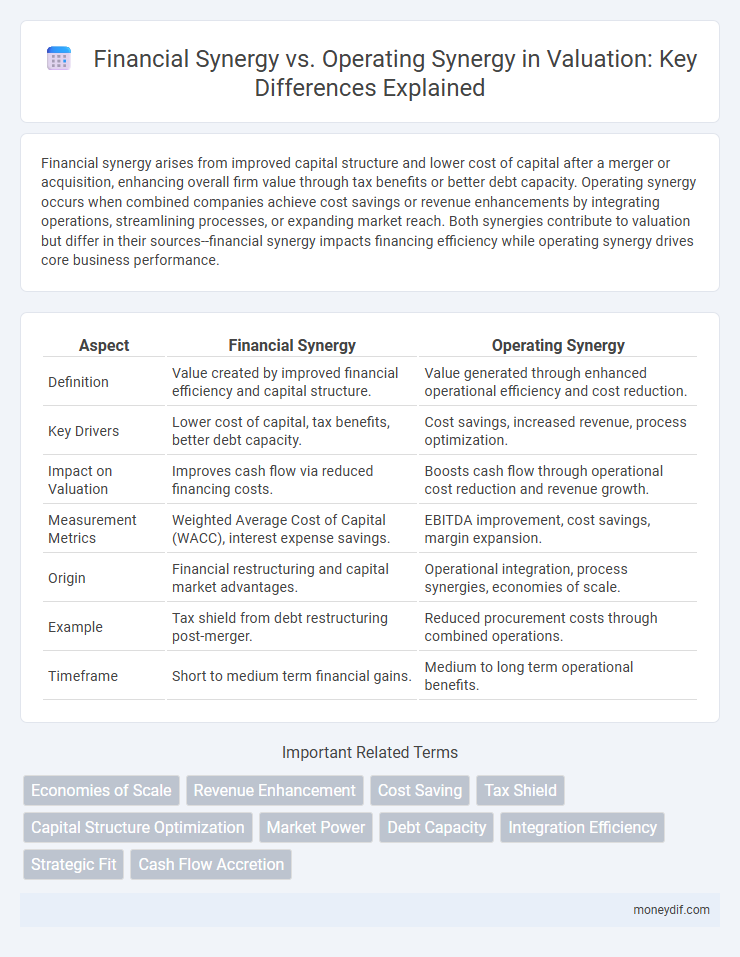
Financial synergy arises from improved capital structure and lower cost of capital after a merger or acquisition, enhancing overall firm value through tax benefits or better debt capacity. Operating synergy occurs when combined companies achieve cost savings or revenue enhancements by integrating operations, streamlining processes, or expanding market reach. Both synergies contribute to valuation but differ in their sources--financial synergy impacts financing efficiency while operating synergy drives core business performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Financial Synergy | Operating Synergy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Value created by improved financial efficiency and capital structure. | Value generated through enhanced operational efficiency and cost reduction. |
| Key Drivers | Lower cost of capital, tax benefits, better debt capacity. | Cost savings, increased revenue, process optimization. |
| Impact on Valuation | Improves cash flow via reduced financing costs. | Boosts cash flow through operational cost reduction and revenue growth. |
| Measurement Metrics | Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC), interest expense savings. | EBITDA improvement, cost savings, margin expansion. |
| Origin | Financial restructuring and capital market advantages. | Operational integration, process synergies, economies of scale. |
| Example | Tax shield from debt restructuring post-merger. | Reduced procurement costs through combined operations. |
| Timeframe | Short to medium term financial gains. | Medium to long term operational benefits. |
Introduction to Synergies in Valuation
Financial synergy in valuation refers to the added value from improved financial metrics such as tax benefits, reduced cost of capital, and enhanced cash flow stability after a merger or acquisition. Operating synergy focuses on increased efficiency gains, cost savings, or revenue enhancements that arise from integrating operations, resources, or technologies. Both synergies play a critical role in accurately estimating the combined entity's value and justifying transaction premiums in M&A deals.
Defining Financial Synergy
Financial synergy occurs when combined entities achieve a lower cost of capital by optimizing debt capacity, tax benefits, and improved credit ratings after a merger or acquisition. It enhances firm value through financial structuring advantages rather than operational efficiencies or cost savings. Unlike operating synergy, which derives from revenue growth and expense reduction, financial synergy primarily leverages capital market benefits and risk diversification.
Defining Operating Synergy
Operating synergy refers to the cost savings and enhanced revenue opportunities that arise when two companies combine their core operations, typically resulting from improved efficiencies, economies of scale, and streamlined processes. This type of synergy focuses on tangible improvements in the production, distribution, and management functions, directly impacting operating margins and cash flow generation. Unlike financial synergy, which centers on capital structure optimization and tax benefits, operating synergy drives value through enhanced operational performance and competitive advantages.
