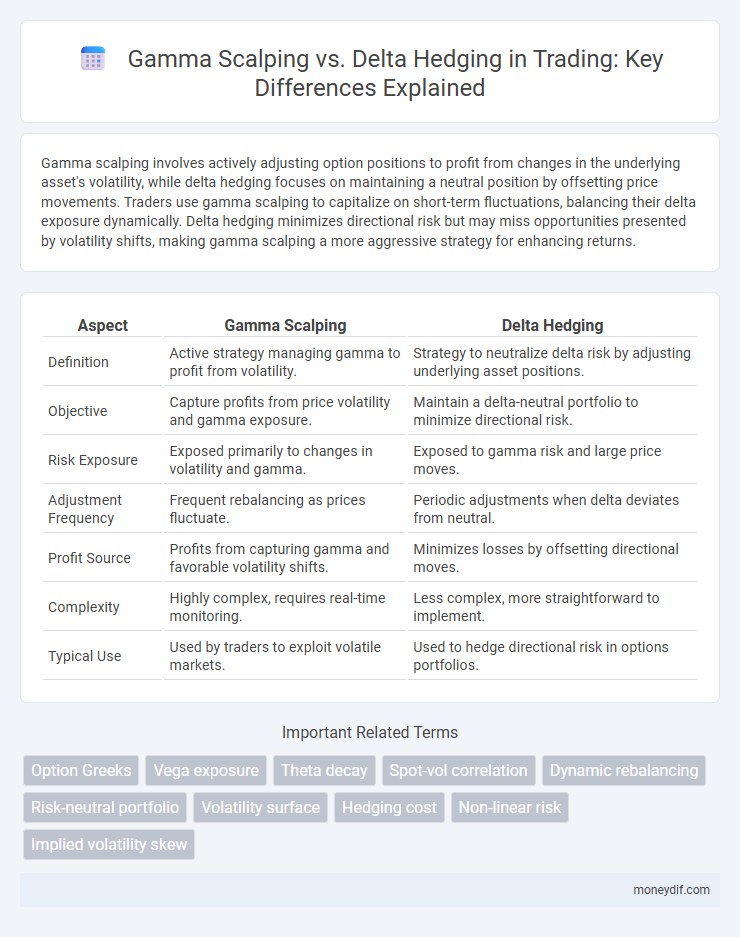
Gamma scalping involves actively adjusting option positions to profit from changes in the underlying asset's volatility, while delta hedging focuses on maintaining a neutral position by offsetting price movements. Traders use gamma scalping to capitalize on short-term fluctuations, balancing their delta exposure dynamically. Delta hedging minimizes directional risk but may miss opportunities presented by volatility shifts, making gamma scalping a more aggressive strategy for enhancing returns.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Gamma Scalping | Delta Hedging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active strategy managing gamma to profit from volatility. | Strategy to neutralize delta risk by adjusting underlying asset positions. |
| Objective | Capture profits from price volatility and gamma exposure. | Maintain a delta-neutral portfolio to minimize directional risk. |
| Risk Exposure | Exposed primarily to changes in volatility and gamma. | Exposed to gamma risk and large price moves. |
| Adjustment Frequency | Frequent rebalancing as prices fluctuate. | Periodic adjustments when delta deviates from neutral. |
| Profit Source | Profits from capturing gamma and favorable volatility shifts. | Minimizes losses by offsetting directional moves. |
| Complexity | Highly complex, requires real-time monitoring. | Less complex, more straightforward to implement. |
| Typical Use | Used by traders to exploit volatile markets. | Used to hedge directional risk in options portfolios. |
Introduction to Gamma Scalping and Delta Hedging
Gamma scalping involves actively managing options positions to capture profits from changes in the underlying asset's price volatility by continuously adjusting delta exposure. Delta hedging focuses on neutralizing portfolio risk by maintaining a delta-neutral position, frequently rebalancing as the underlying asset price moves. Both strategies aim to reduce directional risk, but gamma scalping capitalizes on volatility, while delta hedging primarily limits exposure to price fluctuations.
