Stop loss and take profit are essential trading tools that help manage risk and secure profits by automatically closing positions at predetermined price levels. Stop loss minimizes potential losses by exiting a trade when the price moves against the trader's position, while take profit locks in gains by closing the trade once a target price is reached. Effective use of both strategies enhances discipline and helps traders maintain consistent profitability in volatile markets.
Table of Comparison
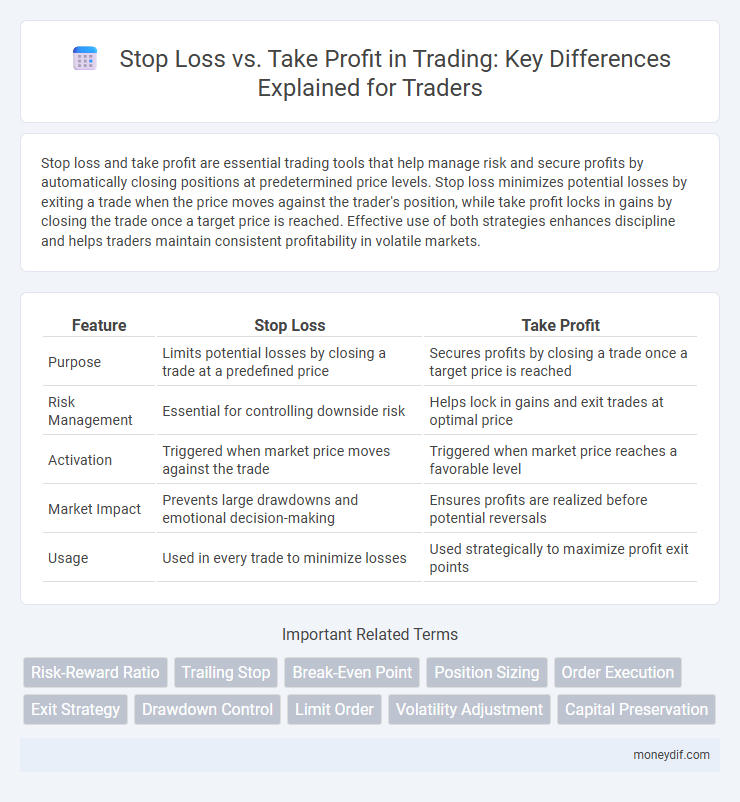
| Feature | Stop Loss | Take Profit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Limits potential losses by closing a trade at a predefined price | Secures profits by closing a trade once a target price is reached |
| Risk Management | Essential for controlling downside risk | Helps lock in gains and exit trades at optimal price |
| Activation | Triggered when market price moves against the trade | Triggered when market price reaches a favorable level |
| Market Impact | Prevents large drawdowns and emotional decision-making | Ensures profits are realized before potential reversals |
| Usage | Used in every trade to minimize losses | Used strategically to maximize profit exit points |
Understanding Stop Loss and Take Profit: Key Definitions
Stop Loss represents a predetermined price level at which a trader exits a losing trade to minimize further losses and protect capital. Take Profit is a target price set to automatically close a profitable position, securing gains before the market reverses. Understanding these orders is crucial for effective risk management and optimizing trade outcomes in forex, stocks, and other financial markets.
Choosing Between Stop Loss and Take Profit Strategies
Traders prioritize stop loss orders to limit potential losses by automatically exiting a trade at a predetermined price, protecting capital during market volatility. Conversely, take profit orders secure gains by closing positions once a target price is reached, ensuring profits are realized before market reversals. Selecting between stop loss and take profit strategies depends on risk tolerance, market conditions, and trading objectives to balance loss prevention and profit maximization effectively.
Psychological Impact of Stop Loss vs Take Profit
Stop Loss orders help mitigate emotional trading by limiting potential losses and reducing anxiety during market volatility. Take Profit targets provide a psychological sense of achievement and discipline by locking in gains at predetermined levels. Balancing both tools enhances trader confidence and mental resilience, minimizing impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed.
Risk Management: Balancing Losses and Gains
Effective risk management in trading requires balancing stop loss and take profit orders to protect capital and secure profits. A well-placed stop loss limits potential losses by automatically closing a position when the market moves against the trader's expectations, while take profit orders lock in gains once the price reaches a predetermined level. Optimizing these levels based on market volatility and trading strategy ensures controlled risk exposure and consistent profit realization.
Common Mistakes with Stop Loss and Take Profit Orders
Common mistakes with stop loss and take profit orders include setting stop losses too tight, which triggers premature exits during normal market fluctuations, and placing take profit targets unrealistically far, causing missed opportunities for securing gains. Traders often neglect to adjust these orders as market conditions change, resulting in suboptimal risk management. Overreliance on fixed percentages without considering volatility or support and resistance levels leads to ineffective trade exits.