Key Differences Between Financial and Operating Synergy
Financial synergy arises from improved capital structure and tax advantages, leading to lower cost of capital and increased firm valuation. Operating synergy involves enhanced revenue growth, cost reductions, or improved efficiency through combined business operations. The key difference lies in financial synergy's focus on financing benefits, while operating synergy centers on operational improvements driving cash flow enhancement.
Sources of Financial Synergy
Financial synergy primarily arises from improved capital structure, tax benefits, and enhanced debt capacity, enabling combined firms to lower their overall cost of capital. Access to cheaper financing due to stronger credit ratings and diversified cash flows reduces financial distress risk and increases firm value. These sources of financial synergy play a critical role in mergers and acquisitions, driving valuation premiums beyond mere operational improvements.
Sources of Operating Synergy
Sources of operating synergy primarily include cost reductions through economies of scale, enhanced revenue growth via cross-selling opportunities, and improved operational efficiencies by integrating complementary business processes. These synergies arise from combining resources, technology, and expertise to streamline production, optimize supply chains, and accelerate innovation. Effective identification and realization of operating synergies can significantly improve cash flows and firm value in mergers and acquisitions.
Impact of Financial Synergy on Valuation
Financial synergy enhances valuation by lowering the overall cost of capital through tax savings, improved debt capacity, and reduced financial distress risk, leading to increased firm value. It often results from optimal capital structure adjustments and better access to capital markets, which directly impact cash flow stability and discount rates used in valuation models. Unlike operating synergy, which improves operational efficiency and revenue, financial synergy primarily boosts valuation by optimizing financial strategy and capital allocation.
Impact of Operating Synergy on Valuation
Operating synergy enhances valuation by increasing a company's cash flow through cost reductions and improved operational efficiencies, directly boosting EBITDA margins and free cash flow. This improvement in operational performance reduces the risk profile, leading to a higher enterprise value multiple in valuation models. Financial synergy, while beneficial, primarily affects capital structure and tax savings without directly altering the core operational value drivers reflected in operating synergy benefits.
Real-World Examples: Financial vs. Operating Synergy
Financial synergy often arises from tax benefits, improved debt capacity, or lower capital costs, as seen in mergers like Disney and Pixar where combined financial strength reduced borrowing expenses. Operating synergy focuses on enhanced revenues and cost reductions through operational efficiencies, exemplified by Amazon's acquisition of Whole Foods, which integrated supply chains and expanded market reach. Real-world valuations prioritize measurable financial synergy impacts on cash flows alongside operating gains to accurately assess merger value.
Best Practices in Quantifying Synergies for Valuation
Accurate quantification of financial synergy involves analyzing cost of capital reductions, tax benefits, and improved debt capacity, using discounted cash flow (DCF) models to capture incremental value. Operating synergy measurement emphasizes revenue enhancements and cost-saving opportunities driven by combined operations, requiring detailed projections of cash flow improvements and integration efficiencies. Best practices recommend disaggregating synergies, validating assumptions with historical data, and performing sensitivity analysis to ensure robust valuation outcomes.
Important Terms
Economies of Scale
Economies of scale drive cost reductions through increased production volumes, enhancing operating synergy by lowering per-unit expenses in merged companies. Financial synergy complements this by improving capital access and reducing borrowing costs, thereby strengthening overall firm value beyond operational efficiencies.
Revenue Enhancement
Revenue enhancement through financial synergy focuses on optimizing capital structure and tax benefits, whereas operating synergy targets increased sales and market expansion by combining complementary business operations.
Cost Saving
Financial synergy enhances cost saving by reducing capital expenses and improving funding efficiency, while operating synergy lowers costs through streamlined operations and increased productivity.
Tax Shield
Tax shield enhances financial synergy by reducing taxable income through debt interest deductions, whereas operating synergy improves overall efficiency and cash flow without directly affecting tax liabilities.
Capital Structure Optimization
Capital structure optimization leverages financial synergy by reducing capital costs through debt and equity balance while enhancing operating synergy by aligning internal resources and operational efficiencies to maximize firm value.
Market Power
Market power enhances financial synergy by improving access to capital markets and reducing cost of capital, while operating synergy primarily drives efficiency gains and cost reductions within combined operations.
Debt Capacity
Debt capacity reflects a company's ability to incur additional debt without jeopardizing financial stability, often enhanced through financial synergies such as tax shields and improved credit profiles achieved in mergers. In contrast, operating synergies influence debt capacity indirectly by boosting cash flows and profitability, thereby supporting higher leverage through stronger operational performance.
Integration Efficiency
Integration efficiency maximizes financial synergy by enhancing cash flow and cost savings while operational synergy drives productivity improvements through streamlined processes and resource optimization.
Strategic Fit
Strategic fit maximizes financial synergy by enhancing capital efficiency and risk reduction while operating synergy improves cost savings and productivity through integrated business processes.
Cash Flow Accretion
Cash flow accretion from financial synergy often arises through enhanced capital structure and tax benefits, while operating synergy drives accretion by improving revenue growth and reducing costs.
Financial Synergy vs Operating Synergy Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com