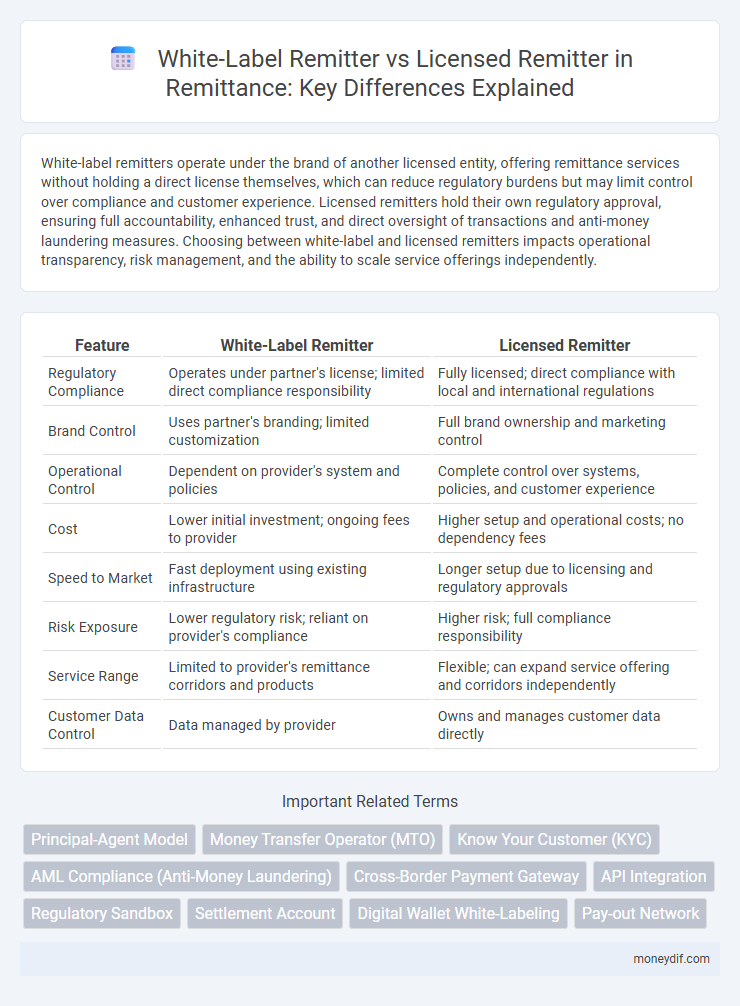
White-label remitters operate under the brand of another licensed entity, offering remittance services without holding a direct license themselves, which can reduce regulatory burdens but may limit control over compliance and customer experience. Licensed remitters hold their own regulatory approval, ensuring full accountability, enhanced trust, and direct oversight of transactions and anti-money laundering measures. Choosing between white-label and licensed remitters impacts operational transparency, risk management, and the ability to scale service offerings independently.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | White-Label Remitter | Licensed Remitter |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Operates under partner's license; limited direct compliance responsibility | Fully licensed; direct compliance with local and international regulations |
| Brand Control | Uses partner's branding; limited customization | Full brand ownership and marketing control |
| Operational Control | Dependent on provider's system and policies | Complete control over systems, policies, and customer experience |
| Cost | Lower initial investment; ongoing fees to provider | Higher setup and operational costs; no dependency fees |
| Speed to Market | Fast deployment using existing infrastructure | Longer setup due to licensing and regulatory approvals |
| Risk Exposure | Lower regulatory risk; reliant on provider's compliance | Higher risk; full compliance responsibility |
| Service Range | Limited to provider's remittance corridors and products | Flexible; can expand service offering and corridors independently |
| Customer Data Control | Data managed by provider | Owns and manages customer data directly |
Introduction to White-Label vs Licensed Remitters
White-label remitters operate by partnering with licensed money service businesses (MSBs) and utilize the licensed entity's regulatory approvals to offer remittance services under their own brand, eliminating the need for direct licensing. Licensed remitters hold direct licenses from financial authorities and are responsible for compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, transaction monitoring, and reporting obligations. White-label models lower market entry barriers, while licensed remitters provide greater regulatory control and accountability in the remittance ecosystem.
Defining White-Label Remitter Solutions
White-label remitter solutions enable financial institutions and businesses to offer remittance services under their own brand without obtaining a separate money transfer license. These solutions leverage the infrastructure and regulatory compliance of licensed remitters, facilitating faster market entry and reduced operational costs. By partnering with licensed providers, white-label remitters can focus on customer experience and marketing while ensuring secure and compliant cross-border money transfers.
Understanding Licensed Remitter Models
Licensed remitter models operate under strict regulatory frameworks that ensure compliance with anti-money laundering and customer protection laws, differentiating them from white-label remitters that often rely on third-party licenses. These licensed entities typically hold direct authorization from financial authorities, enabling transparent transaction monitoring and enhanced risk management. Understanding licensed remitter models is crucial for evaluating operational security, legal accountability, and trustworthiness in international money transfer services.