Understanding Options Greeks: Gamma vs Delta
Gamma represents the rate of change of delta in response to underlying asset price movements, providing insight into the curvature of an option's value. Delta measures an option's sensitivity to price changes of the underlying asset, indicating directional exposure. Traders utilize gamma scalping to dynamically adjust positions as delta shifts, whereas delta hedging aims to maintain a neutral delta position to manage risk.
Core Principles of Gamma Scalping
Gamma scalping involves continuously adjusting the delta hedge to capture profits from fluctuations in the underlying asset's price, optimizing exposure to gamma, which measures the rate of change of delta. This strategy capitalizes on volatility by buying low and selling high within the price movements, maintaining a neutral delta position to minimize directional risk. Effective gamma scalping requires precise monitoring of option Greeks and dynamic rebalancing to exploit price swings while limiting losses from adverse movements.
Fundamentals of Delta Hedging Strategies
Delta hedging strategies involve continuously adjusting a portfolio's position in the underlying asset to maintain a delta-neutral stance, minimizing directional risk from price movements. These fundamentals require precise calculation of delta, the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset, enabling traders to offset potential losses caused by unfavorable price shifts. Effective delta hedging leverages dynamic rebalancing and transaction cost management to optimize risk mitigation in volatile markets.
Key Differences Between Gamma Scalping and Delta Hedging
Gamma scalping actively exploits changes in an option's gamma to adjust the hedge ratio and capture profits from volatility, whereas delta hedging focuses on maintaining a neutral delta position to minimize directional risk. Gamma scalping requires continuous rebalancing to benefit from price movements, while delta hedging primarily aims to stabilize the portfolio's exposure to price fluctuations. The key difference lies in gamma scalping's profit-driven adjustments versus delta hedging's risk management objective.
Risk Management in Gamma Scalping vs Delta Hedging
Gamma scalping involves dynamic adjustments to a portfolio's delta to exploit changes in an option's gamma, effectively managing risk through frequent rebalancing to maintain neutrality. Delta hedging focuses on maintaining a delta-neutral position, reducing directional risk but potentially exposing the portfolio to gamma risk during large price movements. Effective risk management in gamma scalping requires continuous monitoring of both delta and gamma exposure, whereas delta hedging prioritizes mitigating price direction risk but can lead to higher sensitivity to volatility changes.
Profitability and Costs: Gamma Scalping vs Delta Hedging
Gamma scalping often yields higher profitability by exploiting volatility fluctuations, allowing traders to capture gains from directional market moves, whereas delta hedging primarily minimizes risk exposure but incurs continuous adjustment costs. The frequent rebalancing required in delta hedging increases transaction fees and slippage, reducing net returns compared to gamma scalping's opportunistic trading style. Efficient gamma scalping demands sophisticated models and timely execution to maximize profit potential while controlling hedging expenses.
Practical Applications in Volatile Markets
Gamma scalping involves adjusting the hedge dynamically to profit from price volatility by capturing gains from fluctuations in the underlying asset, making it highly effective in volatile markets. Delta hedging focuses on neutralizing directional risk by maintaining a delta-neutral position but requires frequent rebalancing in rapidly changing environments. Traders prefer gamma scalping in volatile markets due to its potential to generate profits from price swings, while delta hedging primarily serves risk management purposes.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Hedging
Gamma scalping employs rapid adjustments in option positions to capitalize on underlying price volatility, utilizing Greeks such as gamma and delta for precise risk management. Delta hedging involves creating a neutral position by offsetting delta exposure through underlying asset trades, often executed using dynamic rebalancing tools and real-time analytics platforms. Advanced software solutions integrate algorithmic strategies and volatility models to optimize hedging effectiveness, minimizing directional risk while maximizing profit potential.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Factors to Consider
Choosing between gamma scalping and delta hedging depends on market volatility, trading goals, and risk tolerance. Gamma scalping is effective in highly volatile markets for capitalizing on rapid price movements, while delta hedging suits traders aiming to minimize directional risk in more stable conditions. Evaluating transaction costs, portfolio size, and the frequency of adjustments is essential for optimizing risk management and maximizing returns.
