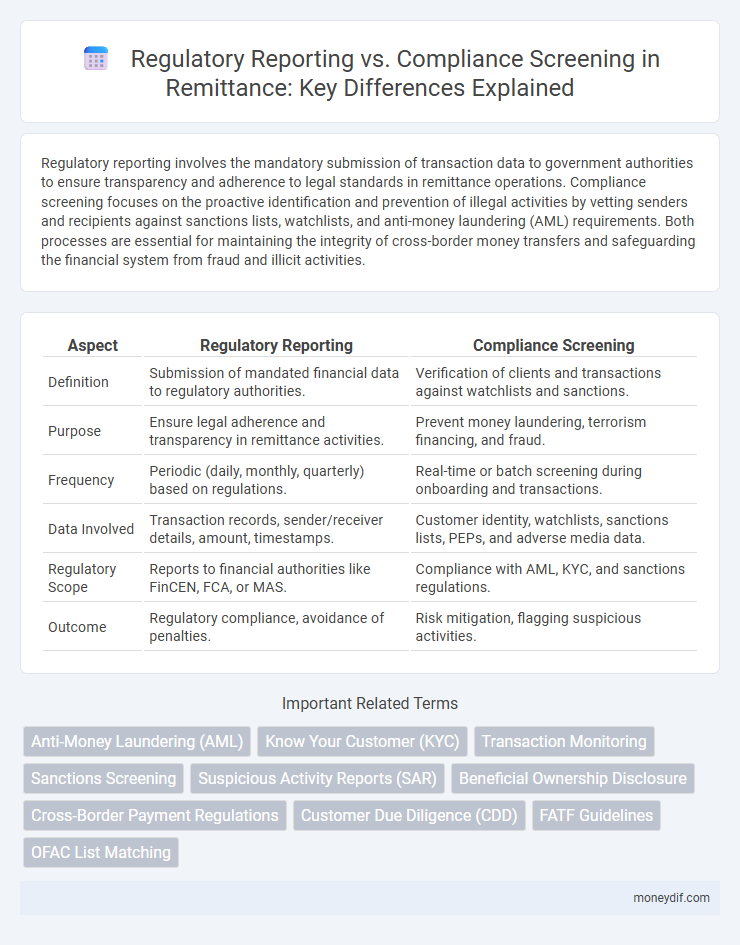
Regulatory reporting involves the mandatory submission of transaction data to government authorities to ensure transparency and adherence to legal standards in remittance operations. Compliance screening focuses on the proactive identification and prevention of illegal activities by vetting senders and recipients against sanctions lists, watchlists, and anti-money laundering (AML) requirements. Both processes are essential for maintaining the integrity of cross-border money transfers and safeguarding the financial system from fraud and illicit activities.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Regulatory Reporting | Compliance Screening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Submission of mandated financial data to regulatory authorities. | Verification of clients and transactions against watchlists and sanctions. |
| Purpose | Ensure legal adherence and transparency in remittance activities. | Prevent money laundering, terrorism financing, and fraud. |
| Frequency | Periodic (daily, monthly, quarterly) based on regulations. | Real-time or batch screening during onboarding and transactions. |
| Data Involved | Transaction records, sender/receiver details, amount, timestamps. | Customer identity, watchlists, sanctions lists, PEPs, and adverse media data. |
| Regulatory Scope | Reports to financial authorities like FinCEN, FCA, or MAS. | Compliance with AML, KYC, and sanctions regulations. |
| Outcome | Regulatory compliance, avoidance of penalties. | Risk mitigation, flagging suspicious activities. |
Understanding Regulatory Reporting in Remittance
Regulatory reporting in remittance involves the systematic submission of transaction data to financial authorities to ensure transparency and prevent illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing. This process requires remittance service providers to accurately capture and report customer information, transaction amounts, and correspondent details within specified timeframes dictated by regulatory frameworks like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) guidelines. Effective regulatory reporting enhances oversight, supports risk management, and maintains the integrity of the global financial system.
Compliance Screening: Definition and Role in Remittance
Compliance screening in remittance involves the systematic verification of transactions and customer information against regulatory databases to prevent money laundering, fraud, and terrorist financing. It plays a crucial role in identifying high-risk individuals and entities by matching data against sanctions lists, politically exposed persons (PEPs), and adverse media reports. Effective compliance screening ensures adherence to anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) regulations, safeguarding financial institutions and the remittance ecosystem.
Key Differences: Regulatory Reporting vs Compliance Screening
Regulatory reporting involves the systematic submission of transaction data to financial authorities to ensure transparency and adherence to legal obligations. Compliance screening focuses on evaluating remittance parties against sanctions lists, watchlists, and risk indicators to prevent money laundering and terrorism financing. Key differences include regulatory reporting's emphasis on data disclosure for oversight versus compliance screening's proactive risk assessment and prevention measures.
Regulatory Frameworks Shaping Remittance Reporting
Regulatory reporting in remittance is governed by frameworks such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) directives that mandate detailed transaction disclosures to monitor and prevent illicit financial flows. Compliance screening focuses on real-time assessments against sanctions lists, politically exposed persons (PEP) databases, and fraud indicators to ensure adherence to these regulatory standards. Together, these frameworks shape remittance reporting by enforcing transparency, risk mitigation, and regulatory accountability within cross-border money transfer operations.
Importance of Compliance Screening for Anti-Money Laundering
Compliance screening plays a critical role in anti-money laundering (AML) by identifying and preventing illicit transactions before they occur, ensuring that remittance service providers do not facilitate money laundering activities. Unlike regulatory reporting, which involves submitting transaction data to authorities after the fact, compliance screening actively monitors customers against watchlists, sanctions lists, and politically exposed persons (PEP) databases in real time. Effective compliance screening reduces risks of legal penalties, safeguards financial institutions' reputations, and enhances overall AML program effectiveness within the remittance industry.
