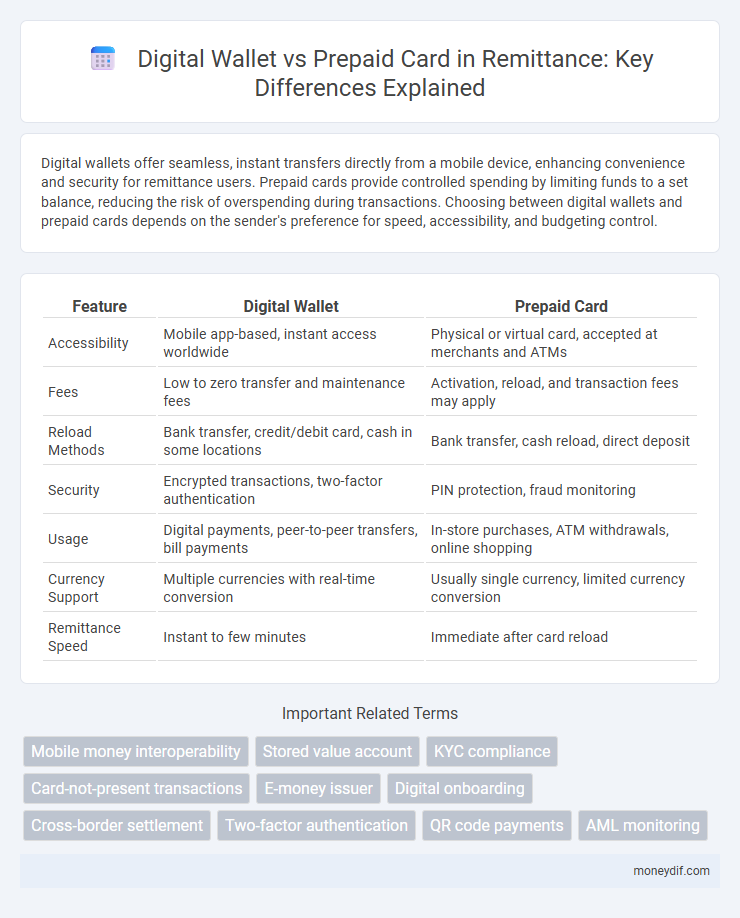
Digital wallets offer seamless, instant transfers directly from a mobile device, enhancing convenience and security for remittance users. Prepaid cards provide controlled spending by limiting funds to a set balance, reducing the risk of overspending during transactions. Choosing between digital wallets and prepaid cards depends on the sender's preference for speed, accessibility, and budgeting control.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Digital Wallet | Prepaid Card |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Mobile app-based, instant access worldwide | Physical or virtual card, accepted at merchants and ATMs |
| Fees | Low to zero transfer and maintenance fees | Activation, reload, and transaction fees may apply |
| Reload Methods | Bank transfer, credit/debit card, cash in some locations | Bank transfer, cash reload, direct deposit |
| Security | Encrypted transactions, two-factor authentication | PIN protection, fraud monitoring |
| Usage | Digital payments, peer-to-peer transfers, bill payments | In-store purchases, ATM withdrawals, online shopping |
| Currency Support | Multiple currencies with real-time conversion | Usually single currency, limited currency conversion |
| Remittance Speed | Instant to few minutes | Immediate after card reload |
Understanding Digital Wallets in Remittance
Digital wallets in remittance streamline cross-border payments by enabling instant transfers directly to users' mobile devices, reducing transaction fees compared to traditional methods. These digital platforms store multiple currencies and offer real-time currency conversion, enhancing convenience for recipients in diverse countries. Unlike prepaid cards, digital wallets provide seamless integration with banking apps and support peer-to-peer transfers, making them a preferred choice for global money movement.
Prepaid Cards: An Overview for Remittance Users
Prepaid cards offer remittance users a secure and convenient way to access funds without requiring a bank account, enabling quick withdrawals and in-store purchases globally. These cards often feature lower fees and enhanced spending control, making them an attractive alternative to traditional cash transfers or digital wallets. Key providers like Visa and Mastercard support prepaid cards, ensuring widespread acceptance and seamless integration with remittance services.
Key Differences: Digital Wallet vs Prepaid Card
Digital wallets enable users to store multiple payment methods securely and facilitate instant online transactions through smartphones, while prepaid cards are physical cards loaded with a specific amount of money for in-store or online purchases. Unlike prepaid cards, digital wallets offer enhanced features such as peer-to-peer transfers, bill payments, and integration with financial apps, providing greater convenience and flexibility. Security measures in digital wallets typically include multi-factor authentication and encryption, whereas prepaid cards rely mainly on PIN protection and can be more vulnerable if lost or stolen.
Security Features: Which Option is Safer?
Digital wallets employ advanced encryption and biometric authentication, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access compared to prepaid cards, which often rely on simple PIN protection. Real-time transaction monitoring and remote disabling capabilities in digital wallets enhance security by enabling immediate response to suspicious activities. Prepaid cards are more vulnerable to physical theft and skimming, whereas digital wallets benefit from continuous software updates that patch security vulnerabilities promptly.
Cost Comparison: Fees and Charges Explained
Digital wallets typically offer lower fees for remittance transactions compared to prepaid cards, as they eliminate the need for physical card issuance and maintenance costs. Prepaid cards often incur activation fees, monthly service charges, and ATM withdrawal fees, increasing the overall cost for users sending money internationally. Choosing a digital wallet can reduce transfer expenses by leveraging lower transaction fees and streamlined currency conversion rates.
