terms
Spread markup
Spread markup in currency exchange represents the difference between the buying and selling rates set by brokers, serving as an indirect cost embedded within the exchange rate margin. This margin typically exceeds transaction fees, making the spread markup a critical factor in overall trade cost evaluation.
Transfer commission
Transfer commissions typically consist of an exchange rate margin and a transaction fee, where the exchange rate margin represents the markup applied to the base currency conversion rate, often resulting in hidden costs. The transaction fee is a fixed or percentage-based charge imposed by the service provider, making it crucial for customers to compare both components to determine the most cost-effective international money transfer option.
Mid-market rate
Mid-market rate represents the midpoint between the buy and sell prices of a currency, serving as the benchmark for exchange rates without added markup. Exchange rate margin refers to the percentage difference applied by currency providers above the mid-market rate, while transaction fees are fixed or variable charges per currency exchange, both impacting the overall cost of currency conversion.
Foreign exchange profit
Foreign exchange profit primarily depends on the exchange rate margin, which represents the difference between the buy and sell rates offered by currency brokers or banks, typically generating higher earnings compared to flat transaction fees. Exchange rate margins leverage market volatility, allowing traders and businesses to capitalize on currency fluctuations more effectively than relying solely on fixed transaction fees.
Wire transfer charge
Wire transfer charges often consist of a transaction fee and an exchange rate margin, where the latter reflects the cost embedded in currency conversion rates above the mid-market rate. The exchange rate margin can significantly impact the total cost, sometimes exceeding the flat transaction fees charged by banks or intermediaries.
Currency conversion fee
Currency conversion fees often comprise exchange rate margins, which are the differences between the mid-market rate and the rate offered by financial institutions, and fixed transaction fees charged per conversion. Understanding the interplay between these two cost components is crucial as exchange rate margins can vary widely depending on providers, while transaction fees are typically transparent and fixed.
Transparent pricing
Transparent pricing in foreign exchange ensures customers understand the true cost by clearly separating the exchange rate margin from the transaction fee. By disclosing both the percentage markup on currency conversion and any flat or variable transaction charges, businesses build trust and enable clients to make informed financial decisions.
Hidden costs
Hidden costs in currency exchange often arise from the exchange rate margin, which is the difference between the market rate and the rate offered by financial institutions. Unlike a transparent transaction fee, the exchange rate margin can significantly increase the overall cost of a transaction by applying less favorable currency conversion, making it essential for consumers to compare both components for accurate cost assessment.
Remittance aggregator
Remittance aggregators optimize cross-border money transfers by balancing exchange rate margins and transaction fees to offer competitive overall costs for users. Lower exchange rate margins often compensate for higher transaction fees, while some aggregators reduce fees but apply wider margins, impacting the total cost of sending funds internationally.
Dynamic pricing
Dynamic pricing in the context of exchange rate margin versus transaction fee optimizes costs by adjusting prices based on real-time currency fluctuations and fee structures to maximize profitability. This approach enables businesses to balance the impact of volatile exchange rates and fixed transaction fees, enhancing competitive pricing strategies for international transactions.
exchange rate margin vs transaction fee Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com