Common Challenges in Regulatory Reporting for Remittance Providers
Regulatory reporting for remittance providers often faces challenges such as data accuracy, timeliness, and consistency across multiple jurisdictions with varying regulatory requirements. Ensuring comprehensive data collection and error-free submission is complicated by the need to integrate diverse transaction systems while adhering to stringent anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) standards. Compliance screening adds complexity by requiring continuous risk assessment to identify suspicious transactions and entities, increasing the operational burden on remittance firms.
Best Practices for Effective Compliance Screening
Effective compliance screening in remittance requires integrating real-time transaction monitoring with comprehensive customer risk profiling to detect suspicious activities promptly. Leveraging advanced AI-driven tools enhances accuracy in identifying potential matches against watchlists, reducing false positives. Regularly updating screening criteria and training staff on evolving regulations ensures alignment with regulatory reporting standards while maintaining operational efficiency.
Technological Solutions for Regulatory Reporting and Compliance Screening
Technological solutions for regulatory reporting and compliance screening in remittance include advanced AI-powered platforms that automate transaction monitoring and real-time data analysis to detect suspicious activities. These systems integrate machine learning algorithms to enhance accuracy in identifying regulatory breaches and streamline the submission of comprehensive reports to financial authorities. Blockchain technology also supports transparency and traceability, ensuring compliance with global anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) regulations.
Impact of Non-Compliance: Risks and Penalties
Non-compliance with regulatory reporting and compliance screening in remittance services exposes businesses to significant risks including financial penalties, legal sanctions, and reputational damage. Failure to adhere to anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) regulations can result in hefty fines imposed by regulatory authorities such as the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) or the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). Persistent breaches may lead to suspension of remittance licenses, increased scrutiny, and loss of customer trust, impacting operational viability and market competitiveness.
Future Trends in Regulatory Reporting and Compliance Screening for Remittance
Future trends in regulatory reporting for remittance emphasize advanced data analytics and real-time transaction monitoring to enhance accuracy and timeliness. Compliance screening leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect suspicious activities more effectively, reducing false positives and improving risk management. Integration of blockchain technology is expected to increase transparency and traceability, further strengthening regulatory alignment and operational efficiency.
Important Terms
Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulatory reporting focuses on fulfilling mandatory disclosures to authorities, ensuring transparency in financial transactions and aiding in the detection of illicit activities. Compliance screening involves continuous monitoring and evaluation of customers, transactions, and counterparties against sanctions lists and risk profiles to proactively prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
Know Your Customer (KYC)
Know Your Customer (KYC) processes are essential for enhancing Regulatory Reporting accuracy by verifying client identities and ensuring transparency in financial transactions. Compliance Screening supports KYC by continuously monitoring clients against sanctions lists, politically exposed persons (PEP) databases, and adverse media to mitigate risks and uphold regulatory standards.
Transaction Monitoring
Transaction monitoring continuously analyzes financial activities to detect suspicious patterns aligned with regulatory reporting requirements, ensuring timely identification of potential money laundering or fraud. Compliance screening complements this by verifying customer identities and transactions against watchlists and sanctions databases, reinforcing adherence to anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) regulations.
Sanctions Screening
Sanctions screening involves identifying individuals or entities on regulatory watchlists to prevent prohibited transactions, while regulatory reporting focuses on the accurate submission of compliance data to authorities. Effective compliance screening ensures adherence to sanctions laws, reducing risks of fines and reputational damage through continuous monitoring and timely reporting.
Suspicious Activity Reports (SAR)
Suspicious Activity Reports (SAR) are critical documents filed to regulatory bodies to report potential money laundering or fraud, serving a key role in regulatory reporting frameworks. Compliance screening involves the ongoing process of monitoring transactions and customer behavior to detect suspicious activities, enabling timely SAR filings and adherence to anti-money laundering (AML) regulations.
Beneficial Ownership Disclosure
Beneficial ownership disclosure enhances transparency by identifying individuals with significant control over entities, crucial for regulatory reporting frameworks mandated by financial authorities. Effective compliance screening leverages this disclosure data to detect risks such as money laundering or tax evasion, ensuring adherence to anti-financial crime regulations and mitigating legal liabilities.
Cross-Border Payment Regulations
Cross-border payment regulations require comprehensive regulatory reporting to ensure transparency and adherence to international financial laws, while compliance screening involves real-time monitoring of transactions against global sanctions lists and anti-money laundering (AML) standards. Effective integration of both processes mitigates risks related to fraud, terrorism financing, and regulatory penalties, enhancing security and trust in cross-border financial systems.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) involves verifying customer identities and assessing risk to ensure compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, directly impacting both regulatory reporting and compliance screening processes. While regulatory reporting focuses on submitting accurate and timely Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) and Currency Transaction Reports (CTRs) to authorities, compliance screening continuously monitors customers against sanctions lists and adverse media to prevent illicit transactions.
FATF Guidelines
FATF guidelines emphasize the critical distinction between regulatory reporting, which involves the mandatory submission of suspicious transaction reports (STRs) to authorities, and compliance screening, focused on ongoing monitoring of customers against sanctions lists and politically exposed persons (PEP) databases. Effective implementation of both processes ensures adherence to anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) standards, minimizing financial crime risks and enhancing transparency in financial institutions.
OFAC List Matching
OFAC List Matching ensures regulatory reporting accuracy by identifying sanctioned entities to prevent unlawful transactions and maintain compliance with U.S. Treasury regulations. Compliance screening leverages real-time OFAC data to detect high-risk individuals and organizations, minimizing financial penalties and reputational damage for institutions.
Regulatory Reporting vs Compliance Screening Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com