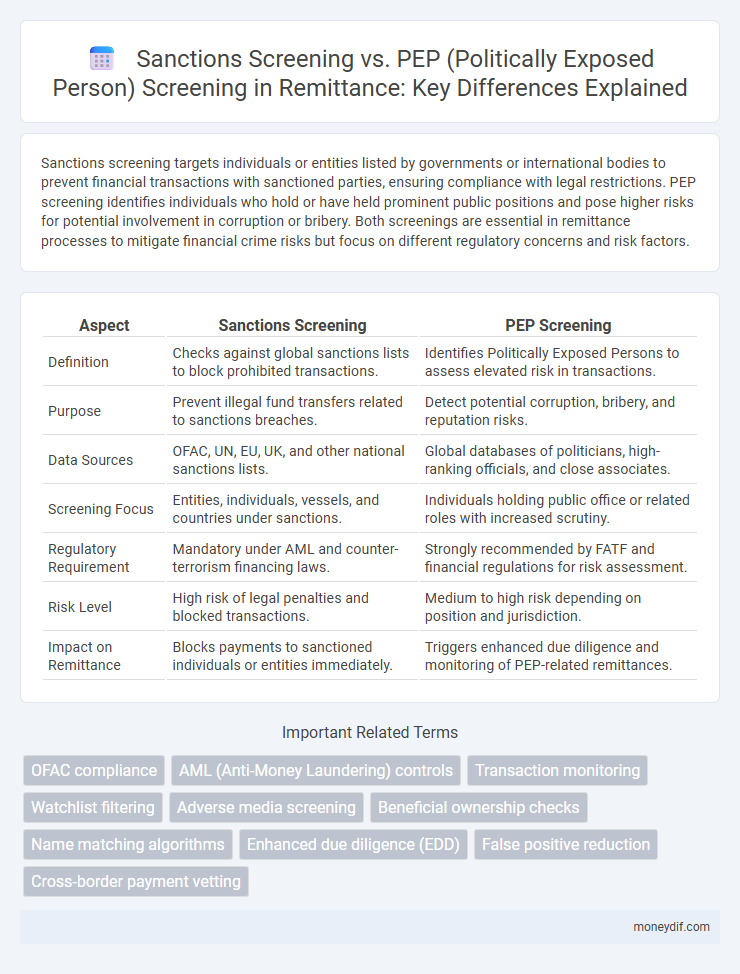
Sanctions screening targets individuals or entities listed by governments or international bodies to prevent financial transactions with sanctioned parties, ensuring compliance with legal restrictions. PEP screening identifies individuals who hold or have held prominent public positions and pose higher risks for potential involvement in corruption or bribery. Both screenings are essential in remittance processes to mitigate financial crime risks but focus on different regulatory concerns and risk factors.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sanctions Screening | PEP Screening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Checks against global sanctions lists to block prohibited transactions. | Identifies Politically Exposed Persons to assess elevated risk in transactions. |
| Purpose | Prevent illegal fund transfers related to sanctions breaches. | Detect potential corruption, bribery, and reputation risks. |
| Data Sources | OFAC, UN, EU, UK, and other national sanctions lists. | Global databases of politicians, high-ranking officials, and close associates. |
| Screening Focus | Entities, individuals, vessels, and countries under sanctions. | Individuals holding public office or related roles with increased scrutiny. |
| Regulatory Requirement | Mandatory under AML and counter-terrorism financing laws. | Strongly recommended by FATF and financial regulations for risk assessment. |
| Risk Level | High risk of legal penalties and blocked transactions. | Medium to high risk depending on position and jurisdiction. |
| Impact on Remittance | Blocks payments to sanctioned individuals or entities immediately. | Triggers enhanced due diligence and monitoring of PEP-related remittances. |
Understanding the Differences: Sanctions Screening vs. PEP Screening
Sanctions screening involves verifying individuals or entities against global sanctions lists to prevent transactions with banned or restricted parties, ensuring compliance with international regulations. PEP screening focuses on identifying individuals holding prominent public positions who may pose higher risks of corruption or money laundering due to their influence and access to government resources. While sanctions screening targets legally prohibited recipients, PEP screening concentrates on risk assessment based on political exposure and the potential for illicit activities.
Key Definitions: What is Sanctions Screening? What is PEP Screening?
Sanctions screening is the process of identifying and blocking transactions involving individuals, entities, or countries subject to government-imposed restrictions or embargoes to prevent illegal financial activities. PEP screening involves monitoring transactions and clients who are politically exposed persons, such as government officials or their close associates, due to the higher risk of corruption or bribery. Both screenings are critical for compliance in remittance services to mitigate financial crime risks and ensure regulatory adherence.
Regulatory Requirements for Remittance Providers
Sanctions screening requires remittance providers to identify and block transactions involving individuals or entities subject to international sanctions lists such as OFAC, UN, or EU sanctions to ensure compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) laws. PEP screening mandates enhanced due diligence for customers holding prominent public positions or their close associates due to their increased risk of involvement in corruption or bribery, aligning with Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations. Both screening processes are integral to regulatory frameworks, ensuring remittance providers mitigate legal risks and uphold global financial transparency standards.
Why Both Sanctions and PEP Screening Matter in Remittance
Sanctions screening prevents dealings with individuals or entities subject to international restrictions, ensuring compliance and avoiding legal penalties in remittance transactions. PEP screening identifies politically exposed persons who may pose higher risks of corruption or money laundering, protecting financial institutions from reputational and regulatory harm. Employing both screenings enhances risk management by addressing distinct but complementary threats in cross-border money transfers.