Important Terms
Option Greeks
Option Greeks measure sensitivities of option prices to underlying variables, with gamma representing the rate of change of delta relative to the underlying asset price. Gamma scalping involves frequently adjusting delta hedges to profit from fluctuations in the underlying asset, while delta hedging focuses on maintaining a delta-neutral position to minimize directional risk without actively exploiting gamma-induced gains.
Vega exposure
Vega exposure measures sensitivity to volatility changes in options portfolios, highlighting the impact of implied volatility shifts on option pricing. Gamma scalping actively manages delta by adjusting positions as the underlying asset price fluctuates, enhancing profit potential from volatility, whereas delta hedging maintains a neutral delta to minimize directional risk without directly addressing vega exposure.
Theta decay
Theta decay measures the time-based erosion of an option's value, significantly impacting strategies like gamma scalping and delta hedging, where frequent adjustments counteract this loss. Gamma scalping exploits high gamma to profit from price volatility despite theta decay, while delta hedging focuses on neutralizing directional risk, often experiencing gradual value decline as theta erodes premium over time.
Spot-vol correlation
Spot-vol correlation significantly impacts the effectiveness of gamma scalping by influencing the dynamic adjustments required in delta hedging strategies; negative correlation typically enhances gamma scalping profitability as price drops coincide with volatility spikes. In delta hedging, managing exposure becomes more complex under varying spot-vol relationships, necessitating continuous recalibration to optimize risk-neutral portfolio performance.
Dynamic rebalancing
Dynamic rebalancing in gamma scalping involves frequently adjusting the hedge to capture the benefits of changing gamma, whereas delta hedging focuses on neutralizing the delta exposure to maintain a risk-neutral position. Gamma scalping leverages the curvature of the option's price to profit from volatility, while delta hedging primarily reduces directional risk by offsetting changes in the underlying asset's price.
Risk-neutral portfolio
A risk-neutral portfolio focuses on eliminating expected directional risk by employing delta hedging, which continuously rebalances the portfolio to maintain a zero delta position. Gamma scalping optimizes this strategy by exploiting changes in gamma to profit from price volatility, adjusting the hedge dynamically to capture gains from market fluctuations while minimizing exposure to directional moves.
Volatility surface
Volatility surface represents implied volatility variations across different strike prices and maturities, crucial for optimizing gamma scalping strategies that rely on capturing profits from changes in delta as the underlying price moves. Gamma scalping enhances risk management beyond delta hedging by continuously adjusting positions to exploit curvature (gamma) in option prices, reducing exposure to directional market movements and improving portfolio stability.
Hedging cost
Hedging cost in gamma scalping involves frequent adjustments to maintain a neutral gamma exposure, leading to potentially higher transaction fees but improved protection against large price swings compared to delta hedging, which focuses solely on neutralizing delta and typically incurs lower ongoing costs. Gamma scalping captures profits from volatility by leveraging option gamma, whereas delta hedging minimizes directional risk but may suffer losses during significant market movements due to gamma exposure.
Non-linear risk
Non-linear risk arises in options trading due to the curvature of the option's price relative to the underlying asset, making gamma scalping essential for managing this exposure by continuously adjusting delta to capture profits from price movements. Delta hedging alone addresses directional risk but fails to mitigate gamma risk, which can lead to significant losses if the underlying price moves sharply and the hedge is not dynamically rebalanced.
Implied volatility skew
Implied volatility skew impacts gamma scalping by altering option premiums across strike prices, which affects the profitability and frequency of rebalancing required compared to delta hedging's focus on maintaining a neutral delta irrespective of volatility changes. Gamma scalping exploits the curvature in option pricing and benefits from pronounced skews, while delta hedging aims to neutralize directional risk without directly capitalizing on implied volatility variations.
gamma scalping vs delta hedging Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com