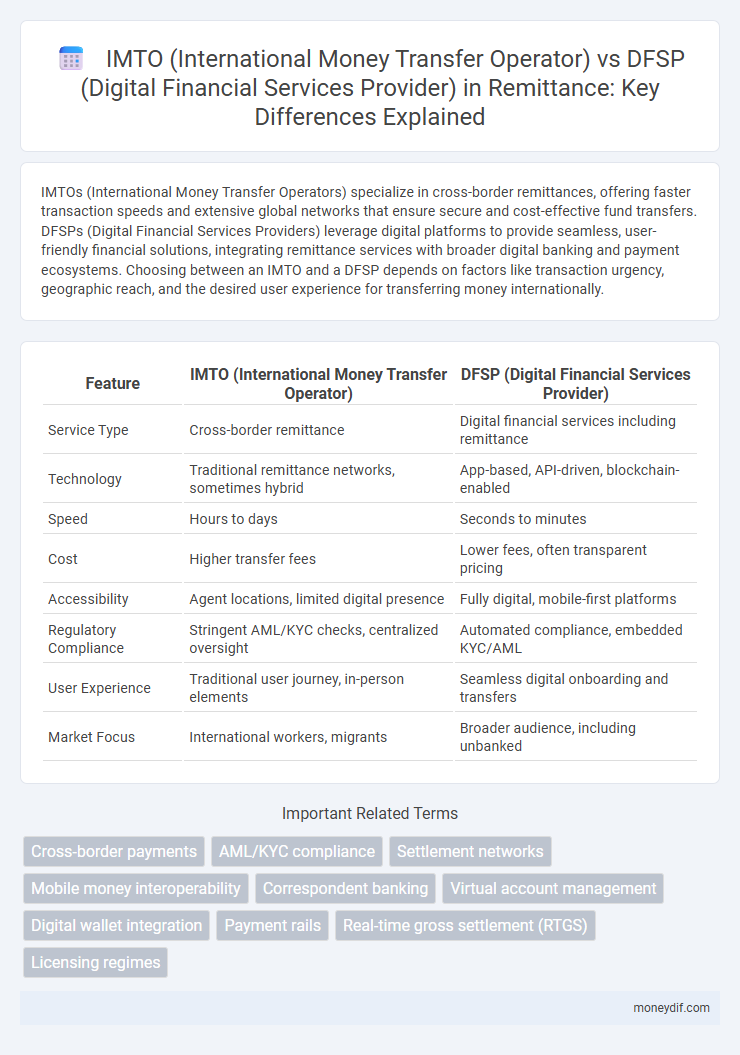
IMTOs (International Money Transfer Operators) specialize in cross-border remittances, offering faster transaction speeds and extensive global networks that ensure secure and cost-effective fund transfers. DFSPs (Digital Financial Services Providers) leverage digital platforms to provide seamless, user-friendly financial solutions, integrating remittance services with broader digital banking and payment ecosystems. Choosing between an IMTO and a DFSP depends on factors like transaction urgency, geographic reach, and the desired user experience for transferring money internationally.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | IMTO (International Money Transfer Operator) | DFSP (Digital Financial Services Provider) |
|---|---|---|
| Service Type | Cross-border remittance | Digital financial services including remittance |
| Technology | Traditional remittance networks, sometimes hybrid | App-based, API-driven, blockchain-enabled |
| Speed | Hours to days | Seconds to minutes |
| Cost | Higher transfer fees | Lower fees, often transparent pricing |
| Accessibility | Agent locations, limited digital presence | Fully digital, mobile-first platforms |
| Regulatory Compliance | Stringent AML/KYC checks, centralized oversight | Automated compliance, embedded KYC/AML |
| User Experience | Traditional user journey, in-person elements | Seamless digital onboarding and transfers |
| Market Focus | International workers, migrants | Broader audience, including unbanked |
Introduction: Understanding IMTOs and DFSPs in Remittance
IMTOs (International Money Transfer Operators) specialize in cross-border remittance by providing secure, regulated channels for sending money internationally, often partnering with banks and cash payout networks. DFSPs (Digital Financial Services Providers) leverage mobile and digital platforms to offer seamless remittance services, integrating with mobile wallets and other financial products to enhance user convenience and accessibility. Both IMTOs and DFSPs play crucial roles in the remittance ecosystem by addressing different customer needs and regulatory environments.
