Micro-remittances involve small, frequent money transfers typically sent by individual workers to support family members, emphasizing convenience and low transaction costs. Bulk-remittances refer to large, aggregated transfers made by organizations or institutions on behalf of multiple senders, optimizing efficiency and reducing processing time. Both methods play crucial roles in facilitating international financial flows, with micro-remittances supporting personal needs and bulk-remittances enabling large-scale fund distribution.
Table of Comparison
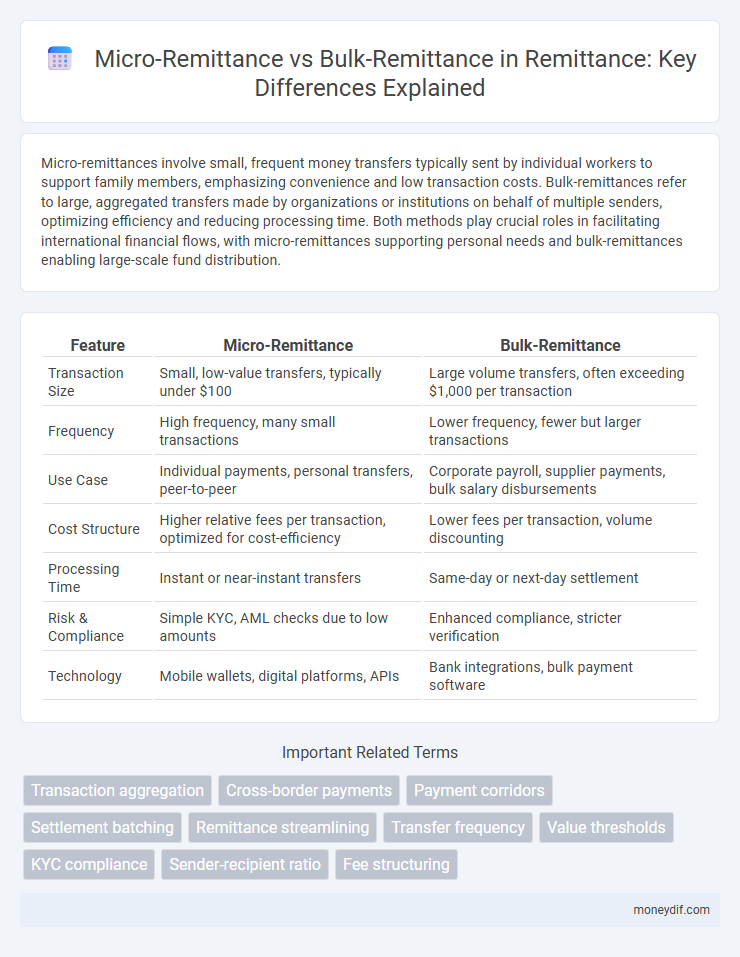
| Feature | Micro-Remittance | Bulk-Remittance |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Size | Small, low-value transfers, typically under $100 | Large volume transfers, often exceeding $1,000 per transaction |
| Frequency | High frequency, many small transactions | Lower frequency, fewer but larger transactions |
| Use Case | Individual payments, personal transfers, peer-to-peer | Corporate payroll, supplier payments, bulk salary disbursements |
| Cost Structure | Higher relative fees per transaction, optimized for cost-efficiency | Lower fees per transaction, volume discounting |
| Processing Time | Instant or near-instant transfers | Same-day or next-day settlement |
| Risk & Compliance | Simple KYC, AML checks due to low amounts | Enhanced compliance, stricter verification |
| Technology | Mobile wallets, digital platforms, APIs | Bank integrations, bulk payment software |
Understanding Micro-Remittance and Bulk-Remittance
Micro-remittance involves small, frequent transfers of money typically sent by individuals to support family expenses or personal needs, often leveraging mobile payment platforms for convenience and low fees. Bulk-remittance refers to large-scale, aggregated money transfers processed by organizations or businesses, enabling efficient disbursement of salaries, benefits, or supplier payments through automated systems. Understanding the distinct operational mechanisms and cost structures of micro-remittance versus bulk-remittance is essential for optimizing financial service delivery and improving cross-border payment efficiencies.
Key Features of Micro-Remittance
Micro-remittance transactions involve sending small amounts of money, typically under $200, catering to frequent, low-value transfers that support individual needs and household expenses. Key features include lower transaction fees, enhanced speed, and easy accessibility through mobile platforms and digital wallets, making them ideal for migrant workers and family support systems. Security protocols and regulatory compliance are tailored to facilitate convenience while minimizing operational costs for both senders and recipients.
Bulk-Remittance: Definition and Use Cases
Bulk remittance refers to the process of transferring large volumes of funds simultaneously, often by businesses, government agencies, or financial institutions to multiple recipients. Common use cases include payroll disbursement, supplier payments, and government social benefit distributions, where efficiency and accuracy in processing numerous transactions are critical. This method reduces operational costs and enhances transparency by consolidating multiple transfers into a single, streamlined transaction.
Transaction Size and Frequency Comparison
Micro-remittances typically involve low-value transactions sent frequently, often daily or weekly, catering to individuals with small payment needs. Bulk remittances consist of larger transaction amounts processed less frequently, usually handled by businesses or organizations for payroll or multiple recipients simultaneously. The distinction in transaction size and frequency directly influences processing costs and method selection in remittance services.
Cost Efficiency: Micro vs Bulk Remittance
Cost efficiency in micro-remittance is often lower due to higher per-transaction fees and administrative overhead, making small transfers more expensive relative to their value. Bulk remittance leverages economies of scale, significantly reducing the average cost per transaction by aggregating multiple payments into a single transfer process. Financial institutions and businesses prefer bulk remittance for large volumes of payments because it enhances cost savings and operational efficiency.
