Domestic trusts offer greater legal protection and regulatory oversight within a familiar jurisdiction, ensuring transparency and ease of administration for wealth management. Offshore trusts provide enhanced privacy and potential tax advantages but may involve complex compliance requirements and stricter international scrutiny. Choosing between domestic and offshore trusts depends on balancing the need for confidentiality, asset protection, and regulatory compliance in wealth planning.
Table of Comparison
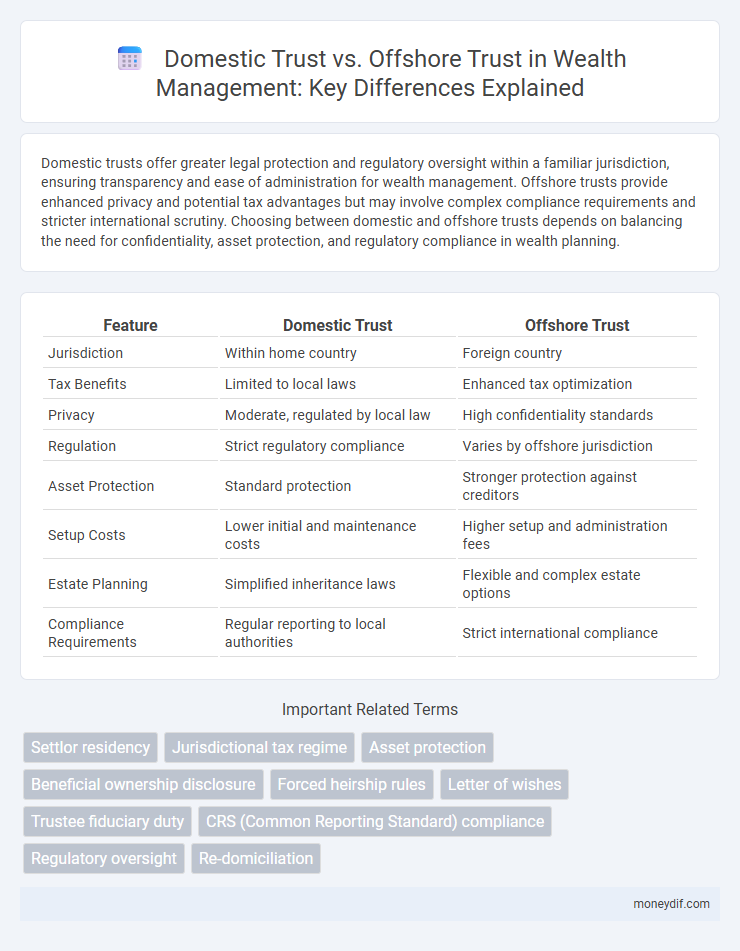
| Feature | Domestic Trust | Offshore Trust |
|---|---|---|
| Jurisdiction | Within home country | Foreign country |
| Tax Benefits | Limited to local laws | Enhanced tax optimization |
| Privacy | Moderate, regulated by local law | High confidentiality standards |
| Regulation | Strict regulatory compliance | Varies by offshore jurisdiction |
| Asset Protection | Standard protection | Stronger protection against creditors |
| Setup Costs | Lower initial and maintenance costs | Higher setup and administration fees |
| Estate Planning | Simplified inheritance laws | Flexible and complex estate options |
| Compliance Requirements | Regular reporting to local authorities | Strict international compliance |
Understanding Domestic Trusts and Offshore Trusts
Domestic trusts are legal arrangements established within the settlor's country, providing greater regulatory oversight, transparency, and easier access to local courts for dispute resolution. Offshore trusts are created in foreign jurisdictions with favorable tax laws and asset protection statutes, often used to safeguard wealth from political or economic instability. Understanding the distinctions in legal frameworks, tax implications, and asset protection benefits is crucial for effective wealth management and estate planning.
Key Differences Between Domestic and Offshore Trusts
Domestic trusts are established and governed under the laws of the settlor's home country, offering easier access to legal recourse and typically lower setup and maintenance costs. Offshore trusts are created in foreign jurisdictions known for favorable tax laws and enhanced asset protection, often providing greater privacy but facing increased regulatory scrutiny and complexity. Key differences include taxation, asset protection levels, legal transparency, and jurisdictional advantages, which influence estate planning and wealth preservation strategies.
Wealth Protection: Domestic vs Offshore Trust Strategies
Domestic trusts offer enhanced legal protections under familiar jurisdictional laws, making wealth preservation more secure against foreign claims and regulatory changes. Offshore trusts provide stronger confidentiality and asset protection by leveraging favorable international laws that resist domestic legal challenges and creditors. Strategic use of both trust types optimizes wealth protection by balancing transparency, legal enforceability, and risk mitigation across multiple jurisdictions.
Tax Implications of Domestic and Offshore Trusts
Domestic trusts are subject to the tax laws of the settlor's country, often resulting in transparent taxation where income is taxed at the grantor or beneficiary level. Offshore trusts can offer tax advantages by deferring or reducing income, capital gains, and inheritance taxes, but they face stringent reporting requirements and anti-avoidance rules in many jurisdictions. Understanding the specific tax implications and compliance obligations of each trust type is essential for effective wealth preservation and estate planning.
