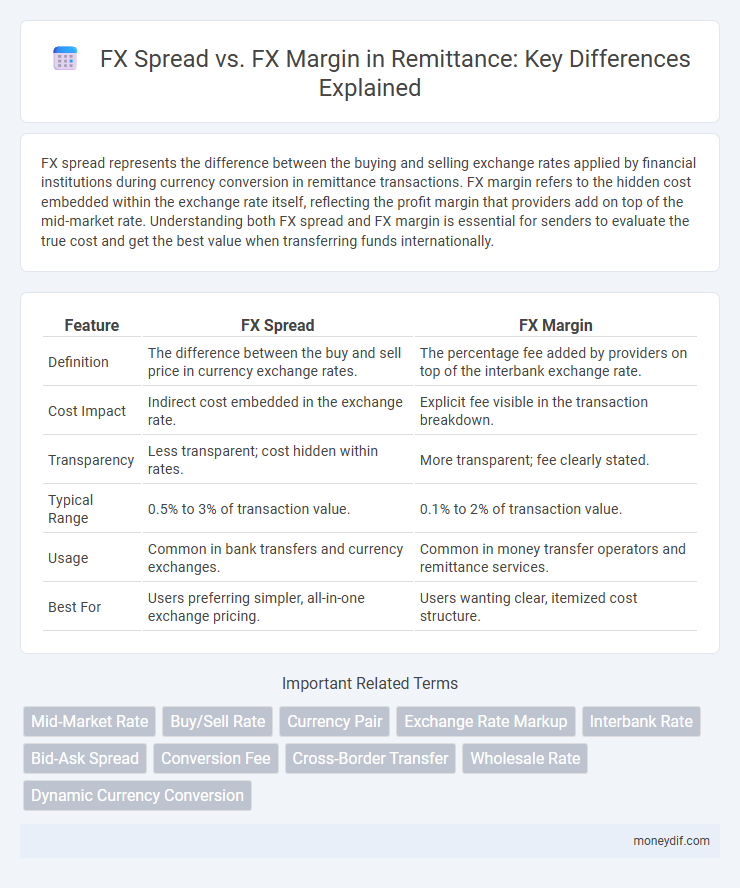
FX spread represents the difference between the buying and selling exchange rates applied by financial institutions during currency conversion in remittance transactions. FX margin refers to the hidden cost embedded within the exchange rate itself, reflecting the profit margin that providers add on top of the mid-market rate. Understanding both FX spread and FX margin is essential for senders to evaluate the true cost and get the best value when transferring funds internationally.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | FX Spread | FX Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The difference between the buy and sell price in currency exchange rates. | The percentage fee added by providers on top of the interbank exchange rate. |
| Cost Impact | Indirect cost embedded in the exchange rate. | Explicit fee visible in the transaction breakdown. |
| Transparency | Less transparent; cost hidden within rates. | More transparent; fee clearly stated. |
| Typical Range | 0.5% to 3% of transaction value. | 0.1% to 2% of transaction value. |
| Usage | Common in bank transfers and currency exchanges. | Common in money transfer operators and remittance services. |
| Best For | Users preferring simpler, all-in-one exchange pricing. | Users wanting clear, itemized cost structure. |
Understanding FX Spread in Remittance
FX spread in remittance refers to the difference between the buy and sell rates of a currency, which impacts the overall cost of transferring money internationally. This spread represents the hidden fee embedded in the exchange rate offered by financial institutions or remittance providers. Understanding FX spread helps senders identify the true exchange cost, enabling them to compare providers and reduce transfer expenses.
What is FX Margin and How Does It Work?
FX margin refers to the difference between the spot exchange rate and the rate at which a financial institution executes a currency transaction for remittance purposes. It functions as a hidden cost embedded within the exchange rate, influencing the total amount received after currency conversion. Understanding FX margin is crucial for senders to estimate the actual value of international money transfers and minimize transfer fees.
Key Differences Between FX Spread and FX Margin
FX spread refers to the difference between the bid and ask prices of a currency pair, representing the cost embedded in each transaction, while FX margin is the collateral required to open and maintain a leveraged position in forex trading. The FX spread directly affects the transaction cost and profitability, whereas FX margin influences the trader's risk exposure and capital needed. Understanding both is crucial for optimizing remittance costs and managing foreign exchange trading effectively.
How FX Spread Impacts Remittance Costs
FX spread directly influences remittance costs by determining the difference between the buying and selling exchange rates offered by money transfer services, thereby affecting the total amount received by the beneficiary. Wider FX spreads increase the cost of currency conversion, reducing the value of sent funds upon arrival, especially in high-volume or frequent remittances. Minimizing FX spread is crucial for cost-effective international money transfers as it ensures a higher exchange rate and maximizes the remittance's purchasing power abroad.
FX Margin: The Hidden Fee in Money Transfers
FX margin represents the hidden fee embedded within international money transfers, differing from the visible FX spread which is the difference between buy and sell currency rates. Money transfer services often mark up the exchange rate beyond the interbank rate, creating the FX margin that increases the overall cost for consumers without being explicitly disclosed. Understanding FX margin is crucial for senders aiming to minimize fees and maximize the value received by beneficiaries in remittance transactions.