Risk Assessment: Sanctions Lists vs. PEP Lists
Risk assessment in remittance relies heavily on comparing sanctions lists and PEP lists to identify high-risk entities. Sanctions screening targets individuals and organizations restricted by governments due to legal or security concerns, while PEP screening focuses on politically exposed persons who pose potential corruption or bribery risks. Effective compliance programs integrate both screenings to mitigate financial crime risks and ensure regulatory adherence.
Technical Approaches: Comparing Screening Processes
Sanctions screening leverages real-time matching algorithms against updated sanction lists from regulatory bodies like OFAC and UN, ensuring immediate identification of restricted entities. PEP screening employs risk-based profiling and dynamic databases that classify individuals based on political exposure, integrating AI-driven pattern recognition to detect indirect associations. Both processes utilize advanced API integrations and machine learning models, but sanctions screening prioritizes exact list matches while PEP screening focuses on complex relational intelligence and behavior analysis.
Common Challenges in Sanctions and PEP Screening
Sanctions screening and PEP screening in remittance processing face common challenges such as false positives, which increase compliance costs and delay transactions. Both require up-to-date, accurate data sources to effectively identify sanctioned individuals and politically exposed persons, ensuring regulatory adherence and risk mitigation. The complexity of global regulations and the evolving nature of sanctions lists demand continuous system updates and staff training to maintain screening effectiveness.
Best Practices for Compliance in Remittance Services
Sanctions screening and PEP screening are critical components of compliance in remittance services, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and preventing financial crime. Best practices include employing advanced risk-based screening technologies that continuously update sanction lists and PEP databases, combined with thorough customer due diligence and ongoing transaction monitoring. Implementing automated alerts for high-risk transactions and maintaining comprehensive audit trails further strengthen compliance frameworks and reduce exposure to regulatory penalties.
Real-World Case Studies: Failures and Penalties
Sanctions screening failures have led to multimillion-dollar fines and reputational damage for financial institutions, as seen in the 2019 case where a major bank processed transactions tied to sanctioned entities, resulting in a $1.3 billion penalty. In comparison, inadequate PEP screening has enabled corruption and money laundering, exemplified by the 2020 scandal involving a global bank that overlooked politically exposed clients, triggering regulatory sanctions and operational overhauls. These real-world cases underscore the critical need for robust, integrated sanctions and PEP screening systems to mitigate compliance risks in remittance transactions.
Future Trends: Innovations in Screening for Remittances
Innovations in screening for remittances are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance sanctions and PEP screening accuracy, reducing false positives and improving compliance efficiency. Blockchain technology is being integrated to create immutable transaction records, facilitating real-time monitoring and faster identification of suspicious activities. Future trends emphasize automated, risk-based screening models that adapt dynamically to evolving regulatory requirements and emerging financial crime patterns.
Important Terms
OFAC compliance
OFAC compliance primarily focuses on sanctions screening to prevent transactions with sanctioned entities, while PEP screening identifies individuals with heightened risk due to their political positions, requiring enhanced due diligence. Effective risk management integrates both sanctions screening and PEP screening to ensure comprehensive adherence to anti-money laundering (AML) regulations and mitigate financial crime risks.
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) controls
Effective AML controls integrate sanctions screening to block transactions with restricted entities and PEP screening to identify high-risk individuals for enhanced due diligence.
Transaction monitoring
Transaction monitoring integrates real-time analysis to detect suspicious activities by matching transaction data against sanctions lists and identifying Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) to mitigate risks of financial crimes. Sanctions screening focuses on blocking transactions involving sanctioned entities or countries, while PEP screening assesses the risk of transactions linked to individuals with prominent public functions susceptible to corruption or money laundering.
Watchlist filtering
Watchlist filtering distinguishes sanctions screening by targeting individuals and entities subject to legal restrictions, while PEP screening focuses on identifying politically exposed persons to assess risks of corruption and bribery.
Adverse media screening
Adverse media screening detects negative news linked to individuals or entities, complementing sanctions screening that targets legally restricted parties and PEP screening focused on identifying politically exposed persons for enhanced risk assessment.
Beneficial ownership checks
Beneficial ownership checks enhance sanctions screening and PEP screening by accurately identifying ultimate owners, reducing risks of illicit activities and regulatory non-compliance.
Name matching algorithms
Name matching algorithms for sanctions screening prioritize exact and fuzzy matching against global watchlists, while those for PEP screening emphasize contextual analysis to identify politically exposed individuals with name variations and aliases.
Enhanced due diligence (EDD)
Enhanced due diligence (EDD) involves deeper risk assessment and verification processes for sanctions screening compared to PEP screening, focusing on identifying individuals or entities subject to international sanctions lists to prevent financial crimes and regulatory breaches.
False positive reduction
False positive reduction in sanctions screening versus PEP screening improves accuracy by refining algorithms to distinguish legitimate alerts from genuine risks based on updated sanction lists and PEP databases.
Cross-border payment vetting
Cross-border payment vetting integrates sanctions screening to block transactions involving prohibited entities while employing PEP screening to identify and mitigate risks associated with politically exposed persons.
sanctions screening vs PEP (Politically Exposed Person) screening Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com