Legal Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Domestic trusts offer greater transparency and align closely with national legal frameworks, facilitating easier compliance with tax regulations and reporting requirements. Offshore trusts, while providing asset protection and potential tax advantages, are subject to stringent international regulations such as FATCA and CRS, increasing the complexity of legal compliance. Choosing between domestic and offshore trusts requires careful analysis of jurisdiction-specific regulations, reporting obligations, and the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Asset Privacy in Domestic vs Offshore Trusts
Domestic trusts often provide limited asset privacy due to stricter local reporting and transparency regulations, exposing beneficiaries to potential public scrutiny. Offshore trusts, established in jurisdictions with robust confidentiality laws, offer enhanced asset privacy by minimizing disclosure requirements and protecting ownership details. Choosing between domestic and offshore trusts depends on the level of privacy needed alongside compliance with international tax and legal frameworks.
Costs and Fees: Domestic Trusts Compared to Offshore Trusts
Domestic trusts typically involve lower setup and maintenance fees due to straightforward regulatory requirements and the availability of local legal expertise. Offshore trusts often incur higher costs linked to legal complexity, cross-border compliance, and specialized administration services. Wealth holders should weigh these cost differences carefully against privacy benefits and asset protection objectives.
Risks and Challenges of Offshore Trusts
Offshore trusts present significant risks including exposure to complex international regulations, increased scrutiny from tax authorities, and potential legal disputes across multiple jurisdictions. The lack of transparency and varying compliance standards can lead to difficulties in asset protection and higher operational costs. These challenges often undermine the intended benefits of privacy and tax optimization associated with offshore trusts.
Establishment and Maintenance Processes
Domestic trusts require compliance with local state laws, involving straightforward establishment through standardized documentation and registration processes that often demand less administrative oversight. Offshore trusts involve complex legal frameworks in jurisdictions like the Cayman Islands or Bermuda, requiring adherence to international regulations, higher setup costs, and ongoing reporting to both the trust jurisdiction and the settlor's home country. Maintenance of domestic trusts typically incurs lower fees and simpler tax filings, while offshore trusts necessitate meticulous management, including legal counsel and financial intermediaries to navigate cross-border compliance and asset protection strategies.
Choosing the Right Trust Structure for Wealth Management
Domestic trusts offer enhanced legal protections and easier regulatory compliance within the settlor's home country, making them ideal for individuals seeking straightforward estate planning. Offshore trusts provide benefits such as asset protection, tax optimization, and confidentiality in jurisdictions like the Cayman Islands or Jersey, appealing to high-net-worth individuals with diverse international assets. Evaluating factors such as regulatory environment, tax implications, and asset protection goals is crucial in choosing the right trust structure for effective wealth management.
Important Terms
Settlor residency
Settlor residency significantly impacts the tax treatment and regulatory obligations of domestic versus offshore trusts, with domestic trusts typically subject to local taxation rules based on the settlor's tax domicile, while offshore trusts often offer tax advantages due to their establishment in low-tax jurisdictions. Understanding the settlor's residency status is crucial for compliance with anti-money laundering laws and for determining the trust's reporting requirements across different jurisdictions.
Jurisdictional tax regime
Jurisdictional tax regimes distinguish domestic trusts by subjecting them to local income tax and reporting requirements, while offshore trusts often benefit from favorable tax treatment and reduced transparency obligations.
Asset protection
Domestic trusts offer asset protection by leveraging favorable state laws such as those in Nevada and Delaware, which provide strong spendthrift provisions and short statute of limitations on fraudulent transfers. Offshore trusts, typically established in jurisdictions like the Cayman Islands or Bermuda, enhance asset protection through greater privacy, protection from foreign judgments, and robust legal frameworks designed to shield assets from creditors and political risks.
Beneficial ownership disclosure
Beneficial ownership disclosure mandates transparency of the ultimate owners in domestic trusts, whereas offshore trusts often face stricter regulatory scrutiny due to higher risks of opacity and tax evasion.
Forced heirship rules
Forced heirship rules restrict the distribution of assets in domestic trusts, whereas offshore trusts often provide greater flexibility in circumventing these mandatory inheritance laws.
Letter of wishes
A Letter of Wishes provides non-binding guidance for trustees managing domestic trusts or offshore trusts, with domestic trusts often subject to local laws and offshore trusts offering enhanced privacy and asset protection.
Trustee fiduciary duty
Trustees managing domestic trusts must strictly adhere to fiduciary duties under local laws, while offshore trust trustees navigate complex international regulations to ensure asset protection and compliance.
CRS (Common Reporting Standard) compliance
CRS compliance requires domestic trusts to report beneficiary information directly to local tax authorities, while offshore trusts often face stricter scrutiny and may need enhanced transparency measures to ensure global tax compliance.
Regulatory oversight
Regulatory oversight of domestic trusts is typically more stringent and transparent compared to offshore trusts, which often benefit from lenient regulations and greater privacy protections.
Re-domiciliation
Re-domiciliation enables transferring a domestic trust to an offshore jurisdiction, optimizing asset protection, tax efficiency, and regulatory compliance based on jurisdictional benefits.
domestic trust vs offshore trust Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com