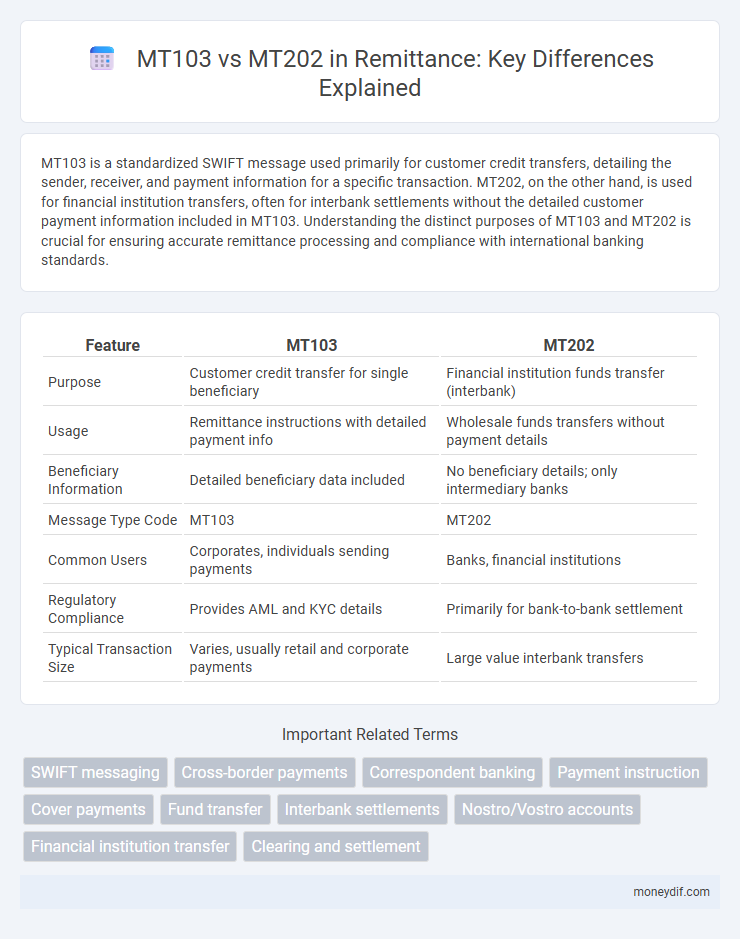
MT103 is a standardized SWIFT message used primarily for customer credit transfers, detailing the sender, receiver, and payment information for a specific transaction. MT202, on the other hand, is used for financial institution transfers, often for interbank settlements without the detailed customer payment information included in MT103. Understanding the distinct purposes of MT103 and MT202 is crucial for ensuring accurate remittance processing and compliance with international banking standards.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | MT103 | MT202 |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Customer credit transfer for single beneficiary | Financial institution funds transfer (interbank) |
| Usage | Remittance instructions with detailed payment info | Wholesale funds transfers without payment details |
| Beneficiary Information | Detailed beneficiary data included | No beneficiary details; only intermediary banks |
| Message Type Code | MT103 | MT202 |
| Common Users | Corporates, individuals sending payments | Banks, financial institutions |
| Regulatory Compliance | Provides AML and KYC details | Primarily for bank-to-bank settlement |
| Typical Transaction Size | Varies, usually retail and corporate payments | Large value interbank transfers |
Understanding MT103 and MT202: Key Differences
MT103 and MT202 are SWIFT message types used in cross-border remittances, with MT103 serving as a customer credit transfer instruction that details the payment from the sender to the beneficiary. MT202 is primarily utilized for bank-to-bank financial institution transfers, often involving the settlement of funds between correspondent banks without revealing customer details. Understanding these key differences aids in selecting the correct message type for accurate processing and compliance in international wire transfers.
Overview of SWIFT Message Types in Remittance
MT103 and MT202 are essential SWIFT message types used in international remittances, with MT103 specifically designed for single customer credit transfers, providing detailed payment instructions and beneficiary information. MT202 is used for interbank transfers, facilitating the movement of funds between financial institutions without including detailed customer data. Understanding the distinction between MT103 and MT202 is critical for efficient payment processing and compliance in cross-border transactions.
MT103 Explained: Purpose and Structure
MT103 is a standardized SWIFT message used for customer credit transfers, providing detailed information about the sender, beneficiary, and payment instructions to ensure transparency and traceability. Its structured format includes fields such as sender's reference, value date, currency, amount, ordering customer, and beneficiary customer, facilitating precise and secure international remittances. Unlike MT202, which is used for bank-to-bank funds transfers without extensive customer details, MT103 serves as a comprehensive document for tracking individual cross-border payments.
MT202 Explained: Purpose and Structure
MT202 is a SWIFT message type used primarily for financial institution transfers, facilitating the movement of funds between banks. Its structure includes fields for ordering institution, beneficiary institution, and details of the transfer, enabling efficient processing of interbank payments. Unlike MT103, which is customer-oriented and used for single customer transactions, MT202 handles multiple payments within one message and supports bank-to-bank settlements.
MT103 vs. MT202: Use Cases in International Payments
MT103 is a detailed SWIFT payment message primarily used for customer credit transfers in international remittances, offering full transaction transparency and beneficiary information. MT202 is designed for financial institution transfers, typically used by banks to move funds between themselves without detailed payment information. MT103 suits scenarios requiring payment traceability and origin details, while MT202 is optimal for interbank settlement and treasury operations in cross-border payments.
Security Features: Comparing MT103 and MT202
MT103 and MT202 are SWIFT message types used in international remittances, with MT103 providing detailed transaction instructions and beneficiary information, enhancing traceability and compliance. MT103 incorporates robust security features including encryption and authentication to ensure the integrity of payment data, facilitating safer single-customer credit transfers. MT202 is designed for bank-to-bank financial institution transfers, emphasizing secure, encrypted financial messaging while omitting beneficiary details to reduce data exposure in interbank settlements.