Calculating Total Remittance Charges: Spread vs Margin
Calculating total remittance charges requires understanding the difference between FX spread and FX margin, where FX spread represents the difference between the buy and sell exchange rates offered by financial institutions, and FX margin refers to the percentage markup added to the mid-market rate by remittance providers. The total cost of a remittance transaction combines the FX margin applied to the transfer amount plus any fixed or variable fees, making it essential to compare both components to determine the most cost-effective service. Monitoring live exchange rates and using transparent calculators can help consumers accurately assess total charges and optimize remittance decisions.
Choosing the Best Provider: FX Spread or FX Margin?
Choosing the best provider for remittance depends on understanding the difference between FX spread and FX margin, as FX spread represents the difference between the buying and selling price of foreign currency, while FX margin refers to the percentage markup on the exchange rate applied by providers. Providers with lower FX spreads often offer more transparent and competitive rates, whereas those charging higher FX margins may include hidden fees affecting the total cost. Evaluating real-time exchange rates, service fees, and customer reviews can help determine whether FX spread or FX margin yields better value for your specific remittance needs.
Transparency in Remittance: Disclosing FX Fees
Transparency in remittance is crucial for consumer trust, particularly regarding FX fees. FX spread refers to the difference between the buying and selling price of currencies, often embedded in the exchange rate without clear disclosure, while FX margin is the explicit fee added by providers on top of the interbank rate. Clear disclosure of both FX spread and FX margin enables senders to understand the true cost of currency conversion and compare remittance services effectively.
Reducing Costs: Tips to Minimize FX Spread and Margin
Reducing the FX spread and margin in remittance transactions significantly lowers overall transfer costs, enhancing the amount received. Utilizing real-time exchange rate comparison tools and choosing providers with transparent fee structures helps minimize hidden charges. Opting for fixed-rate transfers or negotiating lower margins with high-volume providers can further optimize foreign exchange expenses.
The Future of FX Pricing Models in Remittance Services
The future of FX pricing models in remittance services is shifting towards more transparent structures that differentiate between FX spread and FX margin to enhance customer trust. Advanced algorithms and AI-driven platforms enable dynamic pricing, minimizing hidden costs traditionally embedded in FX margins while offering competitive spreads. This evolution supports increased regulatory compliance and consumer demand for clarity in foreign exchange transactions.
Important Terms
Mid-Market Rate
Mid-Market Rate represents the midpoint between the bid and ask prices in the foreign exchange market, serving as the most accurate indicator of the true currency value without added spread costs. FX Spread reflects the difference between the buying and selling prices incorporating broker fees, while FX Margin signifies the percentage markup traders add to the Mid-Market Rate, both influencing the overall transaction cost in currency exchange.
Buy/Sell Rate
Buy/Sell Rate in forex trading reflects the price at which currencies are bought or sold, directly influencing the FX Spread--the difference between bid and ask prices--and the FX Margin, which represents the required collateral for trading. Understanding the relationship between FX Spread and FX Margin helps traders minimize transaction costs and optimize leverage while managing risk effectively.
Currency Pair
Currency pairs in forex trading represent the exchange rate between two currencies, where the FX spread is the difference between the bid and ask price, reflecting the broker's fee. The FX margin is the collateral required to open a position, which varies based on leverage and directly impacts the trader's risk exposure and potential profit.
Exchange Rate Markup
Exchange rate markup refers to the additional cost added by financial institutions on the mid-market FX rate, impacting the overall transaction price. FX spread represents the difference between the bid and ask prices in currency trading, while FX margin indicates the profit percentage embedded in the exchange rate, both crucial for understanding currency conversion costs.
Interbank Rate
The interbank rate represents the wholesale exchange rate at which major banks trade currencies, serving as the benchmark for calculating both FX spreads and FX margins in retail forex transactions. FX spreads reflect the difference between bid and ask prices derived from the interbank rate, while FX margins incorporate additional costs or profit markups applied by brokers beyond the interbank spread.
Bid-Ask Spread
The bid-ask spread in foreign exchange (FX) trading represents the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept, directly influencing the FX margin traders pay as the cost embedded in spreads. FX spread measures market liquidity costs in pips, while FX margin refers to the required collateral to open a leveraged position, both crucial factors in managing trading expenses and risk exposure.
Conversion Fee
Conversion fees often incorporate FX spread, which reflects the difference between the buy and sell rates in currency exchange, whereas FX margin refers to the markup added by financial institutions on the interbank exchange rate to generate profit. Understanding the distinction between FX spread and FX margin is crucial for accurately assessing the total cost incurred during currency conversion transactions.
Cross-Border Transfer
Cross-border transfers typically involve FX spreads, which represent the difference between the bid and ask currency exchange rates, affecting the overall cost of currency conversion. FX margin, on the other hand, refers to the additional percentage or fixed fee charged by financial institutions over the interbank rate, directly influencing the total expense borne by the sender or recipient during international money transfers.
Wholesale Rate
Wholesale rates in foreign exchange typically feature a tighter FX spread compared to retail rates, reflecting lower transaction costs and higher liquidity among large institutions. FX margin, often expressed as a percentage added to the mid-market rate, represents the profit markup included in the wholesale rate, influencing the effective cost of currency conversion.
Dynamic Currency Conversion
Dynamic Currency Conversion (DCC) enables cardholders to see transaction amounts in their home currency at the point of sale, with fees often composed of FX spread and FX margin. The FX spread refers to the difference between the interbank exchange rate and the rate offered, while the FX margin is an additional fee applied by providers to cover processing costs and profit, both impacting the overall cost of international transactions.
FX Spread vs FX Margin Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com