Key Differences Between IMTOs and DFSPs
IMTOs (International Money Transfer Operators) primarily facilitate cross-border remittance services by partnering with banks and financial institutions to transfer funds internationally, often subject to regulatory oversight and correspondent banking networks. DFSPs (Digital Financial Services Providers) offer a broader range of digital financial solutions, including mobile wallets, online banking, and peer-to-peer payments, leveraging technology platforms to provide instant, low-cost domestic and international transfers. Key differences include IMTOs' emphasis on traditional remittance corridors and compliance compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, while DFSPs focus on seamless user experience, integrated digital ecosystems, and expanding financial inclusion through innovative tech-driven services.
Regulatory Frameworks: IMTO vs. DFSP
International Money Transfer Operators (IMTOs) operate under stringent regulatory frameworks emphasizing anti-money laundering (AML), know your customer (KYC) compliance, and cross-border transaction monitoring, often requiring licenses from multiple jurisdictions. Digital Financial Services Providers (DFSPs), while also bound by AML and KYC regulations, face evolving digital finance policies that prioritize data privacy, cybersecurity standards, and fintech innovation compliance, leading to adaptive regulatory environments. Regulatory authorities increasingly demand interoperability and transparency from both IMTOs and DFSPs to ensure secure, compliant, and efficient remittance flows across borders.
Technology Adoption in IMTOs and DFSPs
IMTOs traditionally rely on legacy banking systems, whereas DFSPs leverage advanced technologies like blockchain, APIs, and mobile platforms to enhance remittance speed and transparency. DFSPs' agile adoption of digital tools enables real-time cross-border transactions and seamless integration with digital wallets, which challenges the slower, costlier processes of IMTOs. The ongoing technological shift positions DFSPs as key players in expanding financial inclusion through innovative remittance services.
Cost Structures: Fee Comparison
IMTOs typically charge a fixed fee per transaction combined with a percentage-based fee, often resulting in higher overall costs for small remittances compared to DFSPs, which leverage digital infrastructure to offer lower, transparent fees and reduced operational expenses. DFSPs benefit from scalability and automation, enabling cost-effective currency conversion and distribution, particularly in high-volume corridors where IMTO fees can be prohibitive. Cost structures in IMTOs tend to reflect legacy banking partnerships and compliance overheads, whereas DFSPs optimize fees through digital wallets and blockchain technologies, enhancing affordability for end-users.
Speed and Efficiency of Cross-Border Transfers
International Money Transfer Operators (IMTOs) typically offer faster cross-border transfers due to established global networks and dedicated corridors, enabling near-instantaneous transactions in key corridors. Digital Financial Services Providers (DFSPs) leverage advanced technology and mobile platforms to enhance speed and efficiency but may encounter delays from regulatory checks and interoperability challenges across different financial systems. The efficiency of cross-border transfers depends heavily on network reach, compliance infrastructure, and integration capabilities, where IMTOs generally excel in speed while DFSPs drive innovation in user experience and cost reduction.
Accessibility and Reach: Urban vs. Rural Penetration
IMTOs typically dominate urban centers with extensive agent networks and established financial infrastructure, ensuring quick and reliable cross-border money transfers. DFSPs leverage mobile technology to significantly enhance rural penetration by offering digital wallets and mobile remittance services, overcoming geographic and infrastructural barriers. The rising adoption of smartphones and mobile internet in rural areas accelerates DFSPs' ability to provide accessible and cost-effective remittance solutions beyond traditional urban hubs.
Security and Compliance Measures
International Money Transfer Operators (IMTOs) prioritize robust security frameworks with strict anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) protocols to ensure compliance across borders. Digital Financial Services Providers (DFSPs) leverage advanced encryption technologies and real-time fraud detection systems, enhancing transactional security while adhering to global regulatory standards. Both entities implement comprehensive compliance management systems, but IMTOs often face more stringent regulatory oversight due to their broader geographic reach.
Customer Experience and Innovation
IMTOs specialize in cross-border remittances with extensive global agent networks facilitating cash pickups, emphasizing reliability and wide reach, whereas DFSPs leverage digital platforms to offer instant, secure, and cost-effective transfers enhancing seamless user experience. DFSPs focus on innovation by integrating AI-driven fraud detection, real-time tracking, and mobile wallet interoperability, providing customers with transparency and convenience unmatched by traditional IMTOs. Customer experience in DFSP models benefits from 24/7 access, customizable services, and reduced transaction times, driving financial inclusion and fostering competition in the remittance ecosystem.