MT103 vs. MT202: Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
MT103 and MT202 messages serve distinct functions in remittance processes, with MT103 used for customer credit transfers and MT202 for bank-to-bank transactions. Compliance regulations require stringent monitoring of MT103 transactions to ensure transparency and traceability of funds, reducing risks of money laundering. MT202 messages, while primarily for interbank settlements, must also comply with regulatory standards, emphasizing the importance of accurate beneficiary details and adherence to anti-terrorism financing laws.
Processing Times: MT103 vs. MT202
MT103 transactions typically have longer processing times due to detailed payment information and compliance checks, often taking 1 to 3 business days for full settlement. MT202 messages are designed for faster interbank transfers, generally processed within hours, as they carry less specific payment data and primarily facilitate bank-to-bank fund movement. The difference in processing speed reflects the complexity and purpose of each SWIFT message type in remittance operations.
Fees and Cost Implications: MT103 vs. MT202
MT103 is a SWIFT message used for customer credit transfers, typically incurring explicit fees disclosed upfront, as it includes detailed payment information allowing banks to charge correspondingly for processing. MT202, employed for financial institution transfers or cover payments, usually results in lower fees because it handles bulk transactions without detailed customer data, reducing processing complexity and cost. Choosing between MT103 and MT202 significantly impacts the overall remittance cost, with MT103 being costlier due to transparency and traceability requirements, while MT202 offers cost efficiency for interbank settlements.
Choosing the Right SWIFT Message for Your Remittance Needs
MT103 and MT202 are crucial SWIFT messages used for international remittance, with MT103 designed for single customer credit transfers and MT202 for bank-to-bank financial institution transfers. Selecting MT103 ensures transparency and detailed beneficiary information for cross-border payments, while MT202 facilitates bulk or interbank funds movement without individual remittance details. Understanding your payment's nature and regulatory requirements helps determine whether MT103's traceable customer payment or MT202's streamlined institutional transfer suits your remittance needs.
Important Terms
SWIFT messaging
SWIFT messaging includes MT103 and MT202 messages, where MT103 is a customer credit transfer used for single customer payments, detailing remitter and beneficiary information, while MT202 is a financial institution transfer used for bank-to-bank fund movements without customer details. MT103 ensures transparency and compliance in cross-border payments, whereas MT202 supports interbank settlements and liquidity management within correspondent banking networks.
Cross-border payments
Cross-border payments often utilize MT103 for detailed, customer-specific transaction information, enabling transparency and compliance with regulatory requirements. Conversely, MT202 is employed for bank-to-bank financial institution transfers, focusing on settlement instructions without detailed beneficiary data, streamlining the clearing process.
Correspondent banking
Correspondent banking facilitates international wire transfers with MT103 used for detailed customer credit transfers and MT202 for bank-to-bank financial institution transfers. MT103 messages include comprehensive payment information to ensure transparency and compliance, whereas MT202 messages primarily handle settlement instructions between correspondent banks.
Payment instruction
MT103 is a standardized SWIFT message used primarily for customer credit transfers, providing detailed payment instructions and beneficiary information for international wire transfers. MT202 serves as a financial institution transfer message, facilitating the movement of funds between banks without including beneficiary details, often used to settle multiple MT103 transactions or bank-to-bank payments.
Cover payments
MT103 is a standardized SWIFT message used for single customer credit transfers providing detailed payment information, while MT202 is designed for financial institution transfers without detailed beneficiary data. Cover payments utilize MT103 to transmit payment instructions to the beneficiary bank and MT202 to transfer funds between correspondent banks, ensuring transparency and efficient settlement in cross-border transactions.
Fund transfer
MT103 is a standardized SWIFT message used for single customer credit transfers, providing detailed payment instructions and beneficiary information, whereas MT202 is primarily employed for financial institution-to-institution fund transfers without customer details. The MT103 enhances transparency and traceability for end-to-end payment tracking, while MT202 facilitates bulk or bank-to-bank settlement processes within correspondent banking networks.
Interbank settlements
Interbank settlements involving MT103 and MT202 messages facilitate secure and standardized fund transfers between financial institutions, where MT103 is used for customer credit transfers with detailed payment information, and MT202 serves for bank-to-bank transfers primarily to settle financial institutions' own funds or cover the underlying MT103 transaction. Understanding the distinction between MT103 and MT202 is crucial for accurate processing, regulatory compliance, and efficient reconciliation in international banking transactions.
Nostro/Vostro accounts
Nostro and Vostro accounts represent mirror accounts maintained by two banks to facilitate cross-border fund transfers, where MT103 is a customer credit transfer message used to instruct payments directly to the beneficiary's bank, and MT202 is a bank-to-bank transfer message often used to move funds between correspondent banks. MT103 ensures detailed payment information for reconciliation in Nostro accounts, whereas MT202 handles settlement instructions without individual customer details, impacting the tracking and balancing of Vostro accounts.
Financial institution transfer
MT103 is a standardized SWIFT message used by financial institutions for detailed customer credit transfers, providing comprehensive payment information and beneficiary details to ensure transparency and traceability. MT202, on the other hand, is used for bank-to-bank financial institution transfers, focusing on the settlement of funds between correspondent banks without including extensive beneficiary data.
Clearing and settlement
Clearing and settlement processes for MT103 involve the detailed confirmation of single customer credit transfers, allowing precise tracking and reconciliation of individual payments, while MT202 is primarily used for financial institution-to-institution transfers. MT103 messages facilitate direct settlement instructions in correspondent banking systems, whereas MT202 supports bulk settlement operations, impacting the speed and transparency of interbank clearing.
MT103 vs MT202 Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com