User Demographics and Target Markets
Micro-remittance services primarily cater to individual users such as migrant workers and small-scale entrepreneurs sending low-value transactions frequently to support families in developing countries. Bulk-remittance solutions target corporations, government agencies, and large organizations that require efficient, high-volume transfers for payroll, supplier payments, and social welfare disbursements. Understanding these distinct user demographics and target markets enables financial institutions to tailor their products for optimized transaction costs and enhanced service delivery.
Regulatory Challenges and Compliance
Micro-remittance transactions often face stringent regulatory scrutiny due to their high frequency and volume, requiring robust anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) compliance frameworks to avoid fragmentation risks. Bulk-remittance operations must navigate complex cross-border regulations, necessitating comprehensive reporting mechanisms to ensure adherence to international financial standards and sanctions. Both micro and bulk-remittance services must implement advanced transaction monitoring systems to effectively manage regulatory compliance and mitigate fraud risks.
Technology and Infrastructure Requirements
Micro-remittance systems require lightweight, scalable technology infrastructure capable of handling high transaction volumes with low latency and minimal fees, often leveraging mobile platforms and digital wallets for accessibility. Bulk-remittance solutions demand robust backend systems with enhanced security protocols, batch processing capabilities, and integrations with banking networks to efficiently process large sums and multiple transactions simultaneously. Both models necessitate reliable internet connectivity and regulatory compliance frameworks, but bulk-remittance infrastructures typically involve more complex data management and reconciliation tools.
Security and Risk Management Considerations
Micro-remittance transactions require robust encryption protocols and real-time fraud detection systems to mitigate risks associated with high transaction volumes and smaller amounts, which are often targeted by cybercriminals. Bulk-remittance processes demand stringent compliance checks, multi-factor authentication, and batch transaction monitoring to prevent large-scale fraud and ensure regulatory adherence. Effective security frameworks tailored to each remittance type reduce potential vulnerabilities and enhance overall risk management efficiency.
Future Trends in Micro and Bulk Remittance
Future trends in micro-remittance highlight increased adoption of blockchain technology and digital wallets, facilitating faster, low-cost cross-border transactions for small amounts. Bulk remittance is evolving with AI-driven compliance tools and API integrations that streamline large-scale funds transfer for corporate clients. Both segments are seeing growth in real-time payment systems and enhanced security measures to meet rising demand and regulatory standards.
Important Terms
Transaction aggregation
Transaction aggregation enhances payment efficiency by consolidating multiple micro-remittances into a single bulk-remittance, reducing processing costs and improving settlement speed. This approach leverages aggregated data to optimize reconciliation, minimize transaction fees, and streamline cross-border fund transfers in digital payment ecosystems.
Cross-border payments
Cross-border payments involving micro-remittances typically focus on small-value, frequent transfers with low transaction costs, making them essential for migrant workers sending funds to families. Bulk-remittances, on the other hand, handle large-volume transactions between businesses or institutions, requiring robust compliance and settlement systems to ensure efficiency and security.
Payment corridors
Payment corridors facilitate efficient transfer channels between specific countries or regions, with micro-remittances handling small, frequent transfers often under $200, critical for individual migrants supporting families. Bulk-remittances involve larger, aggregated transactions typically processed by financial institutions or businesses, optimizing costs and speed for high-volume cross-border payments.
Settlement batching
Settlement batching optimizes processing efficiency by grouping multiple micro-remittances into a single transaction, reducing transaction fees and improving reconciliation speed compared to handling numerous individual transfers. Bulk-remittance batching consolidates large payments into one settlement event, streamlining cross-border payments and enhancing liquidity management for financial institutions.
Remittance streamlining
Remittance streamlining enhances transaction efficiency by optimizing micro-remittance for low-value, high-frequency transfers and bulk-remittance for large-scale, batch payments, reducing costs and settlement times. Advanced digital platforms leverage APIs and blockchain technology to seamlessly process both remittance types, improving transparency and compliance across international payment corridors.
Transfer frequency
Transfer frequency significantly differs between micro-remittances and bulk remittances, with micro-remittances typically occurring more frequently but in smaller amounts, facilitating regular individual transactions. Bulk remittances involve less frequent, higher-value transfers often used by businesses or organizations to move funds in large sums efficiently.
Value thresholds
Value thresholds differentiate micro-remittances, typically under $200, from bulk remittances involving larger sums exceeding $1,000 per transaction, impacting regulatory compliance and transaction fees. Financial institutions apply stricter anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements to bulk remittances, while micro-remittance services prioritize low-cost, high-frequency transfers for consumer convenience.
KYC compliance
KYC compliance in micro-remittance transactions focuses on streamlined customer verification to facilitate faster, low-value transfers while mitigating fraud risks with minimal data requirements. In contrast, bulk-remittance processes require comprehensive KYC due to higher transaction volumes and values, necessitating robust identity verification and enhanced due diligence to ensure regulatory adherence and prevent money laundering.
Sender-recipient ratio
The sender-recipient ratio in micro-remittance typically reflects a high number of individual senders transferring small amounts to a single or few recipients, contrasting with bulk-remittance where fewer senders distribute larger sums to multiple recipients simultaneously. This ratio influences transaction costs and processing efficiency, with micro-remittance often incurring higher per-transaction fees due to its fragmented nature compared to the consolidated bulk-remittance system.
Fee structuring
Fee structuring for micro-remittance typically involves higher relative costs due to fixed transactional fees impacting small transfer amounts, whereas bulk-remittance benefits from volume discounts and lower per-unit fees, optimizing cost efficiency for large-sum transfers. Payment providers use tiered pricing models and negotiate fees based on transaction size, channel, and remittance corridors to balance profitability with customer affordability.
micro-remittance vs bulk-remittance Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com