Key Differences Between White-Label and Licensed Remitters
White-label remitters operate under the brand of a licensed entity, offering remittance services without possessing their own regulatory licenses, which limits their control over compliance and customer data. Licensed remitters hold direct licenses from regulatory authorities, allowing them to manage compliance, customer transactions, and risk independently, ensuring greater operational transparency and regulatory accountability. The key difference lies in licensing ownership, regulatory responsibilities, and the degree of control over the remittance process and customer relationship.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Implications
White-label remitters operate under the license and regulatory framework of a parent licensed remitter, limiting their direct legal liabilities but requiring strict adherence to the principal's compliance protocols. Licensed remitters hold their own regulatory approvals, making them fully responsible for anti-money laundering (AML) measures, customer due diligence, and reporting obligations enforced by financial authorities. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties, license suspension, or legal actions, emphasizing the critical nature of robust compliance systems in both models.
Cost Comparison: White-Label vs Licensed Remitters
White-label remitters typically offer lower operational costs due to outsourced compliance and technology infrastructure, enabling competitive pricing with reduced fees for end-users. Licensed remitters incur higher expenses from regulatory compliance, licensing fees, and in-house risk management, which can translate to increased transaction costs. Cost-efficiency in white-label remittance solutions often attracts smaller businesses seeking affordable market entry without the financial burden of full licensing.
Speed to Market and Operational Setup
White-label remitters offer faster speed to market by leveraging pre-built platforms, reducing the need for extensive setup and regulatory approval, which contrasts with licensed remitters requiring comprehensive compliance checks and licensing processes. Operational setup for white-label remitters is streamlined through existing infrastructure and technology stacks, enabling quicker deployment and scalability. Licensed remitters face longer onboarding timelines due to strict regulatory frameworks, but they benefit from full control over compliance and operational strategies.
Customization and Branding Opportunities
White-label remitters offer extensive customization and branding opportunities, enabling businesses to tailor the user interface, payment flows, and customer experience to align closely with their brand identity. Licensed remitters, while compliant with regulatory requirements, often provide limited flexibility in branding and customization due to strict operational frameworks and oversight. Choosing a white-label solution allows for a seamless integration of brand elements, enhancing customer loyalty and market differentiation in the remittance industry.
Risk Management and Security Considerations
White-label remitters leverage third-party platforms, which may introduce heightened operational risks and limit direct control over compliance measures compared to licensed remitters that maintain in-house risk management frameworks. Licensed remitters adhere to stringent regulatory requirements, implement robust anti-money laundering (AML) protocols, and possess dedicated security infrastructures to safeguard transaction integrity. The choice between white-label and licensed remitter solutions significantly impacts the effectiveness of fraud prevention, customer due diligence, and regulatory compliance in remittance operations.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Remittance Business
White-label remitters offer a cost-effective, scalable solution by leveraging established platforms and licensed remittance providers, ideal for businesses seeking rapid market entry without regulatory complexities. Licensed remitters maintain complete control over compliance, customer experience, and branding but require significant investment in licensing, infrastructure, and adherence to stringent AML and KYC regulations. Selecting the right model depends on factors like risk tolerance, growth strategy, regulatory environment, and budget constraints in the remittance market.
Important Terms
Principal-Agent Model
The Principal-Agent Model highlights how white-label remitters act as agents operating under the control and compliance obligations of licensed remitters who are the principals responsible for regulatory adherence and risk management.
Money Transfer Operator (MTO)
Money Transfer Operators (MTOs) utilize licensed remitters to ensure regulatory compliance and security, whereas white-label remitters operate under third-party brands, often prioritizing scalability and reduced operational costs.
Know Your Customer (KYC)
KYC procedures for white-label remitters often rely on the licensed remitter's compliance framework to ensure regulatory adherence and prevent fraud in cross-border transactions.
AML Compliance (Anti-Money Laundering)
Licensed remitters ensure AML compliance through regulatory oversight and mandatory reporting, while white-label remitters rely on their licensed partners to implement anti-money laundering controls and risk assessments.
Cross-Border Payment Gateway
White-label remitters offer customizable, scalable cross-border payment gateways with reduced compliance burdens, while licensed remitters provide direct regulatory oversight and higher trust for secure international money transfers.
API Integration
API integration in white-label remitter solutions allows seamless customization and branding while leveraging licensed remitter infrastructure for compliance and regulatory requirements. Licensed remitters ensure secure transaction processing and adherence to financial laws, whereas white-label platforms focus on user experience and scalability through API-driven functionalities.
Regulatory Sandbox
Regulatory sandboxes enable white-label remitters to test innovative payment services under controlled conditions without full licensing, reducing compliance costs and accelerating market entry. Licensed remitters benefit from established regulatory frameworks, offering broader operational scope but facing stricter scrutiny and higher capital requirements.
Settlement Account
A settlement account enables seamless fund transfers by white-label remitters who operate under third-party branding, while licensed remitters manage settlement accounts directly under regulatory compliance for secure and transparent financial transactions.
Digital Wallet White-Labeling
Digital wallet white-labeling allows businesses to offer customized payment solutions by partnering with licensed remitters, ensuring compliance and secure fund transfers compared to non-licensed white-label remitters.
Pay-out Network
Pay-out Network enables white-label remitters to distribute funds through partner channels without a direct license, whereas licensed remitters operate under regulatory compliance with their own licenses to manage transactions.
white-label remitter vs licensed remitter Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com