Accessibility and Global Reach
Digital wallets offer seamless accessibility through smartphones and internet connectivity, enabling instant remittance transactions worldwide without geographical restrictions. Prepaid cards provide a physical payment option but often require activation at specific locations and face limitations in countries accepting their network. Both methods enhance global reach; however, digital wallets deliver broader accessibility for users in remote or underbanked regions, fostering faster cross-border money transfers.
User Experience: Convenience and Usability
Digital wallets offer seamless user experiences with instant fund transfers, easy access through mobile apps, and integrated multi-currency support enhancing convenience for global remittance users. Prepaid cards provide offline usability and security but may involve activation steps and limited acceptance in certain regions, potentially complicating usability. Optimizing digital wallets for intuitive interfaces and real-time notifications significantly improves convenience compared to managing balance and transactions on prepaid cards.
Speed of Transfer: Digital Wallet vs Prepaid Card
Digital wallets enable instant or near-instant funds transfer, significantly reducing the waiting time for recipients compared to prepaid cards, which often require physical activation or intermediary processing. The speed of transfer using digital wallets is enhanced by direct bank integrations and real-time transaction capabilities, whereas prepaid cards may involve delays due to card issuing and load times. For remittances, digital wallets provide a faster and more seamless experience, improving access to funds immediately after sending.
Integration with Banks and Other Services
Digital wallets offer seamless integration with banks and financial institutions through APIs, enabling real-time fund transfers and instant balance updates. Prepaid cards, while connected to bank networks, often rely on batch processing and manual reloads, limiting their interoperability with other digital services. Enhanced bank integration in digital wallets facilitates smoother remittance experiences, including bill payments and cross-platform transactions.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Remittance Needs
Digital wallets offer instant access to funds and seamless transfer capabilities, making them ideal for frequent remittances and tech-savvy users. Prepaid cards provide greater control over spending and offline usability, suitable for recipients in areas with limited internet access. Assess transaction fees, accessibility, and recipient preferences to determine the best option for your remittance needs.
Important Terms
Mobile money interoperability
Mobile money interoperability enables seamless transactions and fund transfers across diverse digital wallets and prepaid card platforms, enhancing user convenience and financial inclusion. Integrating systems between digital wallets and prepaid cards allows real-time balance updates and cross-platform payment acceptance, driving widespread adoption of cashless payments.
Stored value account
Stored value accounts serve as a digital repository for funds within digital wallets, enabling seamless online and contactless payments, while prepaid cards function as physical or virtual cards loaded with a predetermined balance, offering controlled spending without direct bank account linkage. Both instruments provide budget management and security features, but stored value accounts often integrate with mobile apps for real-time balance tracking, whereas prepaid cards emphasize offline accessibility and widespread merchant acceptance.
KYC compliance
KYC compliance ensures robust identity verification for both digital wallets and prepaid cards, minimizing fraud and enhancing transaction security. Digital wallets leverage real-time KYC processes through biometric and document verification, while prepaid cards require stringent checks to prevent money laundering and ensure regulatory adherence.
Card-not-present transactions
Card-not-present transactions, which occur when neither the cardholder nor the card is physically present during the transaction, are increasingly facilitated by digital wallets offering secure tokenization and biometric authentication. Prepaid cards, while usable for these transactions, lack the advanced fraud protection features of digital wallets, making digital wallets a preferred choice for enhanced security and convenience in e-commerce and mobile payments.
E-money issuer
E-money issuers provide digital wallets that enable secure, instant electronic transactions and fund storage, offering greater convenience and integration with online services compared to traditional prepaid cards. While prepaid cards are physical or virtual payment tools preloaded with funds, digital wallets from e-money issuers support multi-currency accounts, seamless peer-to-peer transfers, and real-time balance updates, enhancing user flexibility and financial management.
Digital onboarding
Digital onboarding streamlines user verification for digital wallets by enabling instant identity checks and enhancing security through biometric authentication, facilitating seamless access to financial services. Prepaid cards offer a complementary solution by providing a secure, reloadable payment method without requiring traditional bank accounts, making them ideal for users who prefer offline transactions or limited credit exposure.
Cross-border settlement
Cross-border settlement via digital wallets offers faster transaction speeds and lower fees compared to prepaid cards, leveraging blockchain technology and real-time currency conversion to enhance efficiency. Prepaid cards provide broader acceptance at physical retail points and ATMs but often incur higher foreign exchange and service charges during international transactions.
Two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication enhances security for digital wallets by requiring an additional verification step such as a biometric scan or one-time password, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Prepaid cards, typically relying on PIN codes or signatures, lack this dynamic authentication layer, making digital wallets a more secure option for protecting financial transactions.
QR code payments
QR code payments enable seamless transactions by linking digital wallets, which store multiple payment methods and support real-time fund transfers, with prepaid cards that limit spending to preloaded amounts, enhancing budgeting control and reducing fraud risk. This integration promotes faster checkout experiences and increased financial accessibility for unbanked or underbanked users in various retail and service environments.
AML monitoring
AML monitoring for digital wallets involves tracking real-time transaction patterns and behavior analytics to detect suspicious activities, leveraging the digital nature of wallet platforms for enhanced data granularity. Prepaid card AML monitoring focuses on identifying unusual load and spend behavior, often incorporating geolocation and cardholder profile validation to mitigate risks associated with anonymous and high-volume transactions.
digital wallet vs prepaid card Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com