Future Trends: IMTO and DFSP Collaboration
IMTOs and DFSPs are increasingly collaborating to leverage blockchain technology and APIs, enhancing cross-border payment speed and transparency while reducing costs. The integration of DFSPs' digital wallets with IMTOs' global networks is driving seamless remittance experiences and real-time fund availability. Future trends indicate a shift towards hybrid models combining regulatory compliance strengths of IMTOs with the innovative agility of DFSPs, fostering financial inclusion worldwide.
Important Terms
Cross-border payments
Cross-border payments facilitated by IMTOs (International Money Transfer Operators) leverage established correspondent banking networks to ensure secure and compliant transfers, while DFSPs (Digital Financial Services Providers) utilize digital wallets and blockchain technologies for faster, cost-effective, and highly transparent transactions. DFSPs often provide enhanced user experience with real-time tracking and lower fees, contrasting with IMTOs' broad global reach and regulated frameworks critical for managing cross-border currency exchange and anti-money laundering compliance.
AML/KYC compliance
AML/KYC compliance for IMTOs focuses on stringent customer identity verification and transaction monitoring to prevent cross-border money laundering risks, while DFSPs emphasize real-time fraud detection and data privacy in digital financial ecosystems. Regulatory frameworks mandate both IMTOs and DFSPs to implement robust anti-money laundering controls tailored to their operational models and risk exposure profiles.
Settlement networks
Settlement networks facilitate instant and secure fund transfers between IMTOs (International Money Transfer Operators) and DFSPs (Digital Financial Services Providers), ensuring seamless cross-border transaction settlements. Leveraging APIs and blockchain technology, these networks optimize liquidity management, reduce settlement time, and enhance compliance with global anti-money laundering (AML) regulations.
Mobile money interoperability
Mobile money interoperability between International Money Transfer Operators (IMTOs) and Digital Financial Services Providers (DFSPs) enhances cross-border transactions by enabling seamless fund transfers across diverse mobile networks and financial platforms. Integrating IMTOs with multiple DFSPs reduces transaction costs, accelerates remittances, and expands financial inclusion for unbanked populations globally.
Correspondent banking
Correspondent banking facilitates cross-border transactions by establishing partnerships between IMTOs and DFSPs, enabling seamless international money transfers through shared correspondent accounts and liquidity management solutions. This collaboration enhances transaction speed, reduces costs, and improves compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations in global remittance corridors.
Virtual account management
Virtual account management streamlines transaction tracking and reconciliation for IMTOs (International Money Transfer Operators) and DFSPs (Digital Financial Services Providers) by enabling real-time allocation of funds to unique virtual accounts linked to individual customers or transactions. This system enhances operational efficiency and compliance, ensuring seamless cross-border payments and digital financial services integration.
Digital wallet integration
Digital wallet integration enhances International Money Transfer Operators (IMTOs) by enabling seamless cross-border transactions and real-time fund accessibility, leveraging APIs from Digital Financial Services Providers (DFSPs) that facilitate secure authentication, compliance, and liquidity management. This collaboration accelerates transaction speed, reduces costs, and expands financial inclusion by bridging traditional money transfers with digital financial ecosystems.
Payment rails
Payment rails for International Money Transfer Operators (IMTOs) emphasize cross-border interoperability and compliance with global financial regulations to facilitate secure and rapid transfers. Digital Financial Services Providers (DFSPs) focus on leveraging digital payment rails such as mobile money platforms, APIs, and blockchain technology to enable seamless, real-time transactions within and across local markets.
Real-time gross settlement (RTGS)
Real-time gross settlement (RTGS) systems facilitate instant, high-value fund transfers, making them essential for International Money Transfer Operators (IMTOs) to ensure immediate liquidity and settlement finality. Digital Financial Services Providers (DFSPs) leverage RTGS to enhance cross-border transaction efficiency, reduce settlement risks, and improve interoperability within digital payment ecosystems.
Licensing regimes
Licensing regimes for International Money Transfer Operators (IMTOs) typically focus on compliance with cross-border remittance regulations, anti-money laundering (AML) standards, and foreign exchange controls, ensuring secure and legally compliant fund transfers. Digital Financial Services Providers (DFSPs) often operate under broader fintech licenses that encompass electronic payment services, digital wallets, and mobile banking, with regulatory frameworks emphasizing consumer protection, data privacy, and interoperability within the national financial ecosystem.
IMTO (International Money Transfer Operator) vs DFSP (Digital Financial Services Provider) Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com