How to Set Optimal Stop Loss and Take Profit Levels
Setting optimal stop loss and take profit levels requires analyzing market volatility and support-resistance zones to minimize losses and maximize gains. Using Average True Range (ATR) helps tailor stop loss distances to current price movements, while identifying key Fibonacci retracement levels can pinpoint realistic take profit targets. Consistently applying a risk-reward ratio of at least 1:2 enhances long-term trading profitability and discipline.
Stop Loss vs Take Profit in Volatile Markets
In volatile markets, stop loss orders are essential for limiting potential losses by automatically closing positions when prices reach predefined levels, helping traders manage risk during rapid price fluctuations. Take profit orders secure gains by locking in profits once prices hit targeted thresholds, preventing profits from eroding in unpredictable market swings. Effective use of both stop loss and take profit strategies enables traders to balance risk and reward, maintaining disciplined trading even amid high volatility.
Automating Stop Loss and Take Profit in Trading Platforms
Automating stop loss and take profit orders in trading platforms enhances risk management by executing trades at predefined price levels without manual intervention. Advanced algorithms monitor market fluctuations in real-time, triggering automatic exits to protect capital and lock in profits. Integration with API-driven trading systems enables seamless automation, improving efficiency and reducing emotional bias in trading decisions.
Comparing Fixed vs Trailing Stop Loss Techniques
Fixed stop loss sets a predetermined exit price to limit losses, offering simplicity and clear risk management, while trailing stop loss dynamically adjusts with favorable price movement to lock in profits. Trailing stops optimize gains by following market momentum but may trigger exits prematurely during market volatility. Fixed stops provide consistent protection, whereas trailing stops enhance flexibility, making their combined use effective for balancing risk and reward in trading strategies.
Real-World Case Studies: Stop Loss vs Take Profit Outcomes
Real-world case studies reveal that traders using stop loss orders often experience reduced downside risk by automatically limiting losses in volatile markets. Conversely, take profit orders help lock in gains by closing positions once targeted price levels are reached, ensuring realized profits in trending conditions. Analysis of trading data shows a balanced strategy incorporating both tools enhances portfolio performance, mitigating emotions and improving risk-reward ratios.
Important Terms
Risk-Reward Ratio
The risk-reward ratio compares potential loss defined by the stop loss level to potential gain set by the take profit target, guiding traders in balancing acceptable risk against profit opportunities. A favorable ratio, typically 1:2 or higher, ensures that potential rewards outweigh risks, enhancing overall trading profitability and risk management efficiency.
Trailing Stop
Trailing Stop dynamically adjusts the stop loss level as the market price moves in favor of the trade, locking in profits while limiting potential losses. Unlike fixed stop loss and take profit orders, the trailing stop offers flexible risk management by automatically securing gains without preset profit targets.
Break-Even Point
The break-even point in trading occurs when profits exactly offset losses, balancing the risk-to-reward ratio between stop loss and take profit orders. Setting a precise stop loss minimizes potential losses while an appropriate take profit maximizes gains, ensuring the trade reaches or surpasses the break-even threshold for profitability.
Position Sizing
Position sizing directly influences risk management by determining the trade volume relative to the stop loss distance, ensuring potential losses remain within predefined limits. Balancing stop loss and take profit levels with appropriate position sizing maximizes reward-to-risk ratios and maintains portfolio stability.
Order Execution
Order execution speed significantly impacts the effectiveness of Stop Loss and Take Profit orders, with faster execution reducing slippage and ensuring precise exit points. Efficient order execution platforms enable traders to manage risk and lock in profits by automatically triggering Stop Loss or Take Profit levels at predetermined price targets.
Exit Strategy
An exit strategy in trading involves setting predefined stop loss and take profit levels to manage risk and secure gains effectively. Stop loss limits potential losses by automatically closing a position at a specified price, while take profit locks in profits once a target price is reached, optimizing overall trade outcomes.
Drawdown Control
Drawdown control is essential for risk management, balancing Stop Loss and Take Profit levels optimizes capital preservation and profit maximization while minimizing equity decline; using a tighter Stop Loss limits losses, whereas setting Take Profit targets ensures gains are secured before market reversal. Effective drawdown control integrates adaptive Stop Loss settings with dynamic Take Profit strategies to maintain a favorable risk-reward ratio and reduce psychological stress during trading.
Limit Order
Limit orders allow traders to set specific entry or exit prices, enhancing control over execution compared to market orders. When combined with stop loss and take profit orders, limit orders help manage risk efficiently by locking in desired profit targets and minimizing losses in volatile markets.
Volatility Adjustment
Volatility adjustment enhances the effectiveness of stop loss and take profit orders by dynamically adapting thresholds based on market fluctuations, reducing premature exits during high volatility. This method improves risk management and profit preservation by aligning trade exit points with real-time price variability.
Capital Preservation
Capital preservation focuses on safeguarding investment principal by effectively balancing stop loss and take profit orders; stop loss limits potential losses by automatically exiting positions at predetermined price levels, while take profit secures gains by closing trades once target profits are reached. Employing precise stop loss and take profit strategies enhances risk management and helps maintain long-term portfolio stability in volatile markets.
Stop Loss vs